* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slides from Lecture 12 - Courses - University of California, Berkeley
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
Oracle Database wikipedia , lookup
Object-relational impedance mismatch wikipedia , lookup
ORACLE and SQLPlus
University of California, Berkeley
School of Information Management
and Systems
SIMS 257: Database Management
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 1
Lecture Outline
• Review
– Databases for Web Applications – Overview
– ColdFusion
– PHP
• DiveShop in ColdFusion
• Introduction to ORACLE and SQL-Plus
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 2
Lecture Outline
• Review
– Databases for Web Applications – Overview
– ColdFusion
– PHP
• DiveShop in ColdFusion
• Introduction to ORACLE and SQL-Plus
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 3
Dynamic Web Applications 2
Web
Server
Internet
Files
CGI
DBMS
Server
database
database
database
Clients
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 4
Server Interfaces
SQL
HTML
DHTML
Web Server
JavaScript
Native
DB
Interfaces
Database
Web DB
CGI
App ODBC
Web Server
API’s
ColdFusion
Native DB
interfaces
JDBC
PhP Perl
Web Application
Server
Adapted from
John P Ashenfelter,
Choosing a Database for Your Web Site
IS 257 – Fall 2004
Java
ASP
2004.10.25 SLIDE 5
Web Application Server Software
•
•
•
•
ColdFusion
PHP
ASP
All of the are server-side scripting
languages that embed code in HTML
pages
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 6
What ColdFusion is Good for
• Putting up databases onto the Web
• Handling dynamic databases (Frequent
updates, etc)
• Making databases searchable and
updateable by users.
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 7
Templates
• Assume we have a database named
contents_of_my_shopping_cart.mdb -- single
table called contents...
• Create an HTML page (uses extension .cfm),
before <HEAD>...
• <CFQUERY NAME= ”cart"
DATASOURCE=“contents_of_my_shopping_car
t"> SELECT * FROM contents ;
</CFQUERY>
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 8
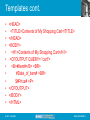
Templates cont.
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
<HEAD>
<TITLE>Contents of My Shopping Cart</TITLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<H1>Contents of My Shopping Cart</H1>
<CFOUTPUT QUERY= ”cart">
<B>#Item#</B> <BR>
#Date_of_item# <BR>
$#Price# <P>
</CFOUTPUT>
</BODY>
</HTML>
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 9
Templates cont.
Contents of My Shopping Cart
Bouncy Ball with Psychedelic Markings
12 December 1998
$0.25
Shiny Blue Widget
14 December 1998
$2.53
Large Orange Widget
14 December 1998
$3.75
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 10
CFIF and CFELSE
<CFOUTPUT QUERY= ”cart">
Item: #Item# <BR>
<CFIF #Picture# EQ"">
<IMG SRC=“generic_picture.jpg"> <BR>
<CFELSE>
<IMG SRC="#Picture#"> <BR>
</CFIF>
</CFOUTPUT>
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 11
PHP
• PHP is an Open Source Software project
with many programmers working on the
code.
– Commonly paired with MySQL, another OSS
project
– Free
– Both Windows and Unix support
• Estimated that more than 250,000 web
sites use PHP as an Apache Module.
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 12
PHP Syntax
• Similar to ASP
<HTML><BODY>
<?php
$myvar = “Hello World”;
echo $myvar ;
?>
</BODY></HTML>
• Includes most programming structures (Loops,
functions, Arrays, etc.)
• Loads HTML form variables so that they are
addressable by name
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 13
Combined with MySQL
• DBMS interface appears as a set of
functions:
<HTML><BODY>
<?php
$db = mysql_connect(“localhost”, “root”);
mysql_select_db(“mydb”,$db);
$result = mysql_query(“SELECT * FROM employees”, $db);
Printf(“First Name: %s <br>\n”, mysql_result($result, 0 “first”);
Printf(“Last Name: %s <br>\n”, mysql_result($result, 0 “last”);
?></BODY></HTML>
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 14
Lecture Outline
• Review
– Databases for Web Applications – Overview
– ColdFusion
– PHP
• DiveShop in ColdFusion
• Introduction to ORACLE and SQL-Plus
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 15
ColdFusion Diveshop
• Examples from Fusion
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 16
Lecture Outline
• Review
– Databases for Web Applications – Overview
– ColdFusion
– PHP
• DiveShop in ColdFusion
• Introduction to ORACLE and SQL-Plus
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 17
Today
• Getting started with ORACLE and SQL-see assignment on website
• More on SQL and SQLPlus for data
manipulation and modification
• Getting Started with ORACLE.
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 18
SELECT
• Syntax:
– SELECT [DISTINCT] attr1, attr2,…, attr3 as
label, function(xxx), calculation, attr5, attr6
FROM relname1 r1, relname2 r2,… rel3 r3
WHERE condition1 {AND | OR} condition2
ORDER BY attr1 [DESC], attr3 [DESC]
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 19
CREATE SYNONYM
• CREATE SYNONYM newname FOR
oldname;
• CREATE SYNONYM BIOLIFE for
ray.BIOLIFE;
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 20
SELECT Conditions
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
= equal to a particular value
>= greater than or equal to a particular value
> greater than a particular value
<= less than or equal to a particular value
<> not equal to a particular value
LIKE ‘%wom_n%’ (Note different wild card)
IN (‘opt1’, ‘opt2’,…,’optn’)
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 21
Aggregate Functions
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
COUNT(dataitem)
AVG(numbercolumn)
SUM(numbercolumn)
MAX(numbercolumn)
MIN(numbercolumn)
STDDEV(numbercolumn)
VARIANCE(numbercolumn)
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 22
Numeric Functions
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
ABS(n)
ACOS(n)
ASIN(n)
ATAN(n)
ATAN2(n, m)
CEIL(n)
COS(n)
COSH(n)
IS 257 – Fall 2004
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
EXP(n)
EXP(n)
FLOOR(n)
LN(n)
LOG(m,n)
MOD(n)
POWER(m,n)
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
ROUND(n)
SIGN(n)
SIN(n)
SINH(n)
SQRT(n)
TAN(n)
TANH(n)
TRUNC(n[,
m])
2004.10.25 SLIDE 23
Character Functions returning character values
•
•
•
•
•
CHR(n)
CONCAT(char1,char2)
INITCAP(char)
LOWER(char)
LPAD(char, n,char2),
RPAD(char, n,char2)
• LTRIM(char, n, cset),
RTRIM(char, n, cset)
IS 257 – Fall 2004
• REPLACE(char, srch,
repl)
• SOUNDEX(char)
• SUBSTR(char, m, n)
• SUBSTRB(char, m, n)
• TRANSLATE(char,
from, to)
• UPPER(char)
2004.10.25 SLIDE 24
Character Function returning numeric values
• ASCII(char)
• INSTR(char1,
char2[,m, n])
• INSTRB(char1,
char2[,m, n])
• LENGTH(char)
• LENGTHB(char)
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 25
Date functions
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
ADD_MONTHS(dt, n)
LAST_DAY(d)
MONTHS_BETWEEN(d1, d2)
NEW_TIME(d, z1, z2) -- PST, AST, etc.
NEXT_DAY(d, dayname)
ROUND(d, fmt) -- century, year etc.
SYSDATE
TRUNC(d, fmt) -- century, year, etc.
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 26
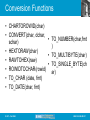
Conversion Functions
• CHARTOROWID(char)
• CONVERT(char, dchar,
•
TO_NUMBER(char,fmt
schar)
)
• HEXTORAW(char)
• TO_MULTIBYTE(char)
• RAWTOHEX(raw)
• TO_SINGLE_BYTE(ch
• ROWIDTOCHAR(rowid)
ar)
• TO_CHAR (date, fmt)
• TO_DATE(char, fmt)
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 27
Create Table
• CREATE TABLE table-name (attr1 attr-type
CONSTRAINT constr1 PRIMARY KEY, attr2 attrtype CONSTRAINT constr2 NOT NULL,…, attrM
attr-type CONSTRAINT constref REFERENCES
owner.tablename(attrname) ON DELETE
CASCADE, attrN attr-type CONSTRAINT
constrN CHECK (attrN = UPPER(attrN), attrO
attr-type DEFAULT default_value);
• Adds a new table with the specified attributes
(and types) to the database.
– NOTE that the “CONSTRAINT and name parts are
optional)
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 28
Create Table
• CREATE TABLE table-name (
attr1 attr-type PRIMARY KEY,
attr2 attr-type NOT NULL,
…, attrM attr-type REFERENCES
owner.tablename(attrname) ON DELETE
CASCADE,
attrN attr-type CHECK (attrN =
UPPER(attrN)
attrO attr-type DEFAULT default_value);
– Without “CONSTRAINT” and name parts
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 29
Types
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
VARCHAR2(size)
NUMBER(p, s)
LONG -- long char data
DATE -- from 4712BC to 4714 AD
RAW(size) -- binary
LONG RAW -- large binary
ROWID -- row reference
CHAR(size) -- fixed length characters
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 30
Alter Table
• ALTER TABLE table-name ADD attr1 attrtype;
• ALTER TABLE table-name ADD attr1
CONSTRAINT xxx constrainvalue;
• ALTER TABLE table-name MODIFY attr1
optiontochange;
• ALTER TABLE table-name DROP COLUMN
attr1;
• Adds, drops or modifies a column in an
existing database table.
– Note: constrainvalue is any column constraint like
‘PRIMARY KEY’, REFERENCES, etc.
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 31
INSERT
• INSERT INTO table-name (attr1, attr4,
attr5,…, attrK) VALUES (“val1”, val4,
val5,…, “valK”);
• OR
• INSERT INTO table-name SELECT col1,
col2, col3 as newcol2, col4 FROM xx, yy
WHERE where-clause;
• Adds a new row(s) to a table.
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 32
DELETE
• DELETE FROM table-name WHERE
<where clause>;
• Removes rows from a table.
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 33
UPDATE
• UPDATE tablename SET attr1=newval,
attr2 = newval2 WHERE <where clause>;
• changes values in existing rows in a table
(those that match the WHERE clause).
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 34
DROP Table
• DROP TABLE tablename;
• Removes a table from the database.
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 35
CREATE INDEX
• CREATE [ UNIQUE ] INDEX indexname
ON tablename (attr1 [ASC|DESC][, attr2
[ASC|DESC], ...])
• Adds an index on the specified attributes
to a table
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 36
System Information In ORACLE
• Find all of the tables for a user
– SELECT * FROM ALL_CATALOG WHERE
OWNER = ‘userid’;
– SELECT * FROM USER_CATALOG; (or CAT)
• Show the attributes and types of data for a
particular table
– DESCRIBE tablename;
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 37
Running commands
• Create file with SQL and SQLPlus
commands in it.
– Use a plain text editor and NOT a word
processor (or save as text only)
• Give the file the extension .sql
• From inside SQLPlus type
– START filename
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 38
Simple formatting in SQLPlus
•
•
•
•
•
SET PAGESIZE 500
SET LINESIZE 79
PROMPT stuff to put out to screen
TTITLE “title to put at top of results”
COLUMN col_name HEADING “New
Name”
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 39
Outputting results as a file…
• SPOOL filename
• Commands
• SPOOL STOP
– File will be created with everything between
the SPOOL commands
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 40
Lecture Outline
• Review
– Databases for Web Applications – Overview
– ColdFusion
– PHP
– DiveShop in ColdFusion
• Introduction to ORACLE and SQL-Plus
• Assignment 3
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 41
Assignment 3
• Assignment 3 and additional instructions are on
the Web site
• Use ORACLE and SQL to answer the following
DiveShop queries…
– What are the names and addresses of the diveshop
customers who are renting snorkels?
– What are the names of the wildlife that Mary Rioux
might see on her trip. Are there any Shipwrecks there
(give names)?
– What sunken ships might be candidates for treasure
hunters whose destination is New Jersey?
– Who is paying the maximum amount for single type
of rental equipment (use price * quantity to determine
amount)?
– At how many sites might you see a "Nassau
Grouper"?
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 42
Assignment 3 (cont)
– What are the names of customers who are
paying in cash?
– Produce a list of all equipment being rented
for a dive vacation that costs more than
$30000, make the list in descending order of
the rental price of the equipment.
– Who is renting teal colored equipment?
– Which locations have an average temperature
of more than 75 degrees farenheit and a
travel cost of under $4000?
– Make up two queries of your own and run
them turn in the queries and the results.
IS 257 – Fall 2004
2004.10.25 SLIDE 43