* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LES01
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
Data Protection Act, 2012 wikipedia , lookup
Data center wikipedia , lookup
Forecasting wikipedia , lookup
Data analysis wikipedia , lookup
Database model wikipedia , lookup
Information privacy law wikipedia , lookup
3D optical data storage wikipedia , lookup
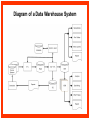
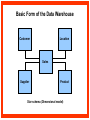
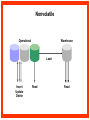
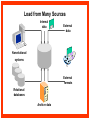
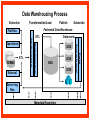
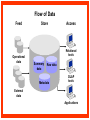
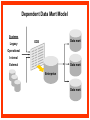
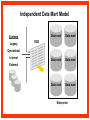
Reviewing Data Warehouse Basics Lessons 1. Reviewing Data Warehouse Basics 2. Defining the Business and Logical Models 3. Creating the Dimensional Model 4. Creating the Physical Model 5. Storage Considerations for the Physical Model 6. Strategies for Extracting, Transforming, and Loading 7. Summary Management 8. Analytical Capabilities Definition of a Data Warehouse “A data warehouse is a subject-oriented, integrated, nonvolatile, time-variant collection of data in support of management’s decisions.” - Bill Inmon “A system that extracts cleans, conforms, and delivers source data into a dimensional data store and then supports and implements querying and analysis for the purpose of decision making.” - Ralph Kimball Basic Elements of the Data Warehouse • Source: Source database or other source form • Data staging area: Intermediate area • Target: Presentation server for the new data warehouse or data mart Source Data staging area Target Diagram of a Data Warehouse System Basic Form of the Data Warehouse Customer Location Sales Supplier Product Star schema (Dimensional model) Data Warehouse and OLTP Database Design Differences Unlike an OLTP database design, a warehouse database design must: • Focus on queries • Allow incremental development • Be a nonvolatile structure • Provide historical data Data Warehouse Features A data warehouse: • Is a repository for information • Improves access to integrated data • Ensures integrity and quality • Provides an historical perspective • Records results • Is used by a broad spectrum of end users for a variety of purposes • Reduces the reporting and analysis impact on operational systems • Requires a major systems integration effort Exploring Data Warehouse Characteristics • Subject-oriented • Nonvolatile • Integrated • Time-variant Subject-Oriented Data is categorized and stored by business subject rather than by application. OLTP applications Equity plans Loans Insurance Savings Data warehouse subject Shares Customer financial information Integrated Data on a given subject is integrated. Savings Customer Current account Loans Nonvolatile Warehouse Operational Load Insert Update Delete Read Read Time-Variant Time Data 01/01 January 02/01 February 03/01 March Data warehouse Load from Many Sources Internal data External data Nonrelational systems External formats Relational databases Archive data Decision Support System (DSS) DSS ODS DW Storage OLAP Analytic Profile of DSS Queries DM Data Warehousing Process Extraction Transformation/Load Data marts ETL DDS DDS NDS Server log files Metadata Repository DDS Portal Access layer(s) Transformations ETL Staging area(s) Operational External Subscribe Federated Data Warehouse Flat files RDBMS Publish Comparing Warehouses and Data Marts Data warehouse Property Scope Subjects Data source Implementation time Versus Data Warehouse Enterprise Multiple Many Months to years Data mart Data Mart Department Single, LOB Few Months Flow of Data Feed Operational data Store Access Relational tools Summary data Raw data Metadata OLAP tools External data Applications Dependent Data Mart Model Systems Legacy Data mart ODS Operational Internal Data mart External Enterprise Data mart Independent Data Mart Model Systems Legacy Data mart Data mart Data mart Data mart Data mart Data mart ODS Operational Internal External Enterprise Data Warehousing Today • Business Intelligence – To help business users understand their business better – To help them make better operational, tactical, and strategic business decisions – To help them improve business performance Data Warehousing Today • Customer Relationship Management – Consists of applications that support CRM activities – Single customer view – Campaign segmentation – Customer analysis – Personalization – Customer loyalty scheme Data Warehousing Today • Data Mining – Known as Knowledge Discovery – Trying to find meaningful and useful information from a large amount of data – Interactive or automated process to find patterns describing the data and to predict the future behavior of the data based on these patterns • Usage – Analyzing the shopping data – Finding out the pattern between crime and location – Customer scoring in CRM in terms of loyalty – Credit Scoring in the credit card industry Data Warehousing Today • Master Data Management (MDM) – Consolidates the master data and processes the data through predefined data quality rules. – Any changes on master data in OLTP are sent to MDM – Publishes data to other systems • Customer Data Integration – Is a MDM for customer data – The process of retrieving, cleaning, storing, maintaining and distributing customer data Future Trends in Data Warehousing • Unstructured Data – Documents, images, audio, video, e-mails • Search – Search engine • Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) • Real-Time Data Warehouse