* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cortes and the Aztecs
Templo Mayor wikipedia , lookup
Bernardino de Sahagún wikipedia , lookup
Tepotzotlán wikipedia , lookup
Aztec cuisine wikipedia , lookup
Human sacrifice in Aztec culture wikipedia , lookup
Aztec religion wikipedia , lookup
Aztec society wikipedia , lookup
Hernán Cortés wikipedia , lookup
National Palace (Mexico) wikipedia , lookup
Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire wikipedia , lookup
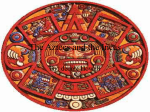
Cortes and the Aztecs Genocide Childhood • At the age of 14, Cortés was sent to study at the University of Salamanca in west-central Spain. This was Spain's great center of learning. • He learned Law and Latin • helped him to justify his unauthorized conquest of Mexico His time in the New World He listened to the tales of those returning from the Indies, who told of discovery and conquest, gold, Indians and strange unknown lands. left for Hispaniola in 1504 where he became a colonist in 1506, Cortés took part in the conquest of Hispaniola and Cuba, receiving a large estate of land and Indian slaves for his efforts from the leader of the expedition. His time in the New World • He listened to the tales of those returning from the Indies, who told of discovery and conquest, gold, Indians and strange unknown lands. • left for Hispaniola in 1504 where he became a colonist Diego Velázquez de Cuéllar • a Spanish conquistador. He conquered and governed Cuba for Spain. • He initially backed Hernán Cortés's famous expedition to Mexico. However when Cortés tried to seize and claim Mexico for himself. Velázquez charged Cortés with exceeding his authority and ordered Pánfilo de Narváez to arrest him. Cortés defeated Narvaez's troops in a surprise attack and persuaded the survivors to join him. Thus Velázquez saw none of the riches which came from Mexico Conquest of Mexico • 1518- Velázquez put him in charge, but revoked his charter • Cortés ignored the orders and went ahead anyway, in February 1519, in an act of open mutiny Conquest of Mexico • Mutiny- open rebellion against constituted authority • Supplies- 11 ships, 500 men, 13 horses and a small number of cannons, he landed in the Yucatan Peninsula in Mayan territory La Malinche or Dona Marina • Through her help, • La Malinche or Doña Cortés learned from the Marina - his future Tabascans about the mistress and mother of wealthy Aztec Empire his child Martín. and its riches. • Malinche knew both • She was one of twenty the (Aztec) Nahuatl slaves given to Cortés language and Maya, by the natives of thus enabling Hernán Tabasco in 1519 Cortés to communicate in both. On the way to the Capital City • Corez marched on • fearing native treachery, Tenochtitlan in midinfamously massacred August 1519, along with thousands of unarmed 600 men, 15 horsemen, members of the nobility 15 cannons, and gathered at the central hundreds of indigenous plaza, then partially carriers and warriors burned the city. At the Capital City • On November 8, 1519, they were peacefully received by the Aztec Emperor Moctezuma II, due to Mexican tradition and diplomatic customs. A God? • Considered by the Aztecs to be either an emissary of the feathered serpent god Quetzalcoatl or Quetzalcoatl himself • The patron god of the Aztec priesthood, of learning and knowledge Prisoner • decided to take Moctezuma as a hostage in his own palace, requesting him to swear allegiance to Charles V. • King Charles I of Spain, who had become Holy Roman Emperor Charles V in 1519, appointed Cortés as governor, captain general and chief justice of the newly conquered territory, dubbed "New Spain” • Cortés was one of the first Spaniards to attempt to grow sugar in Mexico and one of the first to import African slaves to early colonial Mexico. At the time of his death his estate contained at least 200 slaves who were either native Africans or of African descent Aztec Culture • spoke the Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica in the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries • ethnic groups of central Mexico • agricultural basis of maize cultivation • the calendric system of a xiuhpohualli of 365 day Disease • In 1520–1521, an outbreak of smallpox swept through the population of Tenochtitlan and was decisive in the fall of the city. It is estimated that between 10% and 50% of the population fell victim to this epidemic Human Sacrifice • It was extreme in the Aztec Culture • For example, for the reconsecration of Great Pyramid of Tenochtitlan in 1487, the Aztecs reported that they sacrificed 84,400 prisoners over the course of four days