* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HP Unit GTOR - student handout
Hawking radiation wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Gravitational wave wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Equivalence principle wikipedia , lookup
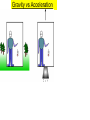
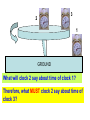
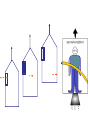
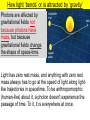
STOR vs GTOR • Special Theory looked at only inertial frames. General theory looks at accelerated frames of reference • Einstein added this 10yrs after special theory to deal with gravity, mass, and acceleration and how it applies to spacetime. Gravity vs Acceleration: Imagine yourself in a spaceship on a launch pad on EARTH holding 2 bricks above the floor. If the bricks are dropped at the same time from identical heights, both bricks accelerate towards floor equally. Now, imagine identical situation in space, FAR from any effects of gravity, what is the result of dropping bricks? Repeat experiment, but now accelerate ship in the direction of ceiling…how does result change from previous scenario? LAUNCH PAD Gravity vs Acceleration Equivalence Principle GRAVITY & TIME Consider a high speed rotating platform with three clocks positioned as shown. Clocks 2 & 3 are rotating and clock 1 is at rest on ground. 2 3 1 GROUND 2 3 1 GROUND What will clock 1 say about the movement of clock 2 What will clock 1 say about the movement of clock 3? What will clock 1 say about the TIME of clock 2? What will clock 1 say about the TIME of clock 3? 3 2 1 GROUND What will clock 2 say about time of clock 1? Therefore, what MUST clock 2 say about time of clock 3? Gravitational Time Dilation This was first measured by Pound and Rebka at Harvard in 1960 in the physics building which was 74 feet high. They compared times between the basement and the top floor. GPS again… Recall that atomic clocks on GPS satellites are affected by their high speed above the earth (STOR). Twin Paradox revisited We showed that Twin who took space journey: Space twin experienced acceleration, therefore could not make claims as to earth twin being younger since space twin was not in inertial frame But what if ship accelerates Imagine 2 people freely floating in space far from towards gravitational effects. One ceiling? Gravity and Light person is outside the ship and the other is inside. If light is shone through a window, it is seen by observer inside the ship to be a straight line, entering and striking the opposite side and the same height it entered. How come we don’t notice light falling/bending like a cannonball shot from cannon? Recall how far objects will fall in 1second here on Earth. |y|= ½ gt2…y = 4.9m In one second, how far will light fall? How far will it travel horizontally in 1 second? We are able to see star at times when sun is not in front of it, so we know its true position. When Sun is blocking star, we can see the apparent position of star during an eclipse. This apparent position is due to how our brains perceive light, illusions. Need eclipse to see apparent position. Einstein predicts the bending of star light! Need solar eclipse to prove this. May 29, 1919, British scientists confirm Einstein’s prediction during solar eclipse. He becomes an instant celebrity. If light is bent due to gravity, then consider 2 rays of light on a wavefront as it passes by a massive object. A and B are in phase (moving together) & comprise the front. Large mass The ray at A moves to C and B moves to D. If CD is to remain in phase (they are if they are from the same wave), then time must be affected in order for them to stay in phase. Large mass AC is a larger distance than BD, but same speed. Therefore AC time must be different than BD time according to outside RF. Bending of light proves time dilation. Black Hole If a large enough star exhausts its nuclear fuel (where then gravity takes over), the star will collapse into a single point of infinite density (Singularity). Now that the star has a new radius, you must recalculate its new gravity (smaller radius, same mass = larger gravity). This applies inside original radius, but not outside. Since the speed of light is the greatest launch speed, that then determines how close you can get to black hole and still turn around. This distance is called the Event Horizon. The gravitational field is so strong that even light isn’t fast enough to escape. The warp in spacetime is so immense that not even light can escape! If light cannot escape, neither can anything else. Everything is dragged back by the gravitational field – A BLACK HOLE. Black because we can’t see it directly. Once inside the event horizon, no information can get out. Schwarzschild Radius The distance from the center of a massive object to the Event Horizon is defined as Every mass has RS, but physical meaning only applies if the radius is outside the mass itself. For example, for the earth to become a black hole based on the formula above, it would have to collapse to less than 1.8cm in diameter to become a black hole. Approaching a black hole First, as astronaut approaches the black hole the difference in the gravitational pull on head compared to (tidal forces) would rip you apart. Earth RF would never see astronaut cross the event horizon. WHY? Einstein redefines Gravity Einstein rejects 250yrs of Newtonian gravity. Gravity & Space Re-interpret gravity as geometry – Space and space-time are not rigid arenas in which events take place. They are influenced by the matter and energy content of the universe. Simply stated for a planet orbiting a star: How light ‘bends’ or is attracted by ‘gravity’ Photons are affected by gravitational fields not because photons have mass, but because gravitational fields change the shape of space-time. Light has zero rest mass, and anything with zero rest mass always has to go at the speed of light along lightlike trajectories in spacetime. To be anthropomorphic (human-like) about it, a photon doesn't experience the passage of time. To it, it is everywhere at once. EXPERIMENTAL TESTS OF GENERAL RELATIVITY • GRAVITATIONAL LENSING • PRECESSION OF MERCURY • GRAVITATIONAL REDSHIFT • GRAVITATIONAL WAVES Gravitational Lensing This was the 1st test to prove Einstein correct with the eclipse of the sun. This can lead to multiple images and even rings if the geometry of the situation is just right. Example: A planet with a mass lower than that of Neptune has been detected as its gravity bent the light from a remote star. This lensing technique adds to our arsenal for spotting small planets outside the Solar System. The famous "Einstein Cross" is a case where a single object is seen four times. In this image, a single object appears as four objects. A very distant quasar is thought to be positioned behind a massive galaxy. The gravitational effect of the galaxy has created multiple images through gravitational lensing on the light from the quasar. #2 Precession of Orbit of Mercury A long-standing problem in the study of the Solar System was that the orbit of Mercury did not behave as required by Newton's equations. The orbits of the planets are slight ellipses as we already know. The elliptical orbits themselves move. This motion is called precession. This is caused by the pull of other planets and predicted by Newton's laws. The predicted precession of the planets all agreed with observation. At one time, the scientific community had proposed there was an undiscovered planet called Vulcan that was causing this peculiar effect. EINSTEIN to the rescue!! Einstein used his GR equations to prove that the orbit of Mercury should precess by an extra 43 seconds of arc per century. #3 Gravitational Redshift According to General Relativity, the wavelength of light passing through a gravitational field will be shifted towards redder regions of the spectrum. Einstein's says that as a photon “fights its way” out of a gravitational field or well, it loses energy. It has to since PE is increasing yet speed MUST stay ‘c’. As previously mentioned, in 1960, this was demonstrated that a beam of very high energy gamma rays was ever so slightly redshifted as it climbed out of Earth's gravity and up an elevator shaft in the Jefferson Tower physics building at Harvard University. The redshift predicted by Einstein's Field Equations for the 74 ft. tall tower was but two parts in a thousand trillion. The gravitational redshift detected came within ten percent of the computed value. Also, a team at Princeton University measured the redshift of sunlight. Though small, given the Sun's mass and density, the redshift matched Einstein's prediction. #4 Gravitational Waves Recall the cosmic catastrophe we already viewed where if the sun were to disappear, the earth could no be released until the gravity wave reached us. Einstein predicted that gravity waves must exist. The first binary pulsar (rotating neutron star), i.e., a pulsar orbiting another star, was discovered by Joseph Taylor and Russell Hulse in 1974. The discovery earned Hulse and Taylor the Nobel Prize in Physics because the object is so exotic and so well suited to testing modern theories of gravitation such as Einstein's General Theory of Relativity. In this system discovered in 1974, it was observed that the two stars' orbits are shrinking at a rate of 1 cm/day. This shrinkage is caused by the loss of orbital energy due to gravitational radiation, which is a travelling ripple in spacetime that is predicted by Einstein's General Relativity Theory but never previously verified. Observations show that the pulsar orbit is shrinking at exactly the rate that general relativity predicts it should, if gravity waves exist and are carrying away the expected amount of energy. • This is the Einstein Gravitational Field Equation. This equation states that the spacetime curvature of anyplace in the universe (left-hand side of the equation) must be equal to the distribution of matter and energy in that part of the universe (right-hand side of the equation). It is this equation that was 50 years ahead of its time when Einstein proposed it. Each subscript refers to each dimension of spacetime…so what looks like 1 equation is actually 16 eqns! (4x4)