* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
X-ray astronomy detector wikipedia , lookup
Planetary nebula wikipedia , lookup
X-ray astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Hayashi track wikipedia , lookup
White dwarf wikipedia , lookup
Astrophysical X-ray source wikipedia , lookup
Main sequence wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Accretion disk wikipedia , lookup
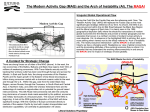
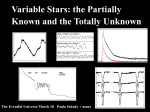
Variable Stars clues: timescale, amplitude, light curve shape, spectrum Eclipsing: Algol B8-M ß Lyr W UMa (hrs-days) B8-G3 Eruptive: single binary SNII 15-20 mag (yrs) flare 1-6 mag (<hr) K-M Pulsating: short P Cepheids:F-K, 1-50d, 1.5mag RR Lyr: A-F, 0.5 day, 1 mag Scuti: A-F, hrs, 0.02 mag F0-K0 (hrs) WD: SNI -20mag (yrs) N -10mag (1000s yrs) DN - 2-7 mag (weeks) NL - erratic Symbiotic: 3mag (erratic) XRB: HMXRB, LMXRB -ray Bursters RS CVn: F,G+KIV, spots long P Mira:M, yrs, 1-5mag S-R: K, M odd ß Ceph: B, 0.5d ZZ Ceti: WD, min Cataclysmic Variables white dwarf primary with a low mass (G-M) secondary, orbital periods of 67 min-2 days Nova: TNR, high mass WD, outbursts 8-15 mag every few thousand yrs, ~20/yr in MW Dwarf nova: disk instability, outbursts 2-7 mag every week-30 yrs Novalike: high, low states on timescales of months, high accretion AM CVn: 2 white dwarfs, orbital periods of 10-45 min Disk Intermediate Polar Polar MAGNETIC ACCRETION DISK ACCRETION . = 1/2GMM For slowly rotating WD: Ldisk = LBL . High M wd/Rwd . Low M 108 K X-rays 9000-40000 K BL Hard X-rays Soft X-rays Cyclotron -WD accretes until thick degenerate envelope leads to TNR -10-6 to 10-4 solar masses ejected (dust can form) -Envelope returns to quasi-static equil (nuclear burning) -Envelopoe gradually ejected by winds, phot recedes, T increases and peak radiaiton in soft X-ray -Constant bol phase lasts until envelope exhausted (1-100 yrs) Typical DN Outburst cycle of the Dwarf Nova SS Cyg Cannizzo & Mattei, 1998, ApJ 505, 344 Outbursts are DISK instabilities Typical CV spectra in DR1 CVs in EDR in Szkody et al. 2002, AJ, 123, 430 Symbiotic stars Late type RG + WD + high excitation emission lines Possible progenitors of Type Ia SN? RS CVn star (convection + high rotation gives spots) K0III Pulsating stars: Asteroseismology • Pulsations Only systematic way to study the stellar interior • Pulsations are observed in stars all over the HR diagram ZZ Ceti stars Pulsations in a star Pulsation period and amplitude depend on the average density. P 1/2 [P=(4π/3G)1/2] Low density long P, high amplitude High density short P, low amplitude Density profile decides how deep the pulsations penetrate in the star. (Deeper the penetration more we learn about the interior) Centrally condensed stars like our Sun have shallow pulsations Uniform density stars like white dwarfs have deep pulsations Cepheids and RR Lyrae Radial pulsators RR Lyrae: A giants, Mv = 0.5, P<1 day Cepheids: F-G SG, P-L relation, P ~ 2-60 days, HeII ionization zone pulsation mechanism P-L relation 1) measure mv with CCD 2) find P from light curve 3) use P-L to get Mv 4) m-M d • White dwarfs show non-radial g-modes on account of their high gravity Periods of 100s to 1000s • These modes are characterized by quantum numbers (k,l,m) similar to atomic orbitals Spherical gravitational potential Spherical electrostatic potential l determines the number of borders between hot and cool zones on the surface m is the number of borders that pass through the pole of the rotation axis k determines the number of times the pulsation wiggles from the center to the surface Two flavors of ZZ Ceti stars (DAVs) cool Teff = 11000K P ~ 1000s Larger amp, more modes, unstable amps hot Teff = 12000K P ~ 200s Less modes, more stability Mira - pulsating RG Period ~ 11 months Flare Stars Flare <15s to 1 hr, repeats hrs - days Amplitude up to 4 mag Opt is thermal brem at T ~ 107K, radio is non-thermal Between flares, spectrum is K-M with CaII, H emission Variable Stars clues: timescale, amplitude, light curve shape, spectrum Eclipsing: Algol B8-M ß Lyr W UMa (hrs-days) B8-G3 Eruptive: single binary SNII 15-20 mag (yrs) flare 1-6 mag (<hr) K-M Pulsating: short P Cepheids:F-K, 1-50d, 1.5mag RR Lyr: A-F, 0.5 day, 1 mag Scuti: A-F, hrs, 0.02 mag F0-K0 (hrs) WD: SNI -20mag (yrs) N -10mag (1000s yrs) DN - 2-7 mag (weeks) NL - erratic Symbiotic: 3mag (erratic) XRB: HMXRB, LMXRB -ray Bursters RS CVn: F,G+KIV, spots long P Mira:M, yrs, 1-5mag S-R: K, M odd ß Ceph: B, 0.5d ZZ Ceti: WD, min Supernovae X-ray Binaries CVs Morford, Ortez Chadney/Fowler Kong Campion Smith Stevens Markert Slinker Sheets Green Belleci Vos Timpe Jennings Filbrandt Magnuson Pulsators Flares Others Mayorga Hua Evans Draper Jewell Hansen