* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Refusing to Go Quietly: GRBs and Their Progenitors
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Advanced Composition Explorer wikipedia , lookup
History of supernova observation wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
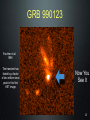
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
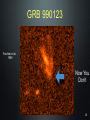
Astrophysical X-ray source wikipedia , lookup
X-ray astronomy satellite wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
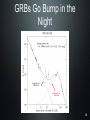
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
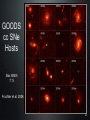
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
X-ray astronomy detector wikipedia , lookup
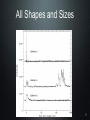
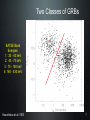
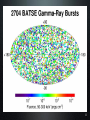
Refusing to Go Quietly: Gamma-Ray Bursts and Their Progenitors Andy Fruchter STScI Hubble Science Briefing 5 Dec. 2013 What Are We Doing Here? • An introduction to Gamma-Ray Bursts (GRBs) • Massive stars and the long bursts • Short bursts and merging neutron star binaries • A new view on the universe 2 The Vela Satellites: Protecting the Free World from Illicit GRBs Designed to detect nuclear tests (in violation of the test ban treaty), the Vela satellites discovered GRBs 3 Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory 4 All Shapes and Sizes 5 Two Classes of GRBs BATSE Band Energies: 1: 20 - 40 keV 2: 40 - 70 keV 3: 70 - 160 keV 4: 160 - 430 keV Kouveliotou et al. 1993 6 Two Classes of GRBs BATSE Band Energies: 1: 20 - 40 keV 2: 40 - 70 keV 3: 70 - 160 keV 4: 160 - 430 keV Kouveliotou et al. 1993 7 8 The Milky Way According to COBE 9 So... • GRBs must be very close -- the Solar System • GRBs must be very far (distant galaxies) 10 But ... • If they are far out in the solar sytem, they must be produced by colliding balls of ice. Throwing snowballs may be more dangerous than we realized! • If they are very far, their energies may be stupendous....something like the rest mass of the sun being turned into gamma-rays! 11 Where Do GRBS Come From? http://www.ibiblio.org/Dave/Dr-Fun/df9804/df980403.jpg 12 13 GRB 990123 • One of the brightest GRBs observed • At its brightest, it was visible through a pair of binoculars • But the light from the burst travelled over 12 billion light years before hitting the binoculars! • Estimated energy in gamma rays of the burst = rest mass of the sun! 14 GRB 990123 Fruchter et al. 1999 The transient has faded by a factor of two million since peak in this first HST image QuickTime™ and a GIF decompressor are needed to see this picture. Now You See It 15 GRB 990123 Fruchter et al. 1999 QuickTime™ and a GIF decompressor are needed to see this picture. Now You Don’t 16 A Side View of a GRB 300,000 light seconds Regions of γ-ray formation Doomed Star Black Hole Internal Shocks? Photosphere? GRB Hitting Interstellar Medium 17 GRBs Go Bump in the Night Expected from GRB Alone Expected from SN Alone 18 The Star Underneath Interestingly, the spectra of the supernovae underneath Long GRBs are missing both Hydrogen and Helium. 19 GRB Hosts Box Width 3.”75 Fruchter et al. 2006 20 GOODS cc SNe Hosts Box Width 7.”5 Fruchter et al. 2006 21 Long GRBs Are Not Just Like Other Supernovae • They like to be on the very brightest parts of their host galaxy (much more so than regular supernovae) • They like their hosts small -- probably to avoid “metals” 22 Artist’s Conception of GRB Environment 23 You Are Here Long GRBs like this Not this 24 Just When You Thought You Were Safe..... 25 A Short-Burst Host Mosaic Images on the left were taken in the blue, on the right in the infrared Short Bursts like all types of galaxies -- small to large, young to old. 26 So What Causes Short Bursts? • Deep searches show no sign of supernovae, and Short GRBs do not greatly favor star-forming hosts, so massive stars are probably out. • Neutron star binaries can merge anywhere between 10 million years and a Hubble time, and are found in all types of galaxies. • But is there an observation that would be a “smoking gun”? 27 28 29 Environment of GRB 130603B 30 SGRB 130603B in Black and White 0.6 µm = visible light 1.6 µm = infrared light 31 What Have We Found? http://www.sciencecartoonsplus.com/gallery/astronomy/astron51_pretty-good-nova.gif 32 If Confirmed • Will conclusively show that short bursts come from merging neutron stars • Will explain much, and perhaps vast majority, of heavy elements 33 Merging Neutron Stars Make Waves http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IZhNWh_lFuI 34 A Future Astronomical Observatory Advanced LIGO will be able to detect gravitational waves that stretch the length of the arms by a fraction of the size of a proton 35 Listening to Neutron Star Mergers Figure: Caltech/Cornell/Cita Collaboration Audio: Ben Farr, Northwestern U. http://hubblesource.stsci.edu/services/events/telecons/media/listening_to_neutron_star_mergers.mp3 36 The Nearest(?) SGRB GRB 080905a 1.5 Billion light years away 37 We Might Not Need a GRB • A kilonova could act as a marker • Large new surveys instruments, such as LSST, could locate kilonovae • These may be our best way to find the first gravitational wave sources 38 The Lesson • When there are two competing theories in science, often one is right and the other is wrong. • But in more interesting cases, they are both right. • Welcome to the progenitors of GRBs! 39