* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Learning Objectives
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
THE DATABASE ENVIRONMENT
Definitions: Data, Information, Database,
Metadata
File Processing Systems
The Database Approach
Components of the Database Environment
Evolution of Database Systems
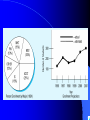
Data versus Information
Monthly Sales Report
for West Region
Sales Rep: Charles Mann
Emp No. 79154
Item
Qty Sold Price
TM Shoes 1200
$100
Some Definitions
Data: Meaningful facts, text, graphics, images,
sound, video segments.
Database: An organized collection of logically
related data.
Information: Data processed to be useful in
decision making.
Metadata: Data that describes data.
Metadata for Class Roster
Descriptions of the properties or characteristics of the
data, including data types, field sizes, allowable
values, and documentation
Data Name
COURSE
SECTION
SEMESTER
NAME
ID
MAJOR
GPA
Data Type Length Value
Description
Alphanumeric
30
Course ID and name
Integer
1 {1,2,...,9} Section number
Alphanumeric
10
Semester and year
Alphanumeric
30
Student name
Integer
9
Student ID
Alphanumeric
4
Student major
Decimal
3 (0, 4.0) Student grade point average
Three file processing systems at
Pine Valley Furniture
Disadvantages of File Processing
Systems
Program-Data Dependence
– data descriptions are included with the application
programs that use the data
Data Redundancy (Duplication of data)
Limited Data Sharing
Lengthy Development Times
Excessive Program Maintenance
SOLUTION: The DATABASE Approach
Central
repository of shared data
Data is managed by a controlling agent
Stored in a standardized, convenient
form
Requires a Database Management System (DBMS)
Database Management System
Application
#1
Application
#2
Application
#3
DBMS
DBMS manages data
resources like an operating
system manages hardware
resources
Database
containing
centralized
shared data
The Database Approach
emphasizes the integration and sharing of data thru the
organization
An enterprise data
model is a graphical
model that shows the
high-level entities for
the organization and
the relationship among
those entities
– ORDER (O_ID, C_ID,
O_Date)
– ORDER_LINE (O_ID,
P_ID, QTY_Ordered)
– An entity is an object
or concept that is
important to the
business
– ERD
Relational Databases
A database application
is used to perform a
series of database
activities (create, read,
update, delete)
– The range of Database
Applications
Advantages
Segment from enterprise data model
Figure 3
Figure 3
Segment from enterprise data model
One customer may place many
orders, but each order is placed
by a single customer
One-to-many relationship
Figure 3
Segment from enterprise data model
One order has many order
lines; each order line is
associated with a single order
One-to-many relationship
Figure 3
Segment from enterprise data model
One product can be in many
order lines, each order line refers
to a single product
One-to-many relationship
Figure 3 Segment from enterprise data model
Therefore, one order involves
many products and one product
is involved in many orders
Many-to-many relationship
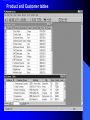
Order and Order_Line tables
Product and Customer tables
Figure 1-4 Order, Order_Line, Customer, and Product tables
Relationships established in special columns that provide links
between tables
Figure 1-5
Client/server
system for
Pine Valley
Furniture
Company
Advantages of the Database
Approach
Data Independence/Reduced Maintenance
– Data independence refers to the separation of data descriptions
from the application programs that use the data
Improved Data Sharing
Increased Application Development Productivity
Enforcement of Standards
Improved Data Quality (Constraints)
Better Data Accessibility/ Responsiveness
Security, Backup/Recovery, Concurrency
The Range of Database Applications
Personal Databases
– support one user
Workgroup Databases
– a workgroup is a relatively small team of people who
collaborate on the same project or application
Department Databases
– support the various functions and activities of a
department
Enterprise Databases
– ERP work with the current operational data
– Data warehouses
Internet Databases
Workgroup database
Figure 1-9 An
enterprise
data
warehouse
Components of the Database
Environment
CASE Tools
Repository - a centralized storehouse for all data definitions, data
relationships, and other system components
Database Management System (DBMS)
Database - organized collection of logically related data
Application Programs
User Interface
Data Administrators
System Developers
End Users
Components of
the Database Environment
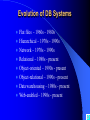
Evolution of Database Technologies
Evolution of DB Systems
Flat files - 1960s - 1980s
Hierarchical – 1970s - 1990s
Network – 1970s - 1990s
Relational – 1980s - present
Object-oriented – 1990s - present
Object-relational – 1990s - present
Data warehousing – 1980s - present
Web-enabled – 1990s - present
Figure 1-2 Three file processing systems at Pine
Valley Furniture
Duplicate
Data
Problems with Data Redundancy
Waste
of space to have duplicate data
Causes more maintenance headaches
The biggest Problem:
– When data changes in one file, could cause
inconsistencies
– Compromises data integrity
Problems with Data Dependency
Each application programmer must maintain their
own data
Each application program needs to include code
for the metadata of each file
Each application program must have its own
processing routines for reading, inserting, updating
and deleting data
Lack of coordination and central control
Non-standard file formats
Costs & Risks of the Database Approach
Up-front costs:
– Installation Management Cost and Complexity
– Conversion Costs
Ongoing Costs
– Requires New, Specialized Personnel
– Need for Explicit Backup and Recovery
Organizational Conflict
– Old habits die hard