* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gravitational redshifts
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
X-ray astronomy satellite wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Advanced Composition Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Standard solar model wikipedia , lookup
Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam wikipedia , lookup
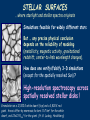
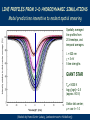
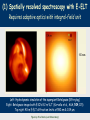
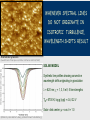
Towards the science case for E-ELT HIRES, Cambridge UK, September 2012 KVA LINE PROFILES & WAVELENGTHS ACROSS STELLAR SURFACES Dainis Dravins – Lund Observatory, Sweden www.astro.lu.se/~dainis STELLAR SURFACES … where starlight and stellar spectra originate Simulations feasible for widely different stars But … any precise physical conclusion depends on the reliability of modeling (metallicity, magnetic activity, gravitational redshift, center-to-limb wavelength changes). How does one verify/falsify 3-D simulations (except for the spatially resolved Sun) ? High-resolution spectroscopy across spatially resolved stellar disks ! Granulation on a 12,000 K white dwarf (top) and a 3,800 K red giant. Areas differ by enormous factors: 7x7 km2 for the white dwarf, and 23x23 RSun2 for the giant. (H.-G. Ludwig, Heidelberg) LINE PROFILES FROM 3-D HYDRODYNAMIC SIMULATIONS Model predictions insensitive to modest spatial smearing Spatially averaged line profiles from 20 timesteps, and temporal averages. = 620 nm = 3 eV 5 line strengths GIANT STAR Teff= 5000 K log g [cgs] = 2.5 (approx. K0 III) Stellar disk center; µ = cos = 1.0 (Models by Hans-Günter Ludwig, Landessternwarte Heidelberg) (1) Spatially resolved spectroscopy with E-ELT Requires adaptive optics with integral-field unit Left: Hydrodynamic simulation of the supergiant Betelgeuse (B.Freytag) Right: Betelgeuse imaged with ESO’s 8.2 m VLT (Kervella et al., A&A, 504, 115) Top right: 40-m E-ELT diffraction limits at 550 nm & 1.04 μm. Figure by Hiva Pazira (Lund Observatory) (2) Selecting portions of stellar disk during exoplanet transits Requires very high S/N in high-resolution spectrometers Figure by Hiva Pazira (Lund Observatory) Towards the science case for E-ELT HIRES, Cambridge UK, September 2012 KVA HIRES quasar spectrum (A.S.Cowie, Univ.of Hawaii) WAVELENGTH SHIFTS OF INTERGALACTIC ABSORPTION LINES Dainis Dravins – Lund Observatory, Sweden www.astro.lu.se/~dainis WHENEVER SPECTRAL LINES DO NOT ORIGINATE IN ISOTROPIC TURBULENCE, WAVELENGTH SHIFTS RESULT Observed solar granulation (Swedish Solar Telescope on La Palma; G.Scharmer & M.G.Löfdahl) SOLAR MODEL Synthetic line profiles showing convective wavelength shifts originating in granulation = 620 nm; = 1, 3, 5 eV; 5 line strengths Teff= 5700 K; log g [cgs] = 4.4; G2 V Solar disk center; µ = cos = 1.0 (Models by Hans-Günter Ludwig, Landessternwarte Heidelberg) WHENEVER SPECTRAL LINES DO NOT ORIGINATE IN ISOTROPIC TURBULENCE, WAVELENGTH SHIFTS RESULT … AND THE SAME MUST APPLY TO ALSO INTERGALACTIC Perseus cluster core in X-rays (Chandra), overlaid with Hα (WYIN). Arc-shaped Hα filaments suggest vortex-like flows. CONVECTION, DRIVEN BY HEATING BY AGNs NEAR CLUSTER CENTERS Density slices at three times. Viscosity stabilizes the bubble, allowing a flattened buoyant “cap” to form. X-ray brightness and inferred velocity field in Per-A can be reproduced. (Reynolds et al.: Buoyant radio-lobes in a viscous intracluster medium, MNRAS 357, 242, 2005) (Even if timescales might be 100 Myr, rather than solar 10 minutes) INTERGALACTIC LINE ASYMMETRIES AND SHIFTS: ANALOGIES AND DIFFERENCES TO STELLAR CONVECTION: • Plausible amount: 1 % of “general” line broadening = 0.5 – 1 km/s ? • Mapping 3-D structure from different shifts in different lines ! • Need line synthesis from 3-D hydrodynamic models ! • Lines closer to cluster centers gravitationally more redshifted • Mapping depth structure from multiple line components ? • Probably useful to have resolving power approaching 1,000,000 ?? • Resolving lateral structure from secular time changes ???