* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download North Star
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Armillary sphere wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Orion (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
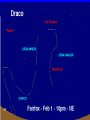
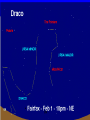
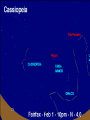
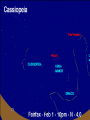
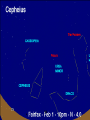
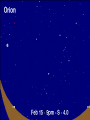
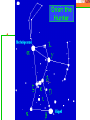
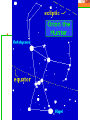
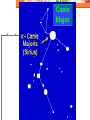
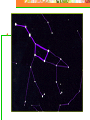
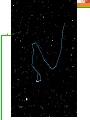
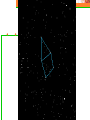
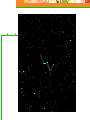
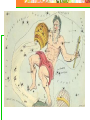
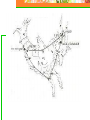
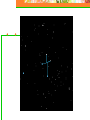
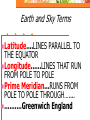
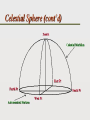
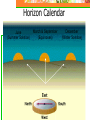
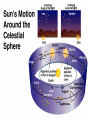
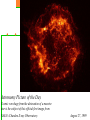
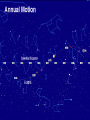
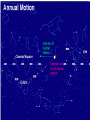
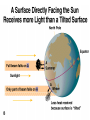
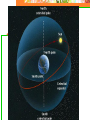
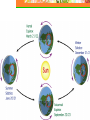
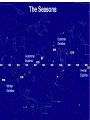
Astronomy Picture of the Day The Constellation Orion Labeling Constellations Bayer System Systematic method to name all the stars that we see. Names the brighter stars by assigning : 1. constellation (using the Latin possessive of the name) 2. Greek letter (Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, . . .) Labeled in an approximate order of decreasing brightness for stars in the constellation. Bayer System Example Orion Constellation Bayer System Example Orion Constellation Betelgeuse is also called Alpha-Orionis Rigel is called Beta Orionis Circumpolar Constellations Constellations that appear year long in the sky Big dipper Little dipper Draco Camelopardalis Cepheus Cassiopeia The Zodiac The constellations that fall on the ecliptic. Star Charts and Coordinate Systems Astronomy Picture of the Day A Star Cluster in the Rosette Nebula Astronomy Picture of the Day This striking pair of galaxies is far, far away ... about 350 million light-years from Earth. Astronomy Picture of the Day The Constellation Orion The changing stars The stars we see change with time of night and season of year - why? The sky is a sphere with Earth at the center. Observer can see only sky above the horizon horizon……..an imaginary plane tangent to Earth at the observer Earth and Sky Terms Latitude….LINES PARALLEL TO THE EQUATOR Longitude……LINES THAT RUN FROM POLE TO POLE Prime Meridian…RUNS FROM POLE TO POLE THROUGH….... ……….Greenwich England Celestial sphere Terms North Celestial Pole….same as North pole South Celestial Pole….same as South pole Celestial Equator……….Projection of earth’s equator out to the sky altitude - the angle of a star above the horizon The North Star, Polaris, is not the brightest star in the sky but remains in a fixed position in the sky. The angle of Polaris above your horizon is the same as your latitude in degrees. Right Ascension Distance R.A. measured eastward along the celestial equator from zero point, called the vernal equinox measured in hours and minutes ……. 15hr 10 min, 23 hr, 5 min Declination Angular (Dec) distance above or below the celestial equator measured in degrees…. 0o, 15o, 30o SC002 The Star Chart North Star The Big Dipper The Little Dipper Cassiopeia. SC001 Star Chart Little dipper Cepheus Draco Orion Gemini Find the coordinates of Betelgeuse. Earth and Sky Terms Right Ascension Declination Ecliptic Vernal Equinox Autumnal Equinox Summer Solstice Winter Solstice Motions of the Sun and Stars Daily Motion Annual Motion. Motions of the Sun and Stars Daily Motion The rising and setting of the stars is caused by the Earth’s rotation about its axis. Horizon Calendar June (Summer Solstice) March & September (Equinoxes) December (Winter Solstice) Stonehenge Astronomy Picture of the Day Cosmic wreckage from the detonation of a massive star is the subject of this official first image from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. August 27, 1999 Motions of the Sun and Stars Annual Motion The Earth’s orbit around the Sun causes different stars and constellations to be visible at different times during the year. The Ecliptic The Sun’s apparent yearly path among the stars. Tip the equatorial circle by 23.5° around a line passing through the Earth Diurnal Motion rotation of Earth from west to east causes objects on celestial sphere to appear to rise in east and set in west daily Solar Day The time it take for the earth to make one complete rotation Takes 24 hours Sidereal Day One rotation of the earth measured by the position of the stars It takes 23hours 56 minutes Seasons What causes seasons on Earth? Answer: The tilt of the Earth's rotational axis. Ecliptic: The path of our Sun across the celestial sphere is called the. It is inclined 23½° with respect to the celestial equator. Earth and Sky Terms Right Ascension Declination Ecliptic Vernal Equinox Autumnal Equinox Summer Solstice Winter Solstice Inclined Pole causes Seasons