* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Database Management Systems (DMS)
Global serializability wikipedia , lookup
Commitment ordering wikipedia , lookup
Serializability wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Access wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Oracle Database wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Ingres (database) wikipedia , lookup
Functional Database Model wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
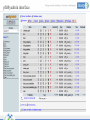
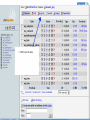
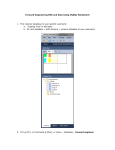
Database Management Systems (DMS) Objectives • To define Database Management Systems (DBMS) • To understand and define various terms and basic functionalities of phpmyadmin interface • Learn to install, configure a MySQL database • To create users on MySQL • To be able to list databases and creating tables • To populate and query databases 22/05/2017 2 Definitions What is a Database? A database is an integrated collection of logically related records or files consolidated into a common pool that provides data for one or more multiple uses. You can think of a database as an electronic filing system. Database Management System (DBMS) Software that organizes the storage of data. A DBMS controls the creation, maintenance, and use of the database storage structures of organizations and of their end users. Database Management System (DBMS) There are several Database Management Systems (DBMS), such as: Microsoft SQL Server Oracle Sybase DBase Microsoft Access 22/05/2017 4 The goal of a DBMS • The goal of a DBMS is to provide an environment that is both convenient and efficient to use in: – Retrieving information from the database. – Storing information into the database. Databases • Databases are usually designed to manage large bodies of information. This involves: – Definition of structures for information storage (data modeling). – Provision of mechanisms for the manipulation of information (file and systems structure, query processing). – Providing for the safety of information in the database (crash recovery and security). – Concurrency control if the system is shared by users. Purpose of Database Systems • • • • • • Data redundancy and inconsistency Difficulty in accessing data Data isolation Multiple users Security problems Integrity problems DBMS Terminologies: • Database: A database is a collection of tables, with related data. • Table: A table is a matrix with data. A table in a database looks like a simple spreadsheet. • Column: One column (data element) contains data of one and the same kind, for example the column postcode. • Row: A row (= tuple, entry or record) is a group of related data, for example the data of one subscription. • Redundancy: Storing data twice, redundantly to make the system faster. Terminologies (cont.) • Primary Key: A primary key is unique. A key value cannot occur twice in one table. With a key, you can find at most one row. • Foreign Key: A foreign key is the linking pin between two tables. • Compound Key: A compound key (composite key) is a key that consists of multiple columns, because one column is not sufficiently unique. • Index: An index in a database resembles an index at the back of a book. • Referential Integrity: Referential Integrity makes sure that a foreign key value always points to an existing row. MySQL Database Case Study, this document will focus on MySQL server MySQL • MySQL is a fast, easy-to-use RDBMS being used for many small and big businesses. • MySQL is released under an open-source license. So you have nothing to pay to use it. • MySQL is a very powerful program in its own right. It handles a large subset of the functionality of the most expensive and powerful database packages. • MySQL uses a standard form of the well-known SQL data language. • MySQL works very quickly and works well even with large data sets. • MySQL is very friendly to PHP, the most appreciated language for web development. Exercise One: • How to install, configure and secure a MySQL database • Logging in and creating users on MySQL Structure of a Database Tables: The basic units in a database are tables and the relationship between them. Unique key: In relational database design, a unique key or primary key is a candidate key to uniquely identify each row in a table. A primary key: Is a special case of unique keys Foreign key: In the context of relational databases, a foreign key is a referential constraint between two tables. Structure of a Database (Cont.) Views: In database theory, a view consists of a stored query accessible as a virtual table composed of the result set of a query. Functions: In SQL databases, a user-defined function provides a mechanism for extending the functionality of the database server by adding a function that can be evaluated in SQL statements. Triggers: A database trigger is procedural code that is automatically executed in response to certain events on a particular table or view in a database. 22/05/2017 14 THE PHPMYADMIN COMMAND PhpMyAdmin provides an easy to use and easy to understand interface to administer your database(s). It was intended to handle the administration of MySQL via a web browser. phMyadmin interface Understanding Tabs in the Interface • • • • • • • • Structure: Lists the structure of the databases SQL: Run SQL query/queries on database MySQL: Search: Search in database Query: Used to write queries and views from table Export: View dump (schema) of database, Export Import: introduce/ import a file Operations: Basic Operations within the database Privileges: Accessing database and user scope to manipulate the database • Drop: Used to delete a database or table • Database tables • Listing and creating database tables Tables • Tables contain records (sometimes called rows), and records contain fields (sometimes called columns) : POPULATING AND QUERYING DATABASES • After creating your database, inserting tables, you need to populate it. • The LOAD DATA and INSERT statements are useful for this. INSERT Statement The INSERT INTO SELECT statement selects data from one table and inserts it into an existing table. Any existing rows in the target table are unaffected. INSERT INTO table2 (column_name(s)) SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1; SELECT Statement The SELECT statement is used to pull information from a table. The general form of the statement is: SELECT what_to_select FROM which_table WHERE conditions_to_satisfy; what_to_select Back- Ups Backup of Mysql database It is very important to do backup of your MySql database, you will probably realize it when it is too late. All the content in the MySql database must also be backed up. Restoring a backup of a MySql database 1. To restore a database, you click the SQL tab. 2. On the "SQL"-page , unclick the show query here again. 3. Browse to your backup of the database. 4. Click Go. FEEDBACK This work is licensed under a Creative Commons AttributionShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. 22/05/2017 27