* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Enterprise Data Management
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
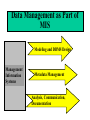
Teaching Data Management An Overview Anne Marie Smith [email protected] [email protected] La Salle University Data Management as Part of MIS Modeling and DBMS Design Management Information Systems Metadata Management Analysis, Communication, Documentation Data Management Goals • Identify enterprise’s core business information needs and effectively use the resulting data • Manage data as an asset, both within a business unit and throughout the enterprise • Provide a central focus for establishing and documenting corporate data policy and for managing data resources (human, system, data objects) • Critically analyze the use and management of data and its related processes Purpose of Data Management • Encourage the management of data from both business unit and enterprise views • Promote the importance of data as a valuable resource – identify, analyze and control critical data objects – flexible usage of data (planning and access) • Manage creation, use, storage, documentation and dissemination of data across the enterprise – redundancy – data sharing – decision support Rationale for Teaching Data Management • Provide a business orientation as foundation for Information Systems methodology • Offer recognition of value of the analysis and understanding of data and its metadata (corporate assets) • Establish information requirements definition and instill data management practices into course organization • Address data quality, data integrity issues • Promote educational use of data management tools and techniques Major Concepts in Teaching Data Management • Architecture (Logical and Physical) • Information Resource Management – Data Administration • Logical Data Modeling, Data Dictionary, Glossary, Standards – Database and Systems Administration – Decision Support / Data Warehousing • Information Analysis – Critical thinking, analytical documentation • Common Data Management Tools and Practices Roles in Enterprise Data Management • • • • • Data Analyst Business Analyst Database Administrator / Database Analyst Technical Writer / Documentation Specialist Data Warehousing Specialist Note: MIS education can prepare students to fill all these roles Organizational Issues in Teaching Data Management • Lack of faculty/instructor understanding and support of data management as a discipline in MIS • Conflicting agendas and lack of information sharing/continuity among MIS instructors • Lack of data management tool/technique training in MIS faculty • Absence of enterprise view of organization • Lack of adequate texts focusing on business/logical data management Address these issues as part of curriculum development and implementation Enterprise Data Management Tools • • • • • • Data Dictionary/Repository Business Intelligence/Business Rules Directory Data Modeling and DBMS Design Process Modeling and Systems Design Data Mining and Business Analysis Communication and Documentation Effective use of these tools and techniques can contribute greatly to the students’ experiences in learning data management Applying Data Management in the Classroom • Design course around the actual implementation of data management in a business/organization • Lectures on data management topics drawn from texts and available articles • Develop student project – divide students into small teams – each team functions as a data management consulting company – team “implements” each topic each week for a fictitious company in need of data management • Essay tests gauge student’s use of analysis and communication skills, and concept understanding Continuous Process Improvement • Establish an strategy for teaching data management strategy in an MIS curriculum and implement review processes based on CPI • Continuous focus on instructional quality, relevance to the business community and student learning • Value of MIS instruction increases as confidence in its consistency, management, relevance and quality increase – Data Management is very relevant to current and future business needs in MIS – read W. E. Deming, and L. English Communication and Documentation • All educational activities should require proper use of critical thinking, analytical skills and communication (oral and written) skills • Development of texts and related material for teaching data management is needed • MIS instructors should participate in the development of an MIS curriculum that incorporates the teaching of data management in the database areas Learning Outcomes • • • • Analytical skills Critical thinking skills Investigation and discovery skills Concepts of data management to complement standard database administration lessons • Oral and written communication skills • Consulting and concept implementation skills Conclusion • Teaching Data Management is essential to the success of an MIS curriculum • Value of data management in the classroom is related to the university’s commitment to exploring the changing and varied roles of MIS in the business communities of today and tomorrow • Proper use of tools and techniques can dramatically increase the effectiveness of this approach to teaching Data Management Questions and Answers Anne Marie Smith [email protected] [email protected] La Salle University