* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Title
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Relational algebra wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
Ingres (database) wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Object-relational impedance mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
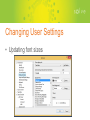
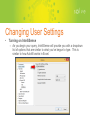
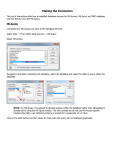
Intro to SQL Management Studio Please Be Sure!! Make sure that your access is read only. If it isn’t, you have the potential to change data within your database. There is NO undo button!! Accessing Your Database • • • • Opening Management Studio Connecting to database Credentials Structure – Database -> Folders ->Tables ->Columns Changing User Settings • Updating font sizes Changing User Settings • Displaying line numbers if they aren’t already Changing User Settings • Turning on IntelliSense – As you begin your query, IntelliSense will provide you with a dropdown list of options that are similar to what you’ve begun to type. This is similar to how Autofill works in Excel. Changing User Settings • Updating query run times. – Can shorten the amount of time it takes for your query to come back if the table contains a large data set. Important Buttons • New Query • Execute • Stopping a Query Basic Selections • Select * From [Table]; • This will select all columns from the named table • Select [Column] , [Column] , [Column] From [Table]; • This will select the listed columns from the named table • Note: Columns with spaces, dashes or other special characters in their name must be enclosed in a brackets due to naming conventions of SQL Server. Otherwise the brackets are optional. Select using “where” • Select * From [Table] where [Column] <operator> ‘text string’; • This will select all columns of data from the named table if the named column data matches the operator and text string you entered (ex: [Company] = ‘Sample Company’) • Operators • • • • • • = (Equals) <> (Not equal) < (Less than) > (Greater than) <= (Less than or equal to) >= (Greater than or equal to) Aggregate Functions • Sum ( [Column] ) • Will add every value in the particular column • Count ( [Column] ) • Will give the total number of fields that are not null. If you want to count the number of rows use count * • Max ( [Column] ) • Min ( [Column] ) • Avg ( [Column] ) • These will give you the max, min, or average of the data. Using Group by • When using the aggregate functions in a select statement, all fields that are not being aggregated must be included in a group by clause. • Select [Column1] , <aggregate function> [Column2] From [Table] Group by [Column1]; Caution! If you are selecting multiple tables you should be using a “join” statement in order to limit the amount of time a query takes to run. Intro Joins • Joins – Link two tables together on a named column that both tables share • Inner Join – Returns the data set of records in the first table that have a related record in the second table. Intro Joins • Left Outer Join – Returns the entire dataset of the first table. If there is a not a related record in the second table it returns “NULL” Questions? More Info • If you are looking for further instruction, please follow the link below to some videos that may be of assistance http://www.davisware.com/supporttraining/GE/GE%205 %20Training%20Videos/