* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 24 - Cloudfront.net
X-ray astronomy satellite wikipedia , lookup
Advanced Composition Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
History of the telescope wikipedia , lookup
James Webb Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
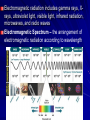
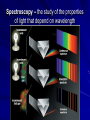
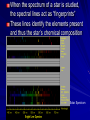
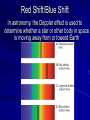
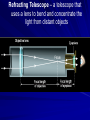
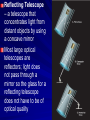
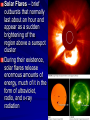
Chapter 24 Studying the Sun Electromagnetic radiation includes gamma rays, Xrays, ultraviolet light, visible light, infrared radiation, microwaves, and radio waves Electromagnetic Spectrum – the arrangement of electromagnetic radiation according to wavelength The Light Spectrum Spectroscopy – the study of the properties of light that depend on wavelength When the spectrum of a star is studied, the spectral lines act as “fingerprints” These lines identify the elements present and thus the star’s chemical composition Solar Spectrum Doppler Effect – the apparent change in frequency of electromagnetic or sound waves caused by the relative motions of the source and the observer Red Shift/Blue Shift In astronomy, the Doppler effect is used to determine whether a star or other body in space is moving away from or toward Earth Refracting Telescope – a telescope that uses a lens to bend and concentrate the light from distant objects Reflecting Telescope – a telescope that concentrates light from distant objects by using a concave mirror Most large optical telescopes are reflectors; light does not pass through a mirror so the glass for a reflecting telescope does not have to be of optical quality Radio Telescope – a telescope designed to make observations in radio wavelengths A radio telescope focuses the incoming radio waves on an antenna, which absorbs and transmits these waves to an amplifier, just like a radio antenna Space telescopes orbit above Earth’s atmosphere and thus produce clearer images than Earth-based telescopes Hubble Space Telescope Sun Facts An “Average” Star Diameter = 109 x Earth Volume = 1.25 x Earth Mass = 332,000 x Earth Density = ¼ x Earth We can divide the sun into four parts: the solar interior; the visible surface, or photosphere; and two atmospheric layers, the chromosphere and corona Photosphere – radiates most of the light we see and can be thought of as the visible “surface” of the sun Chromosphere – A relatively thin layer of hot gases a few km thick above the photosphere Corona – outer most portion of the solar atmosphere, very weak and is visible only when the photosphere is covered Solar Wind – Streams of protons and electrons that boil from the corona Sunspots – dark regions on the surface of the photosphere, an individual spot contains a black center rimmed by a lighter region Sunspots appear dark because of their temperature, about 1500 K less than that of the surrounding solar surface Prominences are ionized gases trapped by magnetic fields that extend from regions of intense solar activity Solar Flares – brief outbursts that normally last about an hour and appear as a sudden brightening of the region above a sunspot cluster During their existence, solar flares release enormous amounts of energy, much of it in the form of ultraviolet, radio, and x-ray radiation Auroras – following solar flares, Earth’s upper atmosphere near the magnetic poles is set alight; also called the northern and southern lights Nuclear Fusion – The process by which the sun produces energy; this nuclear reaction converts four hydrogen nuclei into the nucleus of a helium atom and tremendous energy is released It is believed that a star our size can exist in its stable state for ~10 Billion years, making our sun middleaged at ~4.5 Billion years old