* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Big Bang Theory
Weakly-interacting massive particles wikipedia , lookup
First observation of gravitational waves wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Gravitational lens wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic microwave background wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Nucleosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Flatness problem wikipedia , lookup
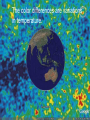
Big Bang Theory An effort to explain what happened at the very beginning of our universe. According to the Big Bang Theory, the universe began about 15 billion years ago. Singularity The theorized beginning of the universe is called the “singularity”. It was about the size of a dime; all particles of matter were contained in an unimaginably dense object. Atoms could not form at first because of the extreme heat. Formation of Elements Within the first minute, 98% of all matter in the universe was formed. It began cooling immediately. • The first particles formed were quarks (make up protons and neutrons), electrons, photons, neutrinos. • First elements formed were hydrogen, helium and deuterium (isotope of hydrogen). Formation of Elements Formation of heavier elements were found in supernovas. Supernova’s occur when giant stars (much bigger than our sun) explode and immense energy is released (equal to a trillion hydrogen bombs detonating!) Formation of Elements The 10 million degree Kelvin (equal to 17,999,500 F) temperatures were adequate to create heavier elements necessary for life (carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, and phosphorous). For a very short period of time (10 –30 sec) the universe doubled itself every 10 –34 second. Law of Gravity This period of great expansion helped establish the law of gravity. All objects have a gravitational force. The larger the object the greater the force (ex. the earth vs. your pen.) This theory also helps explain how the force of gravity began to condense clumps of matter into objects that would eventually form stars and galaxies. Big Bang Theory This theory also helps explain how the force of gravity began to condense clumps of matter into objects that would eventually form stars and galaxies. The Big Bang Theory Evidence Cosmic Background Radiation moves in front of our universe. When viewing the sky with a radio telescope, the sky is not black, but has a faint glow (this is CBR) The color differences are variations in temperature. Doppler Effect Describes the change in wavelength of light or sound that occurs when an object moves toward or away form you. Doppler Effect Astronomers are only concerned with the changes of light wavelengths, not sound. It tells us whether an object is moving towards or away from Earth Large Doppler shifts indicate high speeds Red Shift “Red Shift” means that an object in space in moving away from Earth The Red Shift of distant galaxies tell us that the universe is expanding Red Shift Greater red shifts in the color spectrum of distant galaxies indicate faster speeds Black Holes A region of space resulting from the collapse of a star; extremely high gravitational field that not even light can escape If you fell into a black hole you would eventually be stretched apart (spaghetification)