* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE SKY - n Nebbe
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
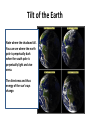
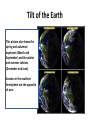
THE SKY CHAPTER 2 (Part 4) Sun Cycle and Seasons Objectives • To be able to interpret and apply the term “brightness” to stars (finishing this objective). • To be able to describe how the sky moves with reference to the Earth’s rotation. • To be able to predict the seasons and describe what causes them. • To be able to synthesize information on astronomical cycles to predict Earth’s climate. Precession • Earth spins like a giant top, and like a giant top, its weight tips it. • Earth is tipped 23.5 degrees from vertical. • Earth’s large mass and rapid rotation keep its axis of rotation pointed toward a spot near the star Polaris. • Due to its rotation, Earth has a slight bulge around its middle – gravity from the sun and moon pull on the bulge twisting Earth on its axis. • The result is that the twisting of the axis of rotation combines with the rotation of the Earth causing precession. • Earth’s axis precesses, taking about 26,000 years for one cycle. Precession • Video showing how Precession works. • Can be found at http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0qHjtp4cd CA Cycles of the Sun • Earth’s rotation on its axis defines the day but its revolution around the sun defines its year. Annual Motion of the Sun • If the Sun were not so strong, you could see it rise in the morning in front of the stars and move across the sky. • Between sunrise and sunset, it moves a distance roughly equal to its own diameter. • As Earth moves around its nearly circular orbit, the sun rises in front of different stars. • So, in March, the sun is in front of Aquarius (people say it is in Aquarius). Annual Motion of the Sun The apparent path of the sun against the background stars is called the ecliptic. Annual Motion of the Sun • • • • Earth circles the sun in 365.25 days. This appears to circle the sky in that period. It moves 1 degree eastward in 24 hours. This “movement” is what gives us seasons. The Seasons • If Earth rotated upright in its orbit, it would not experience seasons; however it is tipped 23.4 degrees on its axis. • Earth goes through a cycle of seasons (except at the equator) because of changes in the amount of solar energy reaching Earth. Tilt of the Earth Note where the shadows fall. You can see where the north pole is perpetually dark when the south pole is perpetually light and vice versa. The directness and thus energy of the sun’s rays change. Tilt of the Earth This picture also shows the spring and autumnal equinoxes (March and September) and the winter and summer solstices (December and June). Seasons in the southern hemisphere are the opposite of ours. Misconception • The seasons don’t occur because Earth moves closer to or farther away from the sun. • In the northern hemisphere we are actually 1.7% closer to the sun during the winter (seasons occur because Earth’s axis is not perpendicular to its orbit). Festivals • All over the world and among the majority of cultures (not so much around the equator), festivals are planned around the solstices and equinoxes. – Ex. Christmas (planned to replace “pagan” celebrations), New Years, “We Xipantu” (sunrise of the new sun) the Mapuche new year celebration in July, etc. – Rosh Hashanah marks the Jewish new year in September.