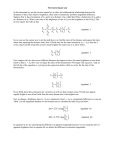
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HR-diagram - Bakersfield College
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
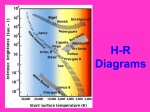
Classification of Stars – HR diagram Objectives: • understand the differences between near and bright visible stars • learn how to use the HR-diagram to classify stars (temperature vs. brightness) • use the HR-diagram to observe the evolution of stars (when a star is born and dies) Lab Books: pages 52-54 worksheet, page 115 HR-diagram – classifies stars using temperature magnitude (brightness) HR-diagram – Hertzbrung-Russell diagram Star color and Temperature Lets review the visible color spectrum. “What do our eyes see”? Low Energy High Energy wavelength R O Y G B I V Star Color and Temperature Yellow Blue RED 2,500 6,000 30,000 K Hot stars Cool stars Long wave lengths R O Y Short wavelengths G B I V Measuring the Brightness of a Star “Stellar Brightness” Magnitude – the brightness of a star Magnitude is measured using (-) and (+) numbers the more (-) the number, the brighter the more (+), the dimmer the star Apparent Magnitude • a stars brightness as it appears from earth • factors controlling apparent magnitude: • how big the star • how hot the star • how far away star Which is brighter? -5 star or 5 star ? Apparent Magnitude of various objects dim bright OBJECT SUN Full Moon Venus Apparent Magnitude -26.5 -12.5 - 4.1 North Naked Pluto HST Sirius Star eye -1.4 2.0 6.0 15 28 Absolute Magnitude • measures the “actual” brightness • two stars with the same absolute magnitude would not be the same apparent magnitude WHY? • To compare absolute brightness • use a standard distance of 32.6 light-years away from earth Example: Apparent Magnitude Absolute magnitude bright dim -26.7 +5 Earth 32.6 ly Distance, Apparent Magnitude, and Absolute Magnitude of Some Stars View from Earth 32.6 ly Name Distance Light-years Apparent Magnitude Absolute Magnitude Sun NA -26.7 5.0 Alpha Centauri 4.27 0.0 4.4 Sirius 8.70 -1.4 1.5 Arcturus 36 -0.1 -0.3 Betelgeuse 520 .08 -5.5 1600 1.3 -6.9 Deneb So, which star is biggest to smallest? Brightness scale – Using Absolute Magnitude -7 -5 Bright -3 -1 0 1 3 5 7 9 Dim The brighter, the bigger the star How are stars classified? – the Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram (HR-diagram) -10 O B A F G K M Absolute Magnitude Very Bright -5 0 +5 +10 Very Dim +20 20,000 14,000 10,000 7000 5000 Surface Temperature (K) 3000 Spectral class: based on their spectrum (color they emit resulting from the chemical make-up) O B A F G K M Oh, Be A Fine Guy (or Gal), Kiss Me O0O1…..O9 B0…..B9 A0…..A9 F…………… Hottest Coolest HR-Diagram Cool, bright Hot, dim 20,000 14,000 10,000 7000 5000 Surface Temperature (K) 3000 O B A F GK M Stellar evolution HR-Diagram Variable Star stage Red Giant Stage Protostar Planetary Nebula Stage White Dwarf Main Sequence Star Black Hole Stage 20,000 14,000 10,000 7000 5000 Surface Temperature (K) 3000 Dust and gasses