* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mesopotamia - Mr. BH Gard
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
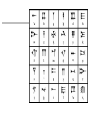
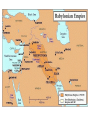
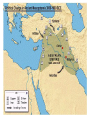
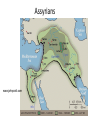
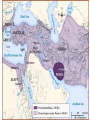
Mesopotamia: “The Cradle of Civilization” Earliest Civilization: the Fertile Crescent • earliest of all civilizations as people formed permanent settlements • Mesopotamia is a Greek word that means “between the rivers”, specifically, the area between the Tigris River and Euphrates River (present day Iraq) • Lasted for approximately 3000 years • Its peoples were the first to irrigate fields, devised a system of writing, developed mathematics, invented the wheel and learned to work with metal Beginnings ▪ About 5000 BC herders and nomads began to settle in the crescent shaped strip from the Mediterannean to the Persian Gulf. Geographic Conditions • Little rainfall • Hot and dry climate • windstorms leaving muddy river valleys in winter • catastrophic flooding of the rivers in spring • Arid soil containing little minerals • No stone or timber resources ▪ Many of these people chose to settle in Mesopotamia, the eastern part of the Fertile Crescent. ▪ Unpredicatable floods meant dams, ditches and canals had to be built to irrigate the crops. Then why live in Mesopotamia? NATURAL LEVEES: embankments produced by build-up of sediment over thousands of years of flooding Natural Levee • create a high and safe flood plain • make irrigation and canal construction easy • provide protection • the surrounding swamps were full of fish & waterfowl • reeds provided food for sheep / goats • reeds also were used as building resources Sumerians Around 3500 B.C. Sumerians began to settle in the lower part of the Tigris-Euphrates river First cities ▪ 3000 B.C. A number of city states have been established –Ur, Uruk and Eridu with populations ranging from 20250,000 Map Map Cities ▪ common culture, language and same gods and goddesses ▪ rectangular in shape ▪ ziggurats ▪ usually governed independently from others ▪ threat of foreign invaders led to unification and kingships ▪ kings were military and religious leaders (theocracy) government • early government was democratic, ruled by citizens • as cities grew, more government and more protection from outsiders was needed • bravest citizen was selected as “lugal” or king…kingship is born – powers limited – kings only served as kings for a short time in crisis then went back to being a regular citizen – as civilization and conflicts grow, kingship becomes permanent – each city-state has its own king and kings fought among other 12 Sumerian city-states to gain power over the entire area Society ▪ male and female roles clearly defined ▪ men heads of households ▪ women could buy and sell property, own businesses and slaves ▪ Importance of commerce and trade leads to development of writing system -cuneiform Writing • Greatest contribution of Mesopotamia to western civilization was the invention of writing • allowed the transmission of knowledge, the codification of laws, records to facilitate trade / farming • Sumerians wrote on wet clay tablets with the point of a reed > then dried in the sun to make a tablet • Scribes were only ones who could read and write and served as priests, record keepers and accountants • As society evolved, the first form of writing was developed called CUNEIFORM (meaning “wedge shaped”), dating to 3500 BC • Cuneiform spread to Persia and Egypt and became the vehicle for the growth and spread of civilization and the exchange of ideas among cultures Cuneiform: “Wedge-Shaped” Writing Cuneiform Cuneiform Cuneiform Writing Deciphering Cuneiform Cuneiform Gilgamesh Gilgamesh • Gilgamesh is an ancient story or epic written in Mesopotamia more than 4000 years ago • Gilgamesh is the first known work of great literature and epic poem • Epic mentions a great flood • Gilgamesh parallels the Nippur Tablet, a sixcolumned tablet telling the story of the creation of humans and animals, the cities and their rulers, and the great flood Gilgamesh Epic Tablet: Flood Story Religion • Position of King was enhanced and supported by religion gods were worshipped at huge temples called ziggurats Polytheistic religion consisting of over 3600 gods and demigods • Kingship believed to be created by gods and the king’s power was divinely ordained • Belief that gods lived on the distant mountaintops • Each god had control of certain things and each city was ruled by a different god Prominent Mesopotamian gods •Enlil (supreme god & god of air) •Ishtar (goddess of fertility & life) •An (god of heaven) •Enki (god of water & underworld) •Shamash (god of sun and giver of law) • Kings and priests acted as interpreters as they told the people what the god wanted them to do (ie. by examining the liver or lungs of a slain sheep) The Sumerians believed they had been created to serve their gods, and they served their gods with sacrificial offerings. They believed that the gods controlled the past and the future, that the gods had revealed to them the skills that they possessed, including writing, and that the gods had provided them with all they needed to know. They had no vision of their civilization having developed by their own efforts. They had no vision of technological or social progress. http://www.fsmitha.com/h1/ch01.htm religion The Mesopotamians believed: •The world was a flat disk that was surrounded by a vast hollow space and that this was enclosed in an over-arching heaven. •The sea was all around the earth...top bottom and sides. •The universe had been born of these waters. Daily menu for the god Anu at Uruk: • • • • • • • • • • • • • • 12 vessels of wine 2 vessels of milk 108 vessels of beer 243 loaves of bread 29 bushels of dates 21 rams 2 bulls l bullock 8 lambs 60 birds 3 cranes Do not copy, interest only. I 7 ducks found it interesting, anyway 4 wild boars 3 ostrich eggs 3 duck eggs Ziggurat at Ur Temple “Mountain of the Gods” Ziggurats • • Ziggurat of Ur -2000BCE • • • • Large temples dedicated to the god of the city Made of layer upon layer of mud bricks in the shape of a pyramid in many tiers (due to constant flooding and from belief that gods resided on mountaintops) Temple on top served as the god’s home and was beautifully decorated Inside was a room for offerings of food and goods Temples evolved to zigguratsa stack of 1-7 platforms decreasing in size from bottom to top Famous ziggurat was Tower of Babel (over 100m above ground and 91m base) Science and innovations ▪ wagon wheel ▪ arch ▪ sundial ▪ potter's wheel ▪ number system (base 60) ▪ 12 month calendar ▪ bronze Mesopotamian Harp Board Game From Ur Sophisticated Metallurgy Skills at Ur Empires Sargon Arsenault ▪ 2000s B.C.Sumerian city-states fall to foreign invaders ▪ Akkadians Sargon I (of Akkad) conquers Sumer in the south and then north, uniting all city states of Mesopotamia –First empire builder (many different peoples, lands controlled by one ruler) Kingdom of Ebla resisted Sargon, but fell to his grandson and eventually to the Amorites (Hyksos) ▪ Amorites destroy Ebla and continue south to conquer Sumerian cities including Babylon, which would be their new capital and name of their empire Amorite Empire/Early Babylonian ▪ under Hammurabi, the sixth king of the Babylonian dynasty, the entire Mesopotamian region is brought under central control ▪ Appointed governors, tax collectors and judges to control lands ▪ Babylon becomes major trade centre Code of Hammurabi • To enforce his rule, Hammurabi collected all the laws of Babylon in a code that would apply everywhere in the land • Most extensive law code from the ancient world (c. 1800 BC) • Code of 282 laws inscribed on a stone pillar placed near temples for all to see. • Hammurabi Stone depicts Hammurabi as receiving his authority from god Shamash • Set of divinely inspired laws; as well as societal laws • Punishments were designed to fit the crimes as people must be responsible for own actions • Consequences for crimes depended on rank in society (ie. only fines for nobility) • Established the idea that rule of law is an important part of society. Hittites (1600 B.C.) • Hittites (pronounced Hit ites) invaded from Asia Minor and raided Babylonia then went home – First to have iron weapons – Spoke wheeled chariots – Legal system emphasized payment over punishment Assyria • Assyrian Empire replaced Babylonian Empire • Assyria located in hilly northern Mesopotamia – Powerful horse and chariot army to protect lands – Soldiers only ones with iron swords and spear tips – Battering rams, ladders and tunnels to overcome city walls Sennacherib (son of Sargon II) • • • • • • made Nineveh among the most splendid capitals captured 46 cities in Palestine captured 200,150 people demanded massive tributes totally destroyed Babylon killed by his own sons Esarhaddon (son of Sennacherib) 2Kings 19:37 And it came to pass, as he was worshipping in the house of Nisroch his god, that Adrammelech and Sharezer his sons smote him with the sword: and they escaped into the land of Armenia. And Esarhaddon his son reigned in his stead. • • • • rebuilt Babylon in splendor used diplomacy and words to secure borders rather than terror 671 B.C. invaded Egypt because rest of lands were secure overtook Egypt in less than a month, conquered Memphis (capital) in less than a day Assyrian Empire • 850-650 BC Assyrians conquer most of Fertile Crescent – Syria, Babylonia, Egypt, Israel • Peak under Ashurbanipal • Chose native kings , governors to rule conquered lands • Conquered rulers paid tribute – No tribute led to destruction and exile Enemies • Assyrian cruelty led to increased enemies – Exiled peoples tried to gather forces to fight Assyrians – Assyrians had to continuously put down revolts. • Assyrian Empire falls in 609 B.C. – Defeated by combined forces of the Medes and Chaldeans – Nineveh is burned to the ground FYI Why so unpopular? • Ashurnasirpal (r. 884-860 B.C.): “I flayed the chief men of the rebels and I covered the walls with their skins. . . . Some of them were enclosed alive within the bricks of the wall, some were crucified with stakes along the wall . . . From some of them I cut off their hands and fingers, from others their noses and ears, of many I put out their eyes.” www.britannica.com Assyrians www.johnpratt.com Neo (New) Babylonian Empire 612538 BC • King Nebuchadnezzar – Greatest Babylonian king – Extended empire to greatest limits – Captured Jerusalem – Built great wealth and turned city of Babylon into one of greatest cities in the world www.about.com Babylon • Babylon home to two of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World • walls of Babylon • hanging gardens of Babylon Persian Empire (550-331 BC) • Persians and Medes warriors and cattle herders • migrated from central Asia to modern day Iran Cyrus: The Achaemenid Empire • emerges as Persian leader and conquers the Medes and Babylonian empire – Benevolent ruler; allows Jews to return an rebuild Solomon’s temple – Organizes empire into satraps • Son Cambyses conquers Egypt (525 BC) • Son in Law Darius had the task of organizing the vast empire Darius (the Great) • divided empire into twenty provinces (satrapies) • Governors (satraps) were Persian, minor officials were locals • Improved and expanded old Assyrian roads • Dies in 486 BC while Empire is in conflict with the meddlesome Greeks. FYI Xerxes 486-465 BC et al. • Continues war against the Greeks – Setback at Thermopylae – Disaster at Salamis • Artaxerxes (son) sees gradual decline of Persian Empire • Artaxerxes dies, his son Xerxes II murdered by his half brother, Sogdianus. Only after a few weeks, he was murdered by his another half brother Ochus. Ochus was one of Artaxerxes' illegitimate sons. On ascending the throne he changed his name from Ochus to Darius II. Indeed, his name in Greek was Nothos meaning "bastard". FYI Down and downer • Darius II – Peloponnesian War alliance with Sparta • Artaxerxes II – Gradual decline • Artaxerxes III – Gradual decline • Darius III – Mano to mano with Alexander the Great Religion • Persians were tolerant of other beliefs and allowed conquered peoples to keep own languages, religions and laws. • Zoroaster, a religious reformer, taught that world was divided between good (Mazda and his angels) and evil (Ahriman and his demons) • Every good man was to side with Mazda and when he died his good deeds would be weighed against his bad deeds.