* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download warehouse_chapter13
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
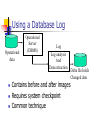
Transportation: Refreshing Warehouse Data Chapter 13 Developing a Refresh Strategy for Capturing Changed Data Consider load window Identify data volumes Identify cycle Know the technical infrastructure Plan a staging area Determine how to detect changes Operational databases User Requirements and Assistance Users define the refresh cycle IT balances requirements against technical issues Document all tasks and processes Employ user skills Operational databases Load Window Time available for entire ETT process Plan Test Prove Monitor Load Window 0 3am 6 User Access Period Load Window 9 12pm 3 6 9 12 Load Window Plan and build processes according to a strategy. Consider volumes of data. Identify technical infrastructure. Ensure currency of data. Consider user access requirements first High availability requirements may mean a small load window User Access Period 0 3am 6 9 12pm 3 6 9 12 Scheduling the Load Window Requirements Load cycle Receive data File 1 File FTP 2 0 3 Control File File Names File types Number of files Number of loads First-time load or refresh Date of file Data range Records in file - counts Totals - amounts Control 4 process Open and read files to verify and analyze 3 am Scheduling the Load Window 6 5 Verify, analyze, reapply Load into warehouse File 1 File 2 3 am 8 7 Index data Create summaries 9 Update metadata Parallel load 6 am 9 am Scheduling the Load Window 11 10 Back up warehouse Create Views for Specialized tools 12 13 Users Access Publish Summary data User access 6 am 9 am Capturing Changed Data for Refresh Capture new fact data Capture changed dimension data Determine method for capture of each Methods: - Wholesale data replacement - Comparison of database instances - Time stamping - Database triggers - Database log Hybird techniques Wholesale Data Replacement Operational databases T1 T2 Expensive Limited historical data, if any Data mart implementations Time period replacement T3 Comparison of Database Instance Yesterday’s Operational database Today’s Operational database Database comparison Delta file holds Changed data Simple to perform, but expensive in time and processing Data file: - Changes to operational data since last refresh - Used by various techniques Time and Date Stamping Operational data Delta file holds Changed data Fast scanning for records changed since last extraction Date Updated field No detection of deleted data Database Triggers Operation Server (DBMS) Trigger Trigger Trigger Changed data intersected at the server level Extra I/O required Maintenance overhead Using a Database Log Operational data Operational Server (DBMS) Log Log analysis And Data extraction Contains before and after images Requires system checkpoint Common technique Delta file holds Changed data Verdict Consider each method on merit. Consider a hybrid approach if one approach is not suitable. Consider current technical, existing operational, and current application issues. Applying the Changes to Data You have a choice of techniques: Overwrite a record Add a record Add a field Maintain history Add version numbers Overwriting a Record Customer ID John Doe Single Customer ID John Doe Married Easy to implement Loses all history Not recommended Adding a New Record 1 Customer Id John Doe Single 1 Customer Id John Doe Single 1A Customer Id John Doe Married History is preserved; dimensions grow. Time constraints are not required. Generalized key is created. Metadata tracks usage of keys. Adding a Current Field Customer Id John Doe Single Customer Id John Doe Single Married 01-JAN-96 Maintains some history Loses intermediate values Is enhanced by adding an Effective Date field Limitations of Methods for Applying Changes Complete history impossible Dimensions may grow large Maintenance overload 1234 Comer 1234 Comer 1 Main Street 200 First Ave 555-6789 222-3211 1234 Comer 1234-01 Comer 1 Main Street 200 First Ave 555-6789 222-3211 1234 Comer 1234-01 Comer 1 Main Street 200 First Ave Effective Date 555-6789 01-Apr-93 222-3212 01-Jun-97 Maintaining History HIST_CUST Time CUSTOMER Sales Product One-to-many relationship Always retain current record Consistently able to refer to record history History Preserved History enables realistic analysis. History retains context of data. History provides for realistic historical analysis. - Reflect business changes - Maintain context between fact and dimension data - Retain sufficient data to relate old to new Version Numbering Avoid double counting Facts hold version number Customer Time Sales Customer.CustId Version Customer Names 1234 1 Comer 1234 2 Comer Customer.CustId Version Sales Facts 1234 1 11,000 1234 2 12,000 Product Purging and Archiving Data As data ages, its value depreciates. Remove old data from the warehouse: - Archive for later use - Purge without copy Techniques for Purging Data TRUNCATE: Retains no rollback DELETE: Retains redo and rollback ALTER TABLE: Removes a partition PL/SQL: Uses database triggers Techniques for Archiving Data Export to dump file from tables Import to tables from dump file ALTER TABLE EXCHANGE partitions EXP Database IMP .dmp Verdict Defined by business requirements Must be managed Final Tasks Update metadata - ETT - User Publish data - Availability - Changes - Subject area basis Use database roles to prevent and allow access Publishing Data Control access using database roles 24-hour operation may be requested Compromise between load and access Consider - Staggering updates - Using temporary tables - Using separate tables ETT Tool Selection Criteria Overlap with existing tools Availability of meta model Supported data sources Ease of modification and maintenance Required fine tuning of code Ease of change control Power of transformation logic Level of modularization Power of error, exception, resubmission features Intuitive documentation Performance of code ETT Tool Selection Criteria Activity scheduling and sophistication Metadata generation Learning curve Flexibility Supported operation systems Cost Transportation Tools Information Oracle Platinum Technology OpenBridge SQL*Loader Gateways PL/SQL Precompilers InfoPump Platinum Info Transport Replication Server Utilities Oracle Symmetric and Heterogeneous Replication Gateways and Middleware Brio Technology Information Co. Information Builders Oracle Platinum Technology Prism Software AG DataPrism OpenBridge EDA/SQL Gateways InfoHub Prism Manager Entire Transaction Propagator Summary This lesson discussed the following topics: Capturing changed data Applying the changes Purging and archiving data Publishing the data, controlling access, and automating processes Identifying tools for transporting data into the warehouse