* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint - Chandra X
X-ray astronomy satellite wikipedia , lookup
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
X-ray astronomy detector wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
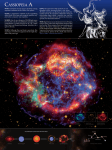
Chandra Science Highlights IC 443: A Supernova Remnant with a Newly Discovered Neutron Star 5,000 light years from Earth This Chandra image shows a point-like source of X-rays inside a cloud of high energy particles which is embedded in the supernova remnant IC443. Using this image, along with radio data from the Very Large Array, three high school students found evidence that the point-like source is a rotating neutron star, or pulsar. The comet-shaped appearance of the cloud of highenergy particles indicates that the neutron star is moving through the remnant. Credit: NASA/NCSSM/C. Olbert et al. Scale: Image is 1 x 0.8 arcmin • • • • • Chandra X-ray Observatory ACIS Image High resolution observations revealed the existence of soft (kT ~ 0.24 keV) point source of X-rays -presumably a neutron star-- embedded in a nebula of cometary morphology within the supernova remnant. Interpreting the cometary nebula as due to a pulsar wind with a bow shock due to its motion through the remnant permits an estimate of the velocity of the neutron star, and the age of the remnant. The age of the supernova remnant is estimated to be 30,000 years. The velocity of the neutron star is estimated to be about 200 km/sec. The three high school students won first place in the Siemens-Westinghouse Science and Technology Competition in Washington, DC for their work with the Chandra data. December 2000