* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT
Oracle Database wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Ingres (database) wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Functional Database Model wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
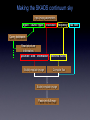
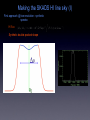
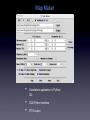
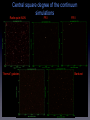
The SKADS sky and databases F. Levrier, R. Wilman, D. Obreschkow, H.-R. Klöckner, S. Rawlings (Oxford Astrophysics) D. Olteanu, S. Young (Oxford e-Research Center) DS2-T1 MEETING LISBON JANUARY 7, 2008 Output from continuum and line simulations • • ASCII files large quantities of data (~45 Gb) Example: continuum simulations - 235,301,766 sources Source type Sources Components Radio-quiet AGN 36,132,566 1 FRI 23,853,134 3 FRII 2,354 5 “Normal” galaxies 168,046,330 1 Starburst galaxies 7,267,382 1 Data distribution and map making • • • • Query data based on position, source type, flux limit... Requires database structure (MySQL / PostgreSQL) Continuum simulations database + HI line simulations database For each database : source tables + cluster table Example: continuum simulations database Source table Cluster table • • • Unique source index per substructure NULL values for Q,U,V fluxes Max. number of entries per table: 1,000,000 Making the SKADS continuum sky Input map parameters region - source types - resolution - frequency - flux limit Query databases Read structure information position - size - orientation - reference fluxes Build template image Compute flux Scale template image Paste into full map Making the SKADS HI line sky (I) First approach @ low resolution : synthetic spectra HI flux Synthetic double-peaked shape Making the SKADS HI line sky (II) Second approach @ high resolution : template cubes from R. Boomsma • • • • • • Galaxy models made of “clouds” Placed according to density profile Orbiting according to velocity curve 5 galaxy types (spirals and irregulars) QuickTime™ and a Animation decompressor are needed to see this picture. 46 inclination values (0-90 degrees) 5 asymptotic velocities scale / rotate / paste S0-Sab Map Maker • • • Standalone application in Python / IDL SQL/Python interface FITS output Central square degree of the continuum simulations Radio-quiet AGN “Normal” galaxies FR I FR II Starburst Where we stand, where we’re going • • • • • • • • • Database implementation IDL to python conversion of Map Maker Release of central square degree data in the test phase (~100 Mb) http://webmail.jb.man.ac.uk/skadswiki/ContsimVersion4 Testing of simulation output (T. Mauch, F. Abdalla, T. Kitching) Hosting of the database server by OeRC Implementation of web interface for database and imaging queries Release of Map Maker Release of the full simulations Interface with a MeqTrees sky model Measurement Set Generator MeqTrees interfaces with AIPS++ Measurement Sets, but it doesn’t build them from scratch Local MS generator: python interface to a glish script from T. Willis Can use existing configurations or generate random ones