* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Second World War Continued
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Collaboration with the Axis Powers wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
German evacuation from Central and Eastern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Britain (film) wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
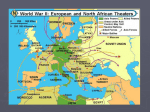
WW II • Invading German troops approach Bydgoszcz, Poland. September 18, 1939. Past IB Questions—Paper 2 • “Wars may be started by a single incident. They are never caused by such an incident.” With refrence to any ONE twentieth century war show how far you agree with this statement. • How comprehensively are the characteristics of “total war” illustrated by the 2nd World War? • “20th century wars have been won by the side with the most money, men and material.” Using at least two examples, each chosen from a different region, show how far you agree with this assertion. • What were the most frequent causes of 20th century wars? Specific evidence from at least three wars should be used. • How and why did technological developments play an important part in 20th century wars? • Assess the social and economic causes of one 20th century war. Past IB Questions—Paper 3 • For what reasons could it be argued that the 2nd World War in Europe was “total war”? • In what ways, and with what results for Europe between 1939 and 1949, was the 2nd World War a “total war”? • With reference to the 2nd World War in Europe, explain the main features and effects of “total war”. 1939 • May… invasion of the rest of Czechoslovakia • May… Pact of Steel with Italy; treaty of friendship & alliance; committed each country to support the other in case of war • Nazi-Soviet Pact 1939 Sept. 1… German invasion of Poland Sept. 3… France & Britain declared war on Germany Sept. 17… USSR attacked Poland Blitzkreig… rapid advances in enemy territory; use of radio to connect commanders, tanks, aircraft Nov…USSR attacked Finland Winter 1939-1940 Dubbed “sitzkreig” by the British press War in the Atlantic already in full swing 1940 April 9… Germany attacked Denmark & Norway May 10… attacked France, going through Belgium, Netherlands & Luxembourg May 10, 1040… Winston Churchill “I would say to the House, as those who have joined this Government, I have nothing to offer but blood, toil, tears and sweat. We have before us an ordeal of the most grievous kind. We have before us many long months of toil and struggle. “You ask what is our policy. I will say, it is to wage war with all our might, with all the strength that God can give us, to wage war against a monstrous tyranny never surpassed in the dark, lamentable catalogue of human crime. “You ask what is our aim? I can answer in one word: Victory. Victory at all costs. Victory in spite of all terror. Victory however long and hard the road may be. For without Victory there is no survival.” First speech as PM; House of Commons, 13 May 1940 • France… • June… evacuation at Dunkirk of 230,00 British 120,000 French • • • • • • • • • June 10… Mussolini declared war on France & invaded June 22… France surrendered; Germany took 2/3; the other 1/3 became Vichy France under a government led by Petain And in the Atlantic Ocean… • Admiral Karl Donitz commanded all German U-boats at the beginning of the war • Britain put their ships into convoys to try to protect them • By October 1939, Germans had sunk 41 merchant ships • In 1939 more ships were sunk than could be built • Surrender of France gave the Germans more ports • Donitz developed the wolf pack system for attacking the British & American convoys • After the US entered the war, German submarines operated off the US East Coast; by June 1942, German U-boats had sunk 505 ships • Battle of Britain… Aug-Oct 1940 • July 1940 it was predicted that the Luftwaffe could defeat the RAF in 6 days • During the battle, for every RAF plane shot down, the Luftwaffe lost two planes; • Sept 7-30--RAF lost 242 planes; Germans lost 433 planes • The British were building a lot more planes than the Germans were building • The British used radar to detect incoming German planes Mussolini’s attempt at conquest • Sept. 1940 troops in Libya invaded Egypt; antiquated weapons, small “tankettes”; no match for the British in Egypt • Erwin Rommel sent to Libya to help the Italians; became known as the “Desert Fox”; he led the Afrika Korps. He failed to defeat the British at Tobruk Eventually defeated by the British at El Alamein in Oct. 1942. German & Italian troops surrendered in Tunisia May, 1943. • Oct. 1940 Mussolini declared war on Greece; attacked from Albania. In 6 weeks, Greeks drove Italians back into Albania. Hitler came to Mussolini’s aid in April 1941, which delayed his plans to invade Russia. The Greek govt. went to London when the Germans captured Crete. • Operation Barbarossa… the invasion of the USSR June 22, 1941 • Siege of Leningrad Nov. 1941 to end of 1943 • German troops reached the outskirts of Moscow • Battle of Stalingrad winter 1942-1943 ** one of the turning points of WW II ** Russian army led by General Zhukov; German army led by General Paulus ** German army was headed for the oil fields in the Caucasus. Stalingrad was attacked both for its name and because it would have left a Russian city in the German rear ** Was a HUGH defeat for the Germans; Paulus, 24 other generals and army of 300,000 Germans were lost ** First defeat for a German army; German retreat from the Eastern Front began Feb. 1943 • Battle of Midway Island June 4-6, 1942 • Another turning point battle, along with the Battle of coral Sea in May, 1942 • US broke the Japanese code • Japanese wanted to sink the aircraft carriers they missed at Pearl Harbor. • The two navies never saw each other; battle was air battle. • All four Japanese aircraft carriers were sunk; established US naval superiority in the Pacific. June 6, 1944 D-Day • Allied invasion of Normandy… also called Operation Overlord or Operation Neptune Bridge at Benouville captured by the British US army troops at Omaha Beach Conferences • Oct. 1943—Moscow Conference Declaration to continue carrying out the war & maintain international peace • Nov. 1943—Tehran Conference Plans for the final destruction of the German army. Agreed to partition Germany at the end of the war, but specific boundaries were not set. • Feb. 1945—Yalta Conference Set policy of unconditional surrender Germany to be divided into four occupation zones Discussed reparations Russia agreed to enter the war in the Pacific First UN meeting set for April, 1945 in San Francisco • July 1945—Potsdam Conference Attended by Truman, Attlee & Stalin Confirmed agreement at Yalta Set up boundaries and commission to run Germany Decided on amount of reparations to be paid by Germany and other Axis countries Surrender terms for Japan Surrender of Japan • Dropping of the atomic bomb on both Hiroshima and Nagasaki mushroom cloud over Hiroshima A-bomb dome in Hiroshima Japan surrendered Aug. 14, 1945 Nagasaki Bibliography • Pictures • • http://www.worldwar2database.com/cgi-bin/slideviewer.cgi?list=poland.slides&dir= &config=&refresh=&direction=forward&scale=0&cycle=off&slide=3&design=default&t otal=18 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:DUNKIRK1940.jpg http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Erwin_Rommel http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Winston_Churchill http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Battle_of_Britain http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/D-Day http://www.pcf.city.hiroshima.jp/frame/Virtual_e/tour_e/guide2_4.html http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nagasaki,_Nagasaki • http://www.ushmm.org/wlc/article.php?ModuleId=10005070 • • • • • • Text • • • • • http://www.mikekemble.com/ww2/uboat.html http://www.ahistoryofgreece.com/worldwarII.htm http://www.winstonchurchill.org http://www.historylearningsite.co.uk/battle_of_stalingrad.htm http://www.2worldwar2.com/blitzkrieg.htm