* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Miss Farrell Welcomes you to South Pointe M.S. 6th Grade
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
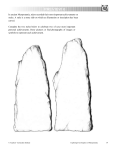
Ch. 6 Four Mesopotamian Empires Hanging Gardens of Babylon Table of Contents Assignment Page Preview 6 Reading Notes 6 Mesopotamia Map GRAPES of Mesopotamia Ch. 6 Vocabulary Processing 5 Hammurabi’s School Rules Timeline Challenge 1 Unit 2 Egypt Geography Challenge 2 49 50-53 54-55 56 57 58 59 60-61 62 63 64-65 Ch. 6 “Four Empires of Mesopotamia” Not united so group after group conquered the area and made empires No one controlled it for very long Four empires 2300 - 539 B.C.E. The Akkadian Empire (2300 B.C.E.) 6.2 The Akkadian Empire This stele represents the Akkadian achievement of… creating the world’s first empire using military skill to defeat Sumer This achievement was important because… it ended the fighting between small city-states 6.3 Life Under Akkadian Rule This stele represents the Akkadian achievement of… sculpting steles (relief sculptures on stones) This achievement was important because… it has given us a history of the Akkadian Empire Sargon Victory Stele The Babylonian Empire (1750 B.C.E.) 6.4 Hammurabi and the Babylonian Empire This stele represents the Babylonian achievement of… developing a code of laws Hammurabi’s Code of Laws This achievement was important because… it was the first code of laws to apply to everyone Unified empire, preserved order 6.5 Life in the Babylonian Empire This stele represents the Babylonian achievement of… developing Babylon as a trading center allowing women to own property and keep money allowing slaves to buy freedom This achievement was important because… it enriched people’s lives and brought new ideas to Babylon Ch.6 Exploring Four Empires of Mesopotamia The Assyrian Empire (650 B.C.E.) 6.6 The Assyrian Empire This stele represents the Assyrian achievement of… • new weapons (battering rams & moveable towers) • war strategies This achievement was important because… • other conquerors copied their weapons and strategies • built powerful empires The Assyrian Empire (650 B.C.E.) 6.7 Life Under the Assyrians This stele represents the Assyrian achievement of… • bas-reliefs (sculpture portrayed as a picture) • aqueducts This achievement was important because… • realism was introduced into sculpture • water was needed in the cities The Neo-Babylonian Empire (600 B.C.E.) 6.8 The Neo-Babylonian Empire This stele represents the Neo-Babylonian achievement of… • building protective walls and a moat around Babylon This achievement was important because… • it kept Babylonians safe The Neo-Babylonian Empire (600 B.C.E.) 6.9 Life in the Neo-Babylonian Empire This stele represents the Neo-Babylonian achievement of… • building the Hanging Gardens of Babylon • first sundial This achievement was important because… • the gardens were an engineering masterpiece • able to tell time using the sun Hammurabi’s Code of Laws (Main Topic) Category 1 details Category 2 details Category 3 details Tree Map: Used to classify or categorize Chaparral Students 6th Grade Ancient History 11 years old Arrowhead 7th Grade Medieval History 12 years old Catalina 8th Grade U.S. History 13 years old Yosemite GRAPES Geography Religion Achievements Politics Economics Social Structures GRAPES •Use key terms •Write 1 or 2 sentences (bullet points okay) •Draw picture •Present to class GRAPES of Mesopotamia (ISN ___) Geography Religion Achievements Politics Economics Social Structures Geography •Mesopotamia – “land between the rivers” •Tigris & Euphrates Rivers •Located in the fertile crescent •Modern-day Iraq Religion •Believed in many gods = polytheism •Believed gods lived in ziggurats •Kings and priests went to ziggurats to pray and ask for the gods’ blessings •Believed that the kings were chosen by the gods**** Achievements •Sumerian Inventions: •Wheel!!! •Plow used to till soil, prepare for planting •Cuneiform – first system of writing Politics •City state was like a country because it had its own farmland and government •Hammurabi’s Code of Laws was the first set of laws ever created •Four Mesopotamian Empires: •Akkadian - Sargon •Babylonian - Hammurabi •Assyrian – war strategies •Neo-Babylonian – Hanging Gardens of Babylon Economics •Farming created a stable food supply •Irrigation techniques improved farming •Surplus of food led to specialized skills (blacksmith, traders, house builder, farmer, weavers, scribes, etc.) Social Structure •Upper class (power & money) – lived in the middle of the city, attended banquets – king, priests, gov’t officials •Common class – farmer, fishermen, blacksmiths, merchants •slaves Epic Gilgamesh •oldest written story on Earth. •Sumer •12 clay tablets in cuneiform •adventures of the historical King of Uruk •between 2750 and 2500 BCE