* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth`s Shape
Impact event wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
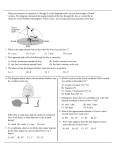
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=taHTA7S_JGk&safe=active Unit 1 Earth’s Dimensions • The Earth has an Oblate Spheroid Shape • Polar Circumference= 40,008 km • Equatorial Circ. = 40,076 km • Polar Diameter = 12, 714 km • Equatorial Diameter= 12, 757km • The Geographic poles are at the ends of the Earth’s Axis of Rotation. The axis is tilted at an angle of 23 ½ degrees • Although the Earth is not a perfect sphere it is very close as compared to the size of its diameter. • The Earth has very little relief compared to its diameter. • If you compare the highest mountain to the deepest ocean we find that the Earth is smooth. EXAMPLE • Mount Everest is 9km high • The Marinas Trench is 11km deep • 20 km as compared to 12, 757km less than 0.2% of the diameter • On a normal 20cm globe Mt Everest would be 1/10th of a millimeter. Evidence of the Earth’s Shape • 1. Altitude to Polaris(North Star)- is located directly over the Earth’s Axis of Rotation. Therefore the angle above the horizon to Polaris in the northern hemisphere is equal to the observer’s latitude •The altitude to Polaris at any place in the Northern Hemisphere is equal to it’s latitude. •The latitude at any given point on the Earth is equal to the angle from the equator to a radius line that extends to the point on the surface • 2. Lunar Eclipses- The shadow of the Earth cast on the moon’s surface is round. • During a lunar eclipse the Earth’s curved shadow is cast on the moon. • 3. Gravity Measurementgravity is the force that pulls all objects toward the center of the Earth. • Weight = mass x gravity • Describe how this can be used to determine the shape of the Earth • As you move away from the Earth gravity decreases. • The distance from the center of the Earth to the poles is less than the distance to the equator, • Therefore gravity is greater at the poles. • 4. As an observer on shore watches a ship sail out to sea the ship will appear to sink into the sea as it passes over the horizon. This occurs due to the ship following the curvature of the Earth. Observer Observer’s Line of Sight Ship 5. Photographs from space are the best evidence of the Earth’s shape. Proofs of the Earth’s Shape • • • • • • • Pictures of the Earth from Space Other Objects in the Sky Lunar Eclipse Ships Sailing Out to Sea The Changing Altitude of Polaris The Change in Gravity on Earth Distance Between Adjacent Lines of Latitude Earth’ Motions Earth rotates on its axis at a rate of 15⁰ per hour. Earth’s rotation causes the apparent motion of the sun They appear to revolve around the Earth, but it doesn’t the Earth is moving around the sun All the stars seem to rotate around Polaris throughout the night. The pattern of stars also change throughout the year. They also move around Polaris. Circumpolar Star Trails Proofs of the Earth’s Rotation • Motion of a Foucault Pendulum –Jean Foucault - 1851 • Coriolis Effect –Deflection in the Northern Hemisphere –Deflection in the Southern Hemisphere Foucault Pendulum at the United Nations Winter Orion Earth Sun Summer Sagittarius Orion Winter Constellation in the Southern Sky Sagittarius - Summer Constellation in the Southern Sky