* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Folie 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
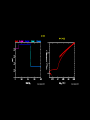
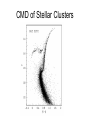
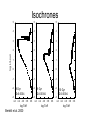
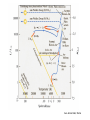
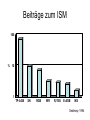
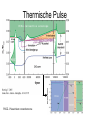
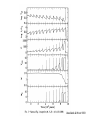
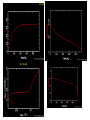
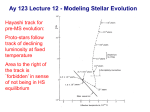
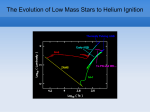
Sternentwicklung Stellar evolution Vorlesung Spätstadien der Sternentwicklung, WS 07/08 Lebzelter & Hron Early concepts Lord Kelvin: source of solar energy is gravitational contraction. Age of the sun is 100 million years Charles Darwin: age of the earth is several billion years. Ernest Rutherford: Radium possible long time energy source O. Gingerich, 1999, Ap&SS 267, 3 Early concepts Zur Anzeige wird der QuickTime™ Dekompressor „TIFF (LZW)“ benötigt. Star form out of meteoritic particles, become first red giants, contract (hot stars), and then cool down (red dwarfs). Lockyer (1890), Russell (1925) Milestones • Understanding of the stellar structure (Eddington) • Understanding of the star‘s composition (Payne, Unsöld) • Understanding of the energy source (Atkinson, Bethe, von Weizsäcker) What is a star? Energy Production Nuclear Timescale E nuklear tnuklear LSonne E nuklear 0.1 0.007 M Sonnec 2 10% of the sun involved E = m c2 0.7% of the mass of a hydrogen core will be converted into energy tnuclear ~ 1010 years core hydrogen burning Effect of hydrogen burning • 4 H transformed into 1 He • mean molecular weight increases • according to the ideal gas law density and T have to increase: kT Pgas mH • core contracts energy production increases and opacity decreases L, R, T increase Iben 1967 Core after H burning • no H no energy production • energy production in shell, core becomes isothermic • H burning shell core increases in mass • maximum core mass ~ 10% stellar mass core collapse • low mass stars: core degenerates first Core and Envelope • Lbottom = Lout star is in TE • Lbottom increases Lout has to increase • R increases more surface more L can be emitted again TE • R increases T decreases at some point opacity increases NO TE star becomes red giant (Hertzsprung-gap!) • Runaway stops at Hayashi-track Hayashi line TE runaway phase Energy trapped no TE TE convection TE Iben 1967 First Dredge Up • Convective zone reaches layers with processed material • Abundance changes on the surface: 12C decreases Li decreases 14N increases 3He increases O ~ constant • 12C/13C drops from 90 (solar) to ~20 Evolution on the RGB • Luminosity provided almost exclusively by thin H burning shell (0.001 – 0.0001 Msolar) • burning rate of H shell determined by size and mass of core • He core mass – luminosity relation Helium core flash • core T increases until He ignition temperature (108 K) – approx. 0.5 Msolar • core material degenerated gas pressure not sensitive to T no cooling by extension thermonuclear runaway • Duration approx. 1 Mio years • Most of the E does not reach the surface • not for stars above 2.25 Msolar Helium Burning Helium Burning • 4He + 4He 8Be 8Be + 4He 12C • Energy production T40 • Energy release per nucleus one order of magnitude less than for H burning • 12C + 16O + 16O + 20Ne + He exhausted 2nd ascent on the giant branch (Asymptotic Giant Branch, AGB) Our Sun Ejection of outer shell 012Milliarden Jahre 4.5 Billion years years 12.4 10 Billion Helium ignition Birth Hydrogen exhausted Today 5600 4500 4000 3200 Aus Sackmann et al. 1993 CMD of Stellar Clusters log L/Lsun Isochrones 5 5 5 4 4 4 3 3 3 2 2 2 1 1 1 0 0 0 -1 -1 -1 -2 -2 8 Gyr Z=0.0004 -3 4.4 4.2 4.0 3.8 log Teff Bertelli et al. 2000 3.6 -3 4.4 -2 9 Gyr Z=0.0004 4.2 4.0 3.8 log Teff 3.6 -3 4.4 10 Gyr Z=0.0004 4.2 4.0 3.8 log Teff 3.6 log L/Lsun Isochrones 4 4 4 3 3 3 2 2 2 1 1 1 0 0 0 -1 -1 -1 -2 -2 10 Gyr Z=0.001 -3 3.9 3.8 3.7 log Teff 3.6 -3 3.9 -2 10 Gyr Z=0.0004 3.8 3.7 log Teff 3.6 -3 3.9 10 Gyr Z=0.0001 3.8 3.7 log Teff 3.6 Literature • Salaris & Cassisi: Evolution of Stars and Stellar Populations • Kippenhahn & Weigert: Stellar Structure and Evolution • Renzini et al. 1992, ApJ 400, 280 Miras Innenleben helium burning Aus: James Kaler, Sterne Beiträge zum ISM 100 % 10 1 TP-AGB SN RGB WR R,YSG E-AGB MS Sedlmayr 1994 Thermische Pulse PDCZ...Pulse driven convection zone Thermische Pulse continuous line...surface luminosity dotted line...He-burning luminosity dashed line...H-burning luminosity Wood & Zarro 1981 Vassiliadis & Wood 1993 Wood & Zarro 1981 shell hydrogen burning