* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is a Scientist? - Cockeysville Middle School
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
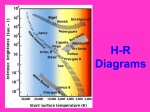
Objective: To distinguish between absolute and apparent magnitude in order to describe the brightness of stars. Astronomy Note: How bright are stars? Drill: 1. Take out your ditto, “Vocabulary of the Universe”. 2. Get a new ditto from the SET. 3. Complete Activity 1, # 1-2. ESS-5A on e STAR: a giant sphere of glowing gases What questions might someone have about the definition? ESS-5A on e STARS Stars are giant spheres of glowing gases. A star is powered by nuclear fusion. This is a process whereby hydrogen atoms are fused together to create helium atoms. In the process a tremendous amount of energy is given off in the form of electromagnetic waves and heat. There are billions of stars in a galaxy. When you look up into the night sky, most of the stars appear to be about the same size. However, in reality the sizes of different stars vary greatly. The closest star to earth is our sun. It is about 150 million km away. This distance is referred to a 1 Astronomical Unit (AU). The next closest star to Earth is Proxima Centauri. It is about 250,000 AU from Earth. ESS-5A on e What are 2 things you learned from the passage? ESS-5A on e Activity 2: Brightness (Magnitude) of Stars Description of the Position of the Flashlight Observation of the Brightness of the Light 1 meters from the screen fairly bright 6 meters from the screen Very dim ESS-5A on e Why do you think there was a difference in the brightness of the two flashlights? Use prior knowledge to support your response. Different Distances ESS-5A on e Did the two flashlights actually differ in their brightness? Explain. Same Brightness: One appeared brighter because it was closer to the screen. ESS-5A on e Read Page 129 in order to distinguish between absolute and apparent brightness. Flip your tag to green when you think you understand. Can you come up with your own examples to explain how they are different? ESS-5A on e Apparent and Absolute Brightness Apparent Brightness: the brightness of a star or object as seen from a particular location. This can be thought of how bright something appears, and is affected by distance. Absolute Brightness: the brightness of a star or object as seen from a standard distance from a particular location. This is the true brightness. It is not affected by distance. ESS-5A on e DISCUSSION ESS-5A on e Is our sun the brightest object in our sky? Explain your answer. ESS-5A on e