* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 st step: Attachment
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
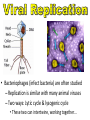
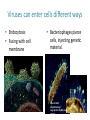
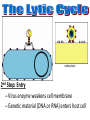
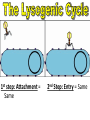
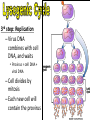
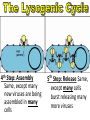
capsid DNA • All Have: – 1) Capsid: coat of protein that surrounds nucleic acid – 2) Nucleic Acid: RNA or DNA • Some Have: – Tail Fibers: Used for attachment (not legs) • Shapes vary tail sheath tail fiber – Enveloped, helical, or polyhedral • Not made of cells or organelles • Can’t reproduce on own • Don’t metabolize energy • Don’t perform cellular processes • Reproduce • Have nucleic acid • Adapt to surroundings • Have organization • Bacteriophages (infect bacteria) are often studied – Replication is similar with many animal viruses – Two ways: Lytic cycle & lysogenic cycle • These two can intertwine, working together… Viruses can enter cells different ways • Endocytosis • Fusing with cell membrane • Bacteriophages pierce cells, injecting genetic material. colored SEM; magnifications: large photo 25,000; inset 38,000x 1st Step: Attachment – Virus lands on cell membrane – Virus attaches to a cell receptor – No attachment = No infection – Virus acts as a “key” to the receptor endocytosis 2nd Step: Entry – Virus enzyme weakens cell membrane – Genetic material (DNA or RNA) enters host cell 3rd Step: Replication – Virus DNA/RNA uses ribosomes to make virus proteins – Virus proteins created by transcription/ translation 4th Step: Assembly –New virus proteins are assembled in the cytoplasm 5th Step: Release – Virus enzyme causes cell membrane to burst – Viruses are released to find new host – Cycle repeats 1st step: Attachment = Same 2nd Step: Entry = Same 3rd step: Replication – Virus DNA combines with cell DNA, and waits • Provirus = cell DNA + viral DNA – Cell divides by mitosis – Each new cell will contain the provirus 4th Step: Assembly Same, except many new viruses are being assembled in many cells 5th Step: Release Same, except many cells burst releasing many more viruses How is HIV contracted? • High risk activities: – 1) Sex (oral, vaginal, anal) – 2) Sharing needles (tattoos, piercings, drugs) • Low risk activities: – 3) Mother to child in womb – 4) Breast milk – 5) Blood transfusions (used to be higher, but sanitation is better now) What is AIDS? New Exposures to HIV (2006) Gender of those living with HIV (2003) • Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome • AIDS results when: – 1) Less then 200 T cells per 1mm³ blood – 2) Multiple symptoms/infections from HIV appear • Therefore, the HIV virus causes the disease AIDS Female Transmission of HIV (2006) Male Transmission of HIV (2006) Want more stats? Go to the Centers for Disease Control’s Website http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/topics/surveillance/united_states.htm