* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 29.3
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Exploration of Jupiter wikipedia , lookup
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
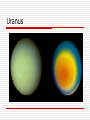
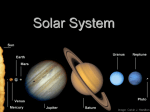
Ch. 29.3 The Outer Planets Consist of the gas giant planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Pluto is recently demoted, and is no longer considered a planet(It’s a dwarf planet). The gas giants are more massive, but much less dense than the inner planets. Thick hydrogen / helium atmospheres, with probable dense cores. Since they are similar to Jupiter, they are also known as Jovian planets. The Gas Giants Jupiter 5th planet from the sun. The largest; over twice the mass of all other planets combined. Orbit period is 12 years. Fastest rotation; once every 9 hours and 50 minutes. Many moons (63 at last count) and at least 4 rings. High internal temp. due to intense pressure (30,000 C). Resulting metallic hydrogen creates enormous magnetic field. Composed of 92% hydrogen and helium (similar to the sun; a failed star?). No solid surface. Alternating swirling (due to rapid rotation) colorful bands suggest ammonia, methane, and water vapor. Great Red Spot is giant rotating storm several hundred years old. Jupiter The Great Red Spot Saturn 6th planet; 2nd largest in the solar system. Avg. temp. -176 C. Many moons (61 at last count) and a large, complex ring system. Rapid rotation, once every 10 hours and 30 minutes. Bands of colored clouds. Least dense planet (lower density than water). Orbit period 29.5 years. Saturn Uranus 7th planet from the sun; 3rd largest. Discovered in 1781 (1st planet discovered since ancient times). Almost 3 billion km from the sun. At least 22 moons and 11 small rings. Horizontal rotation, once every 17 hrs. Orbit period 84 years. Greenish atmosphere color from methane, with atmosphere mostly hydrogen and helium. Surface temp. -214 C. Interior may be water and methane slush. Temp. increases with depth, up to 7000 C in a rock / metal core. Uranus Neptune 8th planet; 4th largest, but very similar to Uranus in size and mass. Orbit period 164 years. Rotates once every 16 hours. 11 moons, 4 rings. Existence predicted before it was discovered, after astronomers noticed variations in Uranus’ expected orbit. Position was determined mathematically, then it was discovered there in the mid-1800’s. 4.5 billion km from the sun. Blue-green color, with white clouds of frozen methane in the upper part of the hydrogen/helium atmosphere. Strong winds, over 1000 km/hr. An Earth-sized storm, the Great Dark Spot. Surface temp. -225 C. Neptune and its large moon Triton