* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction - Department of Computer Science and Engineering
Data vault modeling wikipedia , lookup
Expense and cost recovery system (ECRS) wikipedia , lookup
Information privacy law wikipedia , lookup
Open data in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Business intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
Search engine indexing wikipedia , lookup
Versant Object Database wikipedia , lookup
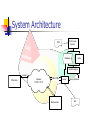
Second semester FYP Presentation 2001~2002 LYU0101 Wireless Digital Information System Supervisor Prof. Michael Lyu Yeung Kam Wah Lam Yee Gordon Overview Introduction Design Direction System Architecture Client Implementation Server Implementation Work Done Introduction PDA become more popular High Bandwidth Wireless Technology Computation power and Memory is increasing BlueTooth, Wireless LAN 3G Demand for provide content to PDA Provide location related information Wireless Digital Information System To build a generic system that allow company provide their content to user Support different application Support multimedia content Same client program for different server Search function Wireless Digital Information System Usage Shopping guild in a Shopping Mall Information search in an Exhibition Showing vacancy in a Car Park Digital video Library client Design Direction Design Direction What’s our goal? (in previous slide) Main Issues we need to concern: Data (format, storage, types) Search Engine (vector,probabilistic model, indexing, ranking, relevance feedback) Platform (hand-held device) Concern 1:Data Use XML as the primary data format To give our user a standard, feasible and extensible way to design the data structure separate the concern on the data and presentation of information Use XSL to change XML into information changes in module or client platform will not affect the data Concern 1:Data Storing XML in Database Database provides us many useful services Other concurrency control Security recoverability of data Data Management and Integration Concern 1:Data Conversion between XML and Database Common Method: Break down XML file into tree nodes and remember its children's node Need to have different schema Need to make use of DTD Our Method: Break down XML file into tree nodes and remember the parent node. Only need one schema: (parent id, node id, type, data) Concern 1:Data <!ELEMENT author ( name, address )> <!ATTLIST author id ID REQUIRED> <!ELEMENT name(firstname?, lastname)> <!ELEMENT firstname(PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT lastname(PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT address ANY > A DTD definition Visualization of DTD in Tree Concern 2: Searching Use Vector Model assign weight to index terms in queries and in XML file (from tf factor, termfrequency and idf factor, inverse document frequency) compute degree of similarity between each XML file and user query give ordering of XML file Concern 2: Searching A full inverted index is built. have a better ranking, e.g. search for “林 怡”, I prefer to have “林怡” in search result, rather than “林保怡”. can help in searching a whole phase. Concern 2: Searching Problem: client may need only ten search results at a time, I can’t send all the result to PDA client at a time !!! Solution: NN-search Methods (R-tree, SS-tree, SR-tree, X-tree, MVP-tree, Atree, VA-file) We choose VA-file Concern 2: Searching VP-tree A-tree Concern 2: Searching VA-file Concern 2: Searching Reason for choosing VA-file: performs much better than the others in high-dimension space(as number of index term may be over thousand) IO page, number of Vector calculation, CPU time in search CPU time on construction Concern 3: Client Platform We choose Pocket PC as our client platform Reason: Pocket PC have better support in Internet Multi-Media Performance processing power of Pocket PC is higher than Palm OS nowadays System Architecture System Architecture Pre-Process System XML Database Index Search Engine request PDA client Network TCP/IP, HTTP XML/HTML Media server server Query & Result XLS System Architecture Server side XML Data is processed and stored in the database A set of XSL is used to format the output Client side Display information Send user requests to server Server Side Four main components at Server Side XML Pre-processor Search Engine XSL transformer TCP Server that Communicate with PDA client incoming: Keyword search, Map search result, XSL and XML set outgoing: HTML, Video xml definition (probably a very simple SMIL), Map xml definition Web server (images) MMS server (videos) XML Pre-processor XML Data Struture + Text Strutural tuples parsing Text Accents, Lexical Building Full spacing, etc Analysis Inverted index Vector and VA-file Builder Vectors and VA-file Relational Database The PDA Client server PDA Client Control Component Main Window Image Window Video Window The PDA Client Main Window HTML Viewer Supported by system provided DLL Interface for information displaying User event will pass to control component to handle The PDA Client Image Window Using to display image Points highlight feature Using as query input interface, user can select a rectangular area as query input The PDA Client Video/Audio window Supported by system provided COM Object Display video to user The PDA Client Why using HTML viewer as main interface Provide feasibility to different servers using their own interface HTML is widely used and designed for display information. Why using system provide library Simplify the program and slim the program size These component is optimized Work Done and Possible Extension Work Done 2001 July ~ Aug Study different wireless network Study different PDA platform Build a trial application on Pocket PC 2001 Sep ~ Dec Design the application and system architecture Build the Pocket PC client Work Done 2002 Jan ~ April Study the searching algorithm Build the server Continue implement the Pocket PC client