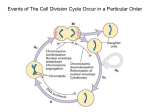
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Management Tools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Storage Edition for Oracle Storage Management Software Suite for Oracle Databases on HP Servers Melissa Stein Product Management October 1999 Agenda VERITAS Product Overview DBA’s Challenges VERITAS Storage Edition for Oracle Enhanced Performance High Availability Faster Recoverability Improved Manageability Summary 2 Database Administrator’s Challenges Optimal database performance 24x7 availability of mission-critical databases Continuous database access Fast recovery Restore from consistent backups Increasing management complexity High growth in data volume • Complex data types (e.g., video, sound) Increasing number of users Diverse database server configurations (e.g. replication servers) 3 Storage Edition for Oracle VERITAS Storage Edition for Oracle enables database administrators to manage Oracle7 and Oracle8 environments with the flexibility of file systems at raw disk performance. Its data redundancy techniques and online administration features increase data reliability and availability. Storage Edition for Oracle enables DBAs to meet their top priorities: optimal performance, availability, recoverability, and manageability of databases 4 Storage Edition 2.0 Architecture Integration of online and offline storage management Oracle Storage Edition for Oracle VxDBA Utility NetBackup Block-level Incremental Backup Extension VERITAS File System with Quick I/O & Storage Checkpoints 5 Feature Overview Quick I/O Raw device performance with File System manageability Asynchronous I/O support Online administration of database storage Storage Checkpoints Enable Block-level Incremental Backup Enable Storage Rollback for immediate “point-in-time” recovery from on-disk images HP-UX 11.0 support 6 Storage Edition for Oracle Enhanced Performance Storage Edition for Oracle Performance Increased performance increased productivity Equal to raw device performance using Quick I/O Large I/O optimization Accelerated I/O performance for large files (e.g., video, images) 8 Database Performance Issues with Conventional File Systems Redundant data buffering System buffer cache Redundant buffer copying Inefficient use of memory Database buffer cache Single writer lock per file at UNIX file system level UNIX file-level lock level lock RDBMS row- or page- Serialized write operations Impact on performance in multi-user client/server environments Asynchronous I/O Supported only on raw devices, not on regular files 9 Building Oracle Databases on Raw Disks vs. File Systems Unique, total storage foundation solution to deliver the best of both worlds Storage Edition for Oracle Raw Disks Conventional File Systems Advantages Disadvantages Advantages Disadvantages Performance Manageability Manageability Performance Best OLTP performance Data Reliability No potential for data loss with data written to disks directly “Invisible” locations for tablespaces Difficult to grow tablespaces Tablespace Lower database organization throughput System-wide (30-90% of backup and raw disk) restore Higher CPU policies overhead Easy to create Data Reliability and expand files for Oracle Potential data loss 10 Raw Disk Performance Quick I/O Database Accelerator Break-through VERITAS File System interface technology Presents regular VERITAS File System files to Oracle as raw character devices Quick I/O regular raw file device Oracle Server Allows parallel updates to database files for increased throughput Oracle handles locking for data integrity Eliminates traditional UNIX file system overhead Removes single-writer lock at file level Bypasses redundant data buffering 11 Quick I/O Performance Comparison to Raw I/O Storage Edition has equal to raw performance 160% performance improvement over traditional file systems Raw Disk Storage Edition Tested configuration included: •HP K570 (4 CPUs and 1 GB of RAM) •HP-UX 11.0 (64-bit) •Storage Edition 2.0 for Oracle •Oracle 8.0.5 (64-bit) •TPC-C scale factor of 100 warehouses Percentage of Raw I/O Performance Raw = 100% 100% Buffered IO Direct IO 80% 60% 40% 20% 0% 50 MB 100 MB 200 MB 300 MB 400 MB 500 MB Oracle Buffer Cache Size 12 Large I/O Optimization VERITAS File System allocates disk space in groups of contiguous blocks or “extents” Extent-based allocation can accelerate I/O by increasing the I/O transfer size in the File System Optimal for large files Large Oracle tablespaces Binary Large Objects (BLOBs) (e.g., images, sounds) 13 VERITAS File System Extent-based Allocation Veritas File Systm Inode Extent Addresses Disk Block Disk Block Disk Block Disk Block Disk Block Disk Block Disk Block Disk Block Disk Block Disk Block Disk Block Disk Block Disk Block Disk Block Disk Block Disk Block Direct Address 0 / Length Direct Address 1 / Length Direct Address 2 / Length Direct Address 3 / Length Direct Address 4 / Length Direct Address 5 / Length Direct Address 6 / Length Direct Address 7 / Length Direct Address 8 / Length Direct Address 9 / Length Single Indirect Block Double Indirect Block 14 Storage Edition for Oracle High Availability The Need for High Availability Many factors contribute to potential downtime Software Hardware People Planned downtime (for maintenance tasks) Downtime impacts business operations Revenue, customer service, and productivity at risk 16 Financial Impact of System Failure Application Industry Average Hourly Cost Brokerage Operations Finance $6.45 Million Credit Card/Sales Auth. Finance $2.6 Million Pay-per-View Media $150 Thousand Home Shopping (TV) Retail $113 Thousand Catalog Sales Retail $90 Thousand Airline Reservations Transportation $89.5 Thousand Tele-Ticket Sales Media $69 Thousand Package Shipping Transporation $28 Thousand ATM Fees Finance $14.5 Thousand Source: Contingency Planning Research 17 Storage Edition for Oracle Availability Online administration Storage reconfiguration and maintenance without downtime Automated, proactive monitoring of file system to avoid unexpected “out-of-space” conditions 18 Online Administration Enables DBAs and system administrators to meet changing database storage requirements without database downtime Supports online tablespace growth • Online resizing of file systems Allows database storage reconfiguration • Defragmenting mounted file systems 19 Online Administration Example Extend a file system Locate new disk space Create a new file system Stop work Copy files to the file system Resume work Select “resize a file system” from a menu Enter the new file system size No interruption to users or applications 20 Intelligent File System Control Policy driven File Management Why ? • Lack of file system free space can cause REACTIVE widespread application failure How ? • Included Agent monitors average available free space of VERITAS File System • If average free space falls below threshold set by the administrator, the agent will automatically grow PROACTIVE the File System and underlying volume if need be to enforce free space policy Configured via VxDBA utility 21 Storage Edition for Oracle Faster Recoverability Storage Edition for Oracle Recoverability Fast database recovery from system crash Fast file system recovery through journaling Database recovery from consistent, stable backups File System snapshots for system and database backups Virtually eliminate database backup window Enables block-level incremental backup to back up only changed data blocks Faster database Recovery from logical error Enables point-in-time recovery from on-disk image 23 Database Recovery Database recovery begins only after file system recovery Journaling File System minimizes database downtime File system recovery only requires replaying the intent log File system recovery time does not depend on file system size Large file system (over 100 GB) usually takes only seconds to verify / recover 24 Consistent Database Backups VERITAS File System’s snapshot mechanism Enables system-wide backups for database and non-database files Reduces backup window for cold database backups to a couple of seconds Simplifies recovery process for hot database backups Supports UNIX utilities like tar and cpio, and off-the-shelf UNIX third party solutions 25 VERITAS File System Snapshot Take a snapshot at 9 AM on Monday /oradata_snapshot /oradata “Original” data blocks A consistent “view” of the file system at 9AM by keeping track of changed data blocks (“copy on write”) Only 5-20% of original storage required Data blocks continue to be updated 26 Full Database Backups with File System Snapshot Cold database backup (or off-line backup) Shutdown the database A couple of seconds of downtime Snapshot Start the database Mount snapshot file system(s) Resume operation Perform backup Unmount snapshot file system(s) Enables database access and backups in parallel Small storage requirement (approx. 15% additional disk space) 27 Hot Database Backups with File System Snapshot Hot database backup (or on-line backup) Reduces recovery window with fewer changes to apply Begin tablespace backup A couple of seconds of changes to apply at recovery End tablespace backup Snapshot Mount snapshot file system(s) Perform backup 28 Key Differentiator: VERITAS Storage Checkpoints Point-in-time snapshot of database Storage Checkpoints maintain changed data blocks as database is being updated Uses efficient copy-on-write technique No post-processing needed to scan for changed data blocks 29 Create a Checkpoint.. Simplified illustration of initializing a storage checkpoint Primary File System Storage Checkpoint (empty) A B C D E The storage checkpoint presents an exact image of the primary file system. 30 and update the filesystem Simplified illustration of initializing a storage checkpoint Primary File System Storage Checkpoint A B C D E1 E As the primary file system is updated, the original data is copied to the storage checkpoint before the new data is written. As the primary file system continues to change, the storage checkpoint accumulates the original data blocks 31 and again.. Simplified illustration of initializing a storage checkpoint Primary File System Storage Checkpoint A B C1 C D E1 E And so the process continues until the next checkpoint is created 32 Benefits of Storage Checkpoints Block-Level Incremental Backup: NetBackup manages Storage Checkpoints and extracts only the changed blocks Storage Rollback: VxDBA utility manages Storage Checkpoints for faster database recoverability from on-disk backup image 33 Traditional Backup Approaches Full backups Shrinking backup windows Approaches to minimize downtime • Hot database backups • Third mirror break-off • Rolling backups (full + tables) File-level incremental backups Poor fit for database environments Other (block-level) incremental backups SQL-BackTrack Oracle8.0’s Recovery Manager (RMAN) Our advantage: Storage Checkpoints 34 Storage Edition: Block-Level Incremental Backups Back up only changed data blocks! Higher data availability Virtually eliminates backup windows Allows more frequent backup schedules Backups contain up-to-date data Enhanced performance Significantly lowers CPU and network resource drain during backups Faster recovery from backups (less redo logs to apply) Requires NetBackup Server engine 3.2 and and database server to be backed up to be a NetBackup client 35 Block-Level Incremental Backup Changed Blocks Since Last Backup VERITAS File System with Storage Checkpoints NetBackup Server NetBackup BLI Extension Minimize Your Database Backup Window Previous Full Backup + Block Level Incrementals Full Restore 36 Cold Database Backups with Storage Checkpoints Enables database access and backup in parallel with minimal interruption Cold database backup (or off-line backup) with a couple of seconds of downtime Shutdown database A couple of seconds of downtime Storage Checkpoint Start the database Perform backup Resume operation Managed by NetBackup 37 Hot Database Backups with Storage Checkpoints Hot database backup (or on-line backup) Reduces recovery window with fewer changes to apply Begin tablespace backup A couple of seconds of changes to apply at Storage Checkpoint recovery End tablespace backup Perform backup Managed by NetBackup 38 Full Backup with Storage Checkpoint /oradata A B C D E storage checkpoint at 1:00AM • Bring the database into a consistent state • Take a storage checkpoint • Resume database operation • Back up from the storage checkpoint • The storage checkpoint presents a “frozen” image of the file system F G H A B C 39 During Full Backup /oradata storage checkpoint at 1:00AM A’ A A • During backup, the database is accessible and being updated • The storage checkpoint continues to present a “frozen” image of the file system B C D E F G G’ H G A B C D E F G H 40 After Full Backup /oradata storage checkpoint at 1:00AM A’ A A B • After the full backup, the database continues to be updated C D’ D D E F G’ G G H’ H H So… Which blocks have changed since the full backup? What are the changes? A’ D’ G’ H’ 41 Block-Level Incremental Backup /oradata A’ Second storage First storage checkpoint at checkpoint at 12:00PM 1:00AM A • Bring the database into a consistent state • Take a second storage chkpt • Resume database operation E • Back up using the storage checkpoints • Before-images saved on the first storage checkpoint indicate which blocks have changed since the full backup F • Changed data is read from /oradata B C D’ D G’ G H’ H A’ D’ 42 During Block-Level Incremental Backup /oradata Second storage First storage checkpoint at checkpoint at 12:00PM 1:00AM A’ A B C C’ D* D’ C D’ D E F G’ H’ H* G H’ H • During backup, the database is being updated • Changes after 12:00PM are saved on the second storage checkpoint • The second storage checkpoint presents a “frozen” image of /oradata at 12:00PM • Changed data is read from the second storage checkpoint or /oradata A’ D’ G’ H’ 43 Restore from BLI Backup Restoring incremental image requires restoring full backup plus all incrementals to get to desired point in time. Benefit: BLI Backup enables more frequent backups More up-to-date backup images Less logs to apply upon restore Faster database recovery Previous Full Backup + Block Level Incrementals Full Restore 44 Storage Rollback Storage Checkpoints are on-disk backup images Consistent, stable images of a file system at a particular point in time Storage Rollback is “restore” from the on-disk backup images or Storage Checkpoints Copies before-images of data blocks back to the live file system Restores without going to tapes 45 Storage Rollback Recovery from Storage Checkpoints = Simply write back changed (blue) blocks to previous state and then apply redo logs to bring database to desired point in time 46 Storage Rollback Example /oradata Images of /oradata and its Storage Checkpoints Second storage First storage checkpoint at checkpoint at 12:00PM 1:00AM A’ A B C’ C D* D’ D E F G’ H* G H’ H 47 Storage Rollback Example /oradata at 1:00AM /oradata at 12:00 PM A A’ B B C C D D’ E E F F G G’ H H’ 48 Storage Rollback to 12:00PM /oradata Second storage checkpoint at 12:00PM A’ B C C’ C D’ D* D’ /oradata at 12:00 PM Before-images on the 12:00PM Storage Checkpoint are copied back to the live file system, /oradata A’ B C D’ E E F F G’ G’ H’ H* H’ H’ 49 Storage Rollback to 1:00 AM /oradata Second storage First storage checkpoint at checkpoint at 12:00PM 1:00AM A’ A A B C C’ C D D* D’ D /oradata at 1:00AM Before-images from 1:00AM and 12:00PM Storage Checkpoints are copied. A B C D E E F F G’ G H H* H’ G G H H 50 The Time Line Difference Between Storage Rollback and BLIB Restore 6:00am 9:00am Storage Checkpoint BLIB 11:00am 1:00pm OOPS! File Lost 3:00pm Storage Rollback 51 Snapshot/Checkpoint Comparison File System Snapshot Storage Checkpoint Full only Block-level Transient Persistent Unaware Aware of each other Separate storage pool Shared storage pool Mount empty disk Coordinate with Oracle states • NetBackup for BLI Backup • VxDBA utility for Storage Rollback 52 Storage Edition for Oracle Improved Manageability Storage Edition for Oracle Manageability Familiar file system administration for Oracle database files Combines raw I/O performance and ease of file system management Large database configuration support Supports large file systems to simplify management Guide to simplify administration of database storage Integration with familiar System Administration Manager (SAM) interface 54 Ease of File System Management Administrative comforts Familiar naming conventions and utilities to manage Oracle database files Datafiles can be grouped together for storage hierarchy Common backup strategies for database and non-database files 55 Large Database Configuration Support Storage Edition can support file systems up to 2 TB in size File system sizes are not limited to underlying device sizes No longer need to manage multiple file systems per database Online resizing further simplifies file system management 56 Database Administrator’s Guide Cookbook for setting up and tuning database environments Tailored for DBAs to optimize database storage layouts Presents various storage configuration options Recommends optimal configurations specific to database application workloads 57 Storage Edition 2.0 for Oracle Summary Enhanced Performance Raw disk performance with ease of file system management Increased throughput for OLTP applications High Availability Proactive, automated file system monitoring agent Increased data reliability and availability for missioncritical databases Online administration Fast database backup and recovery Improved Management Simplified administration for large databases Simplified management through SAM integration 58 Supported Platforms HP-UX 11.0 support Passed MC/ServiceGuard compatibility testing Oracle7 and Oracle8 Support for Oracle 8i planned ORACLE CERTIFIED 59 Storage Edition for Oracle Performance Availability Users Recoverability Network Manageability End-User Applications VERITAS Storage Edition for Oracle HP SAM GUI FS Agent NetBackup BLIB Ext. Applications Oracle Server VERITAS File System + Quick I/O Operating System HP Logical Volume Manager Disks 60 Business Without Interruption 61





































































![[#MODULES-4428] Backup script try to backup sys database when](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005823897_1-f86b001551ca5e83ed406bca77a48421-150x150.png)