* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Part5Unit2TheoryofSolarSystem
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
James Webb Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Directed panspermia wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Galilean moons wikipedia , lookup
Advanced Composition Explorer wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
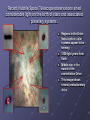
Unit 2 The Earth in Space The Solar System Origin of Our Solar System Today, most astronomers believe our solar system is a by-product of the origin of the sun. The most accepted explanation is the Nebular Hypothesis Immanuel Kant, a German philosopher first proposed in 1755 Terms Related to the Hypothesis Nebula which is an immense cloud of gas and dust particles Planetesimals which are small rocky objects that rotate around a star Accretion is the process of growth by accumulation Protosun was the predecessor of the Sun Nebular Hypothesis 5 billion years ago The solar system was believed to have consisted of a nebula This nebula was slowly rotating and due to some unknown cause, it began to contract under its own gravitational pull. The largest mass accumulated in the center, attracting more dust particles and gas. The areas left behind formed a series of whirlpools The center area grew smaller (matter packed in) and the spinning increased. Example: Think of a figure skater who pulls their arms into a spin. What happens when they extend their arms? The result: The cloud was flattened into a disk-like shape The collapsing, spinning nebula begins to flatten into a rotating pancake Nebular Hypothesis cont’d 100 million years later Majority of mass accumulated in center In the whirlpools areas, planetesimals were forming through the process of accretion. As dust and gas were pulled inward, these planetesimals grew in size increasing in gravitational pull. This pull was strong enough to hold lighter gases like hydrogen and helium This process took about 10 to 30 million years to form the present size of today’s planets Nebular Hypothesis cont’d The pressure of the center mass increased to such levels that the inner temperature of the PROTOSUN reached 11 million oC Result: Thermonuclear explosion which was the lighting of the Sun’s inner core T. Tauri Wind, a solar wind of charged particles Traveled at speeds of 3.3 million km/h throughout the solar system for 9 million years Swept away all gas and dust particles between the planets Stripped the inner planets of their first atmosphere The outer planets held their helium and hydrogen atmospheres Nebular Hypothesis cont’d In the last 4.5 billion years The planetesimals continued to collide with other planets and moons adding to their masses It’s important to recognize that only the largest of these planetesimals could survive the high-energy collisions from meteorites (lower mass planetesimals) These traveled at 30,000 to 75, 000 km/h Asteroids are considered to be left-over planetesimals Why didn’t these asteroids make up a planet? The Asteroid Belt between Mars and Jupiter is thought to be remnants of material that made up the solar system. It’s placement is such that there is competing pull between Jupiter and the Sun Nebular Hypothesis: Explains Major Features of Solar System 1. Explains regular motions of the planets and moons • 2. All revolve in the nearly the same plane, in nearly circular orbits, and nearly all rotate in the nearly same direction as the Sun too Explains all major differences between terrestrial and gaseous (jovian) planets • 3. Mass, distance from Sun, composition, moon and ring systems Explains small bodies • 4. Asteroids and comets, both short- and long-period Explains exceptions to the trends • Terrestrial moons, axial tilts, non-coplanar jovian moons, Triton Nebular Hypothesis: Current Challenges to the Nebular Hypothesis 1. Missing mass in Kuiper Belt • Icy bodies found beyond orbit of Neptune 2. Capture process for Triton • Largest moon of Neptune orbits in opposite direction 3. Sideways rotation of Uranus 4. Discovered “hot Jupiter” exoplanets • These planets are much closer to their parent star then our own Jupiter 5. Discovered exoplanets in binary and trinary stellar systems • Planets with two / three parent stars Kuiper Belt • Disk shaped region of 100’s of icy objects beyond orbit of Neptune http://www.cnes.fr/imagezoom.php?file=p1135_ed77069b38b89947b9f6e5678e9af2adkuiper_pluton.jpg&label=Ou ter+solar+system+and+Kuiper+Belt.+Credits%3A+NASA Difficult to Prove It’s important to remember that this hypothesis is the best explanation to date for the formation of a solar system. It is not yet possible to observe the formation of the other stars to verify the steps outlined (Think distance) No one was around for the first one It is believed that if this hypothesis is true that all solar systems would form the same way – use the same pattern Ways of proving this is through technology Nebular Hypothesis http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PL3YN QK960Y Instrumentation Expanding our Knowledge of the Solar System To improve our understanding of the Solar System technological developments include: 19th Century Optical telescopes 20th Century Radio telescopes Rocketry Telescopes Hubble Technology (4 minutes) Videos\Space_Travel__The_International_ Space_Station.asf Hubble Space Telescope (2 minutes) Videos\Understanding_the_Universe__Th e_Hubble_Space_Telescope.asf Hubble Space Telescope (HST) The HST must be able to talk with controllers on the ground to relay data from its observations and receive commands for its next targets. To communicate, the HST uses a series of relay satellites called the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System (TDRSS), which is the same system used by the International Space Station. Sequence of Events: Incoming light from an object gets received by the HST (2) and converted to digital data. The data is then sent to the TDRSS in orbit (3), which then transmits it to the Ground Receiving Station at White Sands, N.M. (4). The White Sands Facility transmits the data to NASA's Goddard Spaceflight Control Center (5), where HST operations are centered. The data are then analyzed by scientists at the nearby Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, MD. (6). Most of the time, commands are relayed to the HST in advance of a planned observing run; however, real-time commands are possible when necessary. Hubble Space Telescope Photo courtesy NASA / STScI Communications system used by the Hubble Space Telescope. Recent Hubble Space Telescope observations shed considerable light on the birth of stars and associated planetary systems. Regions in the Orion Nebula where solar systems appear to be forming 1500 light years from Earth Middle star in the sword of the constellation Orion This image shows several protoplanetary disks. Think About Voyager 2 Satellite Gone 12 years Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune Information doubled what was known about the solar system Problem It will take decades to get through all the information