* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Microsoft Access wikipedia , lookup
Oracle Database wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Ingres (database) wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
ContactPoint wikipedia , lookup
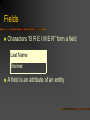
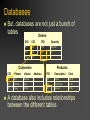
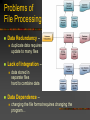
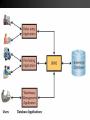
Chapter 5 Database Concepts Why Study Databases? Databases have incredible value to businesses. Very important technology for supporting operations. Vastly superior to spreadsheets and file processing systems Businesses cannot survive without secure, accessible, and flexible data. Database provide a universal standardized way to store data (in a secure way). Foundation Data Concepts Abstract Concepts Entity – person, place, object or event – stored as a record or a table row Attribute – characteristic of an entity – stored as field or table column Foundation Data Concepts Large Database Concepts Database – a collection of related tables Tables – a collection of related records – collection of related entities Record – collection of fields (table row) –represents an entity Field – collection of characters (table column) – represents an attribute Character – single alphabetic, numeric or other symbol Small Fields Characters “B R E I M E R” form a field Last Name Breimer A field is an attribute of an entity Records A bunch of fields form a record First Name Last Name Sex Eric Breimer Yes A record is an entity Weight 263 Tables A bunch of records forms a table First Name Last Name Sex Age Eric Breimer M 46 Joseph Kim M 20 Allie Primo F 21 A table is a group of related entities Databases A bunch of tables form a database Order Table Customer Table Product Table A database can represent a single business or an entire market Databases But, databases are not just a bunch of tables Orders OID CID PID Quantity 001 508 199 500,000 002 508 201 2 003 510 201 1 Customers Products CID FName LName Address PID Description Cost 508 Eric Breimer ... 199 Viagra $45.99 509 Andrew Zych ... 200 Tooth Paste $2.58 510 Greg Smith ... 201 Hair Gel $5.99 A database also includes relationships between the different tables Chapter 5 Relationships & Queries in Databases Types of Relationships ThingA One to One Examples? Analysis Technique ThingB Relationship Man Woman Married Consider ThingA and ThingB Can ThingA be related to more than one ThingB? Can ThingB be related to more than one ThingA? If the two answers are NO, then it is a one to one relationship. Types of Relationships Student Faculty One to Many Examples? Analysis Technique Student Student Advises Get Advisement Consider ThingA and ThingB Can ThingA be related to more than one ThingB? Can ThingB be related to more than one ThingA? If only one answer is yes, then you have a one to many relationship Types of Relationships student takes course Student Many to Many Examples? Analysis Technique Course Student Course Student Student course has a student Consider ThingA and ThingB Can ThingA be related to more than one ThingB? Can ThingB be related to more than one ThingA? If the answers are yes and yes, then the relationship is many to many. How to Model Relationships Orders OID CID PID Quantity 001 508 199 500,000 002 508 201 2 003 510 201 1 Customers Products CID FName LName Address PID Description Cost 508 Eric Breimer ... 199 Viagra $45.99 509 Andrew Zych ... 200 Tooth Paste $2.58 510 Greg Smith ... 201 Hair Gel $5.99 Find the name and hire date of the manager working on the sales manual project Traditional File Processing Sucks File Processing: Data is organized, stored, and processed in independent files of data records Sometimes the files are spreadsheets Sometimes they can can even be Word or Text Documents (eeeck!) Problems of File Processing Data Redundancy – Lack of Integration – duplicate data requires update to many files data stored in separate files hard to combine data Data Dependence – changing the file format requires changing the program… Database Management Approach Consolidates data records into one CENTRAL database that can be accessed by many different application programs. Database Management Software (DBMS) Definition: Software that controls the creation, maintenance, and use of databases DBMS Software Components Database Definition Language and graphical tools to define entities, relationships, integrity constraints, and authorization rights Application Development Graphical tools to develop menus, data entry forms, and reports DBMS Software Components Transaction Processing Controls to prevent interference from simultaneous users and Controls to recover lost data after a failure Database Tuning Tools to monitor and improve database performance Database Interrogation Definition: Capability of a DBMS to report information from the database in response to end users’ requests Query Language – allows easy, immediate access to ad hoc data requests Report Generator - allows quick, easy specification of a report format for information users have requested Natural Language vs. SQL Queries Schemas Schema - A description of the database Subschema – describes a subset of the database and which users have access to this subset Data Definition Language Language Used to describe Schemas and Subschemas Describes relationships between different data Provides a Logical view of the data Data Dictionary Entry A more detailed description of the data in a database Specifies data types and ranges Assists programmers in understanding the data Physical vs. Logical DBMS concentrate on Physical access to the underlying tables Concurrency control Query’s Creating/deleting tables Physical vs. Logical MIS systems are (Logically) interface with a DBMS monthly reports charts automated inquiries Application Development Today, even non-technical staff can use tools to build little programs that use a database. Database Management Systems have all kinds of tools to develop custom application programs and interfaces. Example: The College’s MIS (Banner) is actually an application built on top of a Oracle Database.