* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Viruses - Killeen ISD
Elsayed Elsayed Wagih wikipedia , lookup
Taura syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Canine distemper wikipedia , lookup
Canine parvovirus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
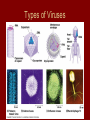
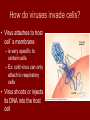
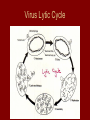
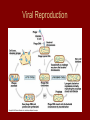
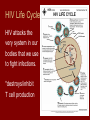
Viruses 10-6 Are they alive? What is a Virus? • Structure that contains genetic material (DNA or RNA) wrapped in protein (capsid) • Does NOT have a cell • Does NOT breathe, eat, produce wastes • Can reproduce, but only if in a host cell Types of Viruses Structure of a Virus How do viruses invade cells? • Virus attaches to host cell’s membrane – is very specific to certain cells – Ex: cold virus can only attach to respiratory cells • Virus shoots or injects its DNA into the host cell Virus Lytic Cycle How do viruses replicate? • Lytic Cycle – Virus DNA takes over cell immediately – New virus parts are made – Host cell bursts releasing new viruses to infect nearby cells – Has a short “incubation time” – Ex: flu, cold, measles Lytic Cycle How do viruses replicate? • Lysogenic Cycle – Viral DNA “hides out” within host’s DNA – Virus DNA gets copied everytime host cells copy – At some point, virus goes into lytic cycle and kills host cells – Has long incubation time (months-years) – Ex: HIV, warts, shingles, herpes Lysogenic Cycle Viral Reproduction HIV Life Cycle HIV attacks the very system in our bodies that we use to fight infections. *destroys/inhibit T cell production Virus Evolution • What makes a virus a “smart” or “successful” virus? – A smart virus is one that does not kill its host right away; moreover, a smart virus wants to be able to survive and reproduce for as long as possible without killing its host. From an evolutionary standpoint, is Ebola a “smart” virus? • What would Darwin say???