* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 24.1 The Study of Light - Buncombe County Schools System
Arecibo Observatory wikipedia , lookup
James Webb Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Allen Telescope Array wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Optical telescope wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
CfA 1.2 m Millimeter-Wave Telescope wikipedia , lookup
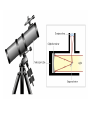
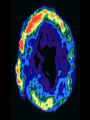
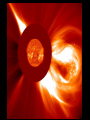
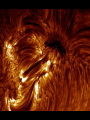
24.1 The Study of Light Visible light from sun is only a small part of what’s emitted Electromagnetic waves – Radio waves, IR, light, UV, X-rays – Wavelength is the difference – ROYGBIV 186,000 miles/hr…all waves Light Comes in “packets” called photons Is both a waves and a particle Radiation pressure is the “push” of the particle of light Spectroscopy = the study of light’s properties Spectra 1. Continuous spectrum - A continuous band of color Spectra 2. Absorption spectrum - Dark lines running through it Spectra 3. Emission spectrum - Bright lines emitted A star’s spectra = its fingerprint…tells what elements are in the star. Doppler Effect The change in frequency, either higher or lower, when wave source is moving. The pith gets higher or lower for sound. Applies to any wave Higher (blue shift) – moving to us Lower (red shift) – moving away A red shift A blue shift 24.2 Tools to Study Space Refracting Telescope Reflecting Telescope Radio Telescopes Hubble Space Telescope Others Refracting Telescope Uses a big lens to focus light – Upside down image – Blue and red light don’t focus at the same place! – Lens is heavy and can distort images – Not the “big” telescopes of today Reflecting Telescope Uses a big mirror to collect light + doesn’t sag (weighs less) + cheaper glass + can be bigger/stronger – the second mirror is in the way of the light Optical Telescope Properties Light gathering power – Amount of light it can get Resolving power – Finer detail ability Magnification power – Magnifies it Radio Telescopes “Sees” radio waves Satellite dishes are good enough Weak signals so the telescopes are huge! Poor resolution so they “hook up” with other radio telescopes VLA = very large array Radio Telescopes Less affected by weather 24/7 viewing See through interstellar dust No observatory = cheaper Detect cool objects (no light seen) Detect human radio signals HST In orbit above earth NO air interference Launched 1990 8 foot mirror 10 billion times stronger than the human eye!!! 24.3 The Sun Just 1 of 10,000,000,000 stars in Milky Way Joe average star Only close star for study 109 earths wide 1.25 million earth’s volume Sun Facts IT’S A GAS…it doesn’t have a solid surface! 4 parts – Interior – Photosphere – Chromosphere – Corona Interior Nuclear fusion provides energy 4 hydrogen make 1 helium & energy Mass is lost in reaction… E = mc2! 4 million tons of hydrogen are lost each second … Can still last for 10 billion yrs! Internal temp = 15 million degrees! Photosphere A 300 mile thick surface covering Looks grainy on surface – From rising/sinking hot gas – Convection currents 90% hydrogen, 10% Helium (sun) 6000 degrees Chromosphere Thin atmosphere layer Oh boy Corona Another thin layer of hot gases Extends 600,000 miles out Hot gas “blows” out from sun = solar winds, at 500 miles/sec Causes the Northern Lights 1,000,000 degrees The Active Sun Spins on axis like planets 25 days at eq, 33 days near top/bot Sunspots = dark regions On an 11 year cycle Prominences – ejected material Solar flares – bright sunspots that eject material and high energy Aurora Borealis – form solar flares A radio image of the sun