* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT Sound 12
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
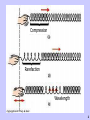
Sound Sound waves travel through a medium and can be visualized by Longitudinal or Compressional waves. As the sound moves through the medium, the particles vibrate against one another causing the compressions: A slinky is a good example of how longitudinal waves behave. 1 Compression Rarefaction Wavelength 2 What is Sound? • A sound wave is a pressure wave with regions of high (compressions) and low pressure (rarefactions) initiated by a vibrating object. • Combination of inertia and restoring force produces harmonic motion and waves • Harmonic motion is an oscillation in pressure and the wave is sound wave 3 1. Medium (solid, liquid or gas) 2. Temperature 4 5 Sound requires contact. 3350 m/s Solid 1525 m/s Liquid 343 m/s Gas So which of the above would be a better medium? Sound does NOT travel in space – there is no air to carry the sound (vacuum) 6 Temperature 343 m/s 20° 322 m/s 0° Do molecules move faster or slower as temperature increases? So would sound travel faster or slower as temperature increases? 7 All waves have 3 things in common. 1. Frequency 2. Pitch 3. Intensity / Amplitude 8 . . .the number of wave crests that pass one place each second. Frequency is measured in Hertz A. B. Frequency and wavelength of sound are inversely related – when frequency goes up the wavelength goes down proportionally 9 Doppler Effect The sound changes to a higher frequency when the source comes towards you... ...and to lower frequency when it moves away 10 Depends on the frequency Higher note / Higher frequency Lower note / Lower frequency White noise – equal mix of all frequencies 11 Which wave do you think has more intensity? A. B. Intensity is defined as the amount of energy (or amplitude) a wave has... The greater intensity, the louder the sound will be. 12 The measurement for intensity or loudness is in DECIBELS (dB). Here are some common sounds and their decibel ratings: Near total silence - 0 dB A whisper - 15 dB Normal conversation - 60 dB Lawnmower - 90 dB A car horn - 110 dB A rock concert or a jet engine - 120 dB Gunshot, firecracker - 140 dB 13 Ultrasonic • Frequency higher than 20,000Hz • Used in Sonar and Medical Diagnosis and treatment. Human Ear 20Hz to 20,000Hz Best hearing between 100-2000 Hz Infrasonic (subsonic) • Frequency lower than 20Hz • Elephant Communication and Butterflies flapping their wings, heavy machinery, thunder Supersonic- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gWGLAAYdbbc • Motion that is faster than sound-do not hear it until it passes you • Example-supersonic jets make sonic boom 14 Sonar • Sound Navigation Ranging • Uses sound to estimate the size, shape and depth of underwater objects. • Examples: Submarines, whales and bats • Sonogram-picture of a baby inside mom Echo • Reflected sound waves • Examples: Shouting in a cave or canyon 15 How Loud is Loud? • Any sound above 85 dB can cause hearing loss, and the loss is related both to the intensity of the sound as well as the length of exposure. • You know that you are listening to an 85 dB sound if you have to raise your voice to be heard by somebody else. • For example, 8 hours of 90 dB sound can cause damage, but any exposure to 140 dB sound causes immediate damage (and causes actual pain). 16 • Resonance • prolonged vibrations of sound at their own natural frequency. • an opera singer can shatter a glass if the singer resonates at the same frequency long enough 17 SOUND in MUSIC Acoustics = the science/study of sound • Music has: definite pitch sound quality repeating rhythm • Types of Instruments: Woodwinds(flute, clarinet) Brass(horns) Stringed(guitar, violin) Percussion(drum, piano) 18 Sound of Music • rhythm – regular time pattern in a sound • musical scale – set of frequencies (pitch) • harmony – how sound works together to create effects desired by the composer • beats – adding two waves that are only slightly different in frequencies • noise-no set pattern and no definite pitch • dead spots-areas where sound waves cancel out 19 Sound of Music • consonance – more than one frequency and it sounds good – frequencies are far enough apart • dissonance – more than one frequency and it sounds bad – frequencies are too close together • quality-describes the differences among sounds of the same pitch and loudness 20 Sound of Music • reverberation-many reflections of sound (echo) • use of carpets, draperies to reduce reverberation • interference-ability of two or more waves to combine and form a new wave 1. constructive-different waves arrive at the same place at the same time and cause an increase in loudness 2. destructive-one wave will arrive with the rarefaction of another wave and cancel each other causing a decrease in loudness 21































![[Ω] (Greek omega - don`t know HTML)](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009955674_1-67374e8d672b72e658259b1a7f5cfb4d-150x150.png)