* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reproduction - Mexico Central School District
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
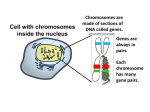
The life process by which an organism produces new individuals of the same kind. This is essential for the survival of the species Asexual Reproduction one parent and Involves ________ results in one or more offspring identical to that are genetically _________ that parent. Cells reproduce by Mitosis A process where a cell divides and creates two daughter cells which are identical to the parent Cell Division happens by series of phases ▪ Interphase, prophase, metaphase,anaphase, and telophase (cytokinesis) ▪ I.P.M.A.T.(C). I.P.M.A.T.C. interphase prophase Please Make Another Two Cells cytokinesis metaphase anaphase telophase chromosomes in cell DNA in chromosomes cell nucleus 4 single-stranded chromosomes duplicated chromosomes duplicated chromosomes 4 double-stranded chromosomes cell nucleus Stage 1: cell copies DNA Copy DNA! DNA cell nucleus INTERPHASE Stage 2: DNA winds into chromosomes Nuclear membrane disappears Spindle Fibers/ Centrioles appear duplicated chromosomes Wind up! cell nucleus PROPHASE double-stranded human chromosomes ready for mitosis Stage 3: Chromosomes line up in middle attached to protein “cables” that will help them move Line up! duplicated chromosomes lined up in middle of cell METAPHASE Stage 4: Chromosomes separate start moving to opposite ends Separate! chromosomes split & move to opposite ends ANAPHASE Stage 5: Cell starts to divide Two nuclei Chromosomes unwind Divide! TELOPHASE Stage 6: DNA unwinds again cells separate completely (cleavage furrow) now they can do their every day jobs Bye Bye! CYTOKINESIS Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division… Binary Fission The cell splits into two identical cells, each containing an exact copy of the original cell's DNA. Nucleus and Cytoplasm divide EQUALLY! Buddingwhere the daughter cell grows out of the parent and gradually increases in size. Yeast cells Hydra Nucleus divides equally Cytoplasm divides unequally Spores Reproductive cell that contains a nucleus and a small amount of cytoplasm Spores are highly resistant to heat Spores are capable of growing into a new organism when conditions allow Produced by bread mold, mushrooms, mosses and ferns Regeneration Development of a new organism from part of a parent Whole organisms are produced – Starfish! Replacement of lost body part Vegetative Propagation Part of a plant (root, stem, leaves) grows into a new plant Seedless fruits & vegetables Commonly used by farmers = quick, easy & successful! Offspring receive half of their genes from one parent and half from the other parent The genes are carried on chromosomes in sex cells known as gametes Male gamete is the sperm cell Female gamete is the ovum (egg) Joining of 2 sex cells (egg & sperm) Do we make egg & sperm by mitosis? No! What if we did, then…. 46 egg + 46 92 sperm zygote Doesn’t work! Gametes are formed by Meiosis Meiosis (reduction division) In series of divisions the number of chromosomes is reduced by half 46 chromosomes to 23 chromosomes half the number of chromosomes 23 46 meiosis 46 diploid egg 23 sperm haploid Fertilization Two gametes (Ovum and Sperm) join to create an offspring Variation Each offspring gets a unique combination of genes, therefore they are not identical to their parents or siblings. Meiosis (reduction division) Spermatogenesis: Creates 4 sperm cells Oogenesis: Creates 1 ovum and 3 polar bodies meiosis fertilization mitosis + development gametes 46 23 meiosis 23 egg 23 46 23 zygote fertilization sperm 46 46 46 46 46 46 4646 46 mitosis & mitosis development Meiosis to make gametes sperm & egg Mitosis to make copies of cells growth repair Development replacement Consistency over time meiosis keeps chromosome number same from generation to generation from Mom Mom Dad offspring from Dad We’re mixing things up here! Change over time meiosis introduces genetic variation ▪ gametes of offspring do not have same genes as gametes from parents ▪ new combinations of traits from Dad variation from Mom offspring new gametes made by offspring Crossing Over – Trading DNA! During prophase 1, sister chromatids intertwine homologous pairs swap pieces of chromosome ▪ DNA breaks & re-attaches tetrad prophase 1 Sexual reproduction allows us to maintain both genetic similarity & differences. Jonas Brothers Baldwin brothers Martin & Charlie Sheen, Emilio Estevez The nucleus is taken from parent with a complete set of genetic information Injected into an egg cell which has had its nucleus removed The egg is implanted in a surrogate mother Result is an organism which is 100% genetically identical to parent Many more to come… Too many to list…