* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download chap3-archi and infra
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
Data Protection Act, 2012 wikipedia , lookup
Data center wikipedia , lookup
Forecasting wikipedia , lookup
Data analysis wikipedia , lookup
Database model wikipedia , lookup
Information privacy law wikipedia , lookup
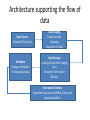
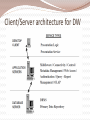
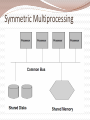
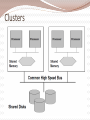
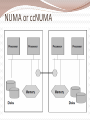
Architecture and Infrastructure Module 2 G.Anuradha What is architecture? • The structure that brings all the components of a data warehouse together is known as the architecture. • Many factors affect the architecture of a DW – Integrated data – Data preparation and storing – Data delivery – Technology • Comprehensive blueprint Architecture in 3 major areas • Data acquisition • Data storage • Information delivery Distinguishing characteristics of architecture • Different Objectives and Scope – For providing strategic information DW should have elaborate architecture – Scope depends on the sources used in the acquisition region • Data Content – Dealing with historical, read only data • Complex Analysis and Quick Response – Drill down, roll up, slice, dice, what if scenarios • Flexible and Dynamic – Design should be dynamic after designing as well • Metadata-driven – Every movement is trapped in it. Test your fundas ACROSS 1. Business dimension(5) 6. Smaller than DW(8) 7. Combining data from different operational systems(10) 8. Initial loading(7) DOWN 2. Remove useful information from operational data(10) 3. Monitoring the entire function (10) 4. Historical(8) 5. Data about entire warehouse(8) Solution Architecture supporting the flow of data Data Source (internal & External) Metadata Storage mechanism for data about data Data Staging Transformation Cleansing Integration of Data Data Storage Loading of data from Staging Area Storing for Information Delivery Information Delivery Dependent data marts, MDDBs, Query and reporting facilities Management and control module • Umbrella component having two important functions – Monitor all ongoing operations – Problem recovery List of services and functions-Data Extraction • Select data sources and determine the types of filters to be applied to individual sources • Generate automatic extract files from operational systems using replication and other techniques • Create intermediary files to store selected data to be merged later • Transport extracted files from multiple platforms • Provide automated job control services for creating extract files • Reformat input from outside sources • Reformat input from departmental data files, databases, and spreadsheets • Generate common application code for data extraction • Resolve inconsistencies for common data elements from multiple sources List of services and functions-Data Transformation • Map input data to data for data warehouse repository • Clean data, deduplicate, and merge/purge • Denormalize extracted data structures as required by the dimensional model of the data warehouse • Convert data types • Calculate and derive attribute values • Check for referential integrity • Aggregate data as needed • Resolve missing values • Consolidate and integrate data List of functions and services-Data staging • • • • • • • • Provide backup and recovery for staging area repositories Sort and merge files Create files as input to make changes to dimension tables If data staging storage is a relational database, create and populate database Preserve audit trail to relate each data item in the data warehouse to input source Resolve and create primary and foreign keys for load tables Consolidate datasets and create flat files for loading through DBMS utilities If staging area storage is a relational database, extract load files Data Storage • loading the data from the staging area into the data warehouse repository • before loading data into the data ware the metadata repository gets populated • For top-bottom approach there could be movements of data from the enterprise-wide data warehouse repository to the repositories of the dependent data marts • For bottom-up approach data movements stop with the appropriate conformed data marts Information Delivery • Information access in a data warehouse is through online queries and interactive analysis sessions • data warehouse will also be producing regular and ad hoc reports. • data warehouse feeds data to proprietary multidimensional databases (MDDBs) where summarized data is kept as multidimensional cubes of information Data stores for information delivery Function and services • Provide security to control information access and monitor user access • Allow users to browse data warehouse content by hiding internal complexities • Automatically reformat queries for optimal execution, from aggregate tables as well • Provide self-service report generation for users, consisting of a variety of flexible options to create, schedule, and run reports • Store result sets of queries and reports for future use • Provide multiple levels of data granularity • Provide event triggers to monitor data loading • Make provision for the users to perform complex analysis through OLAP • Enable data feeds to downstream, specialized decisions support systems such as EIS and data mining Summing up…… • Architecture is the structure that brings all the components together. • The architectural components support the functioning of the data warehouse in the three major areas of data acquisition, data storage, and information delivery. Infrastructure of DW G.Anuradha Infrastructure Elements that enable the architecture to be implemented. Operational – help to keep the DW going People Procedures Training Management software Physical Hardware components Operating system Network, network software Features of Hardware & OS Hardware Scalability Vendor support Vendor stability OS Scalability Security Reliability Availability Preemptive multitasking Memory protection Possible options Mainframes Old hardware Designed for OLTP Expensive Not easily scalable Open System Servers UNIX servers are most opted Robust Adapted for parallel processing NT Servers Medium-sized data warehouses Limited parallel processing Cost effective for small or medium DW Platform Options A computing platform is the set hardware components, operating system, network & network software. Both Online Transaction Processing and Decision Support Systems need a computing platform. Single Platform Option All functions from back-end data extraction to front- end query processing is performed on one platform. Data flows smoothly, no conversions required No middleware required Limitations Legacy platform stretched to capacity Non-availability of tools Multiple legacy platforms Company’s migration policy Hybrid Platform Option Eliminate s the drawbacks of single platform option Data extraction: Each source is extracted on its own computing platform Initial reformatting & merging: The extracted file from each source is reformatted & merged, on their respective platforms Preliminary data cleansing: Verify extracted data for missing values & data types. Transformation & Consolidation: Performed on the platform where the staging area resides. Validation & Final Quality Check Creation of Load Images Options for staging area Legacy platforms – when all data sources are on the same platform, we can create a DW also on the same Data storage platform – the warehouse DBMS runs here. This can be used for staging also. Separate optimal platform – a separate platform for staging data Server Hardware Server hardware is most important Scalability Query processing Data movement options Client/Server architecture for DW Considerations on client workstations Depends on type of users casual user-Web browser and HTML reports Analyst-more powerful workstation machine Practically feasible solution is a minimum configuration on an appropriate platform that would support a standard set of information delivery tools in DW Platform options as DW matures Parallel processing Symmetric multiprocessing Clusters Massively parallel processing Cache-coherent Nonuniform Memory Architecture Symmetric Multiprocessing Clusters Massively Parallel Processing NUMA or ccNUMA Database Software Many operations can be parallelized mass loading of data, full table scans, queries with exclusion conditions, queries with grouping, selection with distinct values, aggregation, sorting, creation of tables using subqueries, creating and rebuilding indexes, inserting rows into a table from other tables, enabling constraints, star transformation Types of parallelization Software Tools Summing up Infrastructure acts as the foundation supporting the data warehouse architecture Data warehouse infrastructure consists of operational infrastructure and physical infrastructure. Hardware and operating systems make up the computing environment for the DW. Several options exist for the computing platforms needed to implement the various architectural components. Summing up Selecting the server hardware is a key decision. Invariably, the choice is one of the four parallel server architectures. Current database software products are able to perform interquery and intraquery parallelization. Software tools are used in the data warehouse for data modeling, data extraction, data transformation, data loading, data quality assurance, queries and reports, and online analytical processing (OLAP). Tools are also used as middleware, alert systems, and for data warehouse administration. METADATA Data dictionary or data catalog Contains data about the data in the DW like data structures files and addresses indexes Types of Metadata Operational Extraction & Transformational End-User Need for a Metadata For using the DW For building the DW For administering the DW Automation of the DW Metadata by functional areas Every DW process occurs in one of these 3 areas Data acquisition Data storage Information delivery Data acquisition - metadata Information Delivery – metadata Types of Metadata Business metadata Portrays DW from the end user perspective Shows business names, not actual file names Less structured as compared to technical metadata Used by business analysts and other end users. Technical metadata Shows the actual structure and content of the DW Acts as a guide to build, maintain and administer the DW Used the the data warehouse administrator, and other IT staff working on the DW. How to provide metadata Metadata requirements Sources Challenges Repository Integration and standards Implementation options