* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3 rd Step: Replication
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
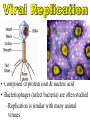
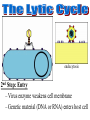
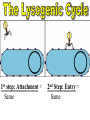
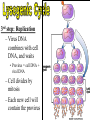
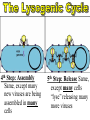
• They are not made of cells or organelles • They cannot reproduce without a host • They do not metabolize energy • They do not perform cellular processes • Reproduce • They have DNA or RNA • They can adapt to surroundings • The have organization • Composed of protein coat & nucleic acid • Bacteriophages (infect bacteria) are often studied – Replication is similar with many animal viruses 1st Step: Attachment – Virus lands on cell membrane – Virus attaches to a cell receptor – No attachment = No infection – Virus acts as a “key” to the receptor endocytosis 2nd Step: Entry – Virus enzyme weakens cell membrane – Genetic material (DNA or RNA) enters host cell 3rd Step: Replication – Virus DNA/RNA uses ribosomes to make virus proteins – Virus proteins created by transcription/ translation 4th Step: Assembly (formation) – New virus proteins are assembled in the cytoplasm 5th Step: Lyse & Release – Virus enzyme causes cell membrane to “lyse” – Viruses are released to find new host – Cycle repeats 1st step: Attachment = Same 2nd Step: Entry = Same 3rd step: Replication – Virus DNA combines with cell DNA, and waits • Provirus = cell DNA + viral DNA – Cell divides by mitosis – Each new cell will contain the provirus 4th Step: Assembly Same, except many new viruses are being assembled in many cells 5th Step: Release Same, except many cells “lyse” releasing many more viruses Retroviruses • Type of RNA virus that contains the enzyme Reverse Transcriptase • 1) Virus RNA is injected into cell • 2) Ribosome uses virus RNA to create virus DNA • 3) Virus DNA combines with cell DNA (becomes latent) • 4) Once active, normal steps of transcription/translation followed How is HIV contracted? • High risk activities: • Low risk activities: – 1) Sex (oral, vaginal, anal) – 2) Sharing needles (tattoos, piercings, drugs) – 3) Mother to child in womb – 4) Breast milk – 5) Blood transfusions MSM = men having sex with men IDU = intravenous drug users