* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Database Design and Data Loading
Semantic Web wikipedia , lookup
Data Protection Act, 2012 wikipedia , lookup
Data center wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
Data analysis wikipedia , lookup
Data vault modeling wikipedia , lookup
3D optical data storage wikipedia , lookup
Database model wikipedia , lookup
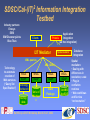
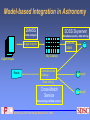
Information Integration in the Geosciences Chaitan Baru Program Director Data and Knowledge Systems SDSC National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center Introduction—SDSC • …Organized Research Unit at UC San Diego • … leading-edge site of NPACI • … one of the nodes in the TeraGrid. Lead the TeraGrid Data and Operations Working Group • … work with several application domains, e.g. Molecular Biology, Neuroscience, Digital Sky, Earth System Science, Environmental Science… via NPACI thrust areas • … also work on non-NPACI projects, including industry, Bioinformatics, Medical Informatics… • … lead some of the data activities in Cal-(IT)2 EarthScope CSIT Workshop, March 25-27, 2002 Scientific Knowledge Management Projects at SDSC • Biomedical Informatics Research Network, BIRN (NIH) • Integrating heterogeneous brain data • National Virtual Observatory • Optimizing a set of “canonical astronomy queries” in SQL • Web service for “cross-matching” catalogs • Joint Center for Structural Genomics, UCSD Cancer Center • Mining medical / bioinformatics data • The Geosciences Network (GEON)… • Information integration is key…IT “grand challenge” EarthScope CSIT Workshop, March 25-27, 2002 GEON: The Geosciences Network • Two testbeds • Broad range of geoscience data sets • Will address IT issues of interest to EarthScope objectives Geoscience • Ramon Arrowsmith, Arizona State University • Maria Luis Crawford, Bryn Mawr • Karl Flessa, University of Arizona • Randy Keller, University of Texas, El Paso • Alan Levander, Rice University • Mian Liu, University of Missouri • Charles Meertens, UNAVCO • John Oldow, University of Idaho • Dogan Seber, Cornell University • Paul Sikora, University of Utah EarthScope CSIT Workshop, March 25-27, 2002 • A.Krishna Sinha, Virginia Tech • Robert Smith, University of Utah CS/IT • Mike Bailey, SDSC • Chaitan Baru, SDSC • Eric Frost, SDSU • Bertram Ludaescher, SDSC • Reagan Moore, SDSC • Phil Papadopoulos, SDSC Education • Mary Marlino, DLESE GEON IT Issues • Prototyping a national information infrastructure for Geosciences • An outgrowth of NSF-sponsored workshops on Geoinformatics • Collaborative activities on-going for about 2 years… • Close collaboration between geoscientists and IT to interlink databases and Grid-enable applications • “Deep” data modeling of 4D data • Situating 4D data in context—spatial, temporal, topic, process • XML-based standards for data exchange • Semantic integration of Geoscience data • Logic-based formalisms to represent knowledge and map between ontologies • Begin to define a UGLS (Unified Geoscience Language Systems), a la UMLS in medicine • Accessing bibliographic information EarthScope CSIT Workshop, March 25-27, 2002 GEON IT Issues • Learning from the BIRN project • The GEON Grid: heterogeneous networks, compute nodes, storage capabilities • Deploy grid and cluster software across GEON • SDSC SRB, ROCKS, Globus • Leverage TeraGrid experience • Sharing data, tools, and compute resources, SETI@home model EarthScope CSIT Workshop, March 25-27, 2002 GEON IT Issues • Advanced visualization capability • Augmented reality facilities • Remote visualization using Visualization Center at Scripps and SDSU Viz lab EarthScope CSIT Workshop, March 25-27, 2002 The Information Integration Landscape • Motivated by applications needs… • Medical/Bio-informatics, Neuroscience, Geosciences, Digital Government • Approaches • • • • • Data Warehouses Database Integration Application Integration Semantic Data Integration Model-based Integration • R&D activities in collaboration with industry partners EarthScope CSIT Workshop, March 25-27, 2002 Data Warehousing • Bring together data from multiple sources • Advantages • Provides high performance access at a single location • Can support OLAP, decision support, data mining • Issues • Cannot avoid “database integration” issues, e.g. schema integration • May not have most up-to-date data in the warehouse • E.g., • SDSC: Protein Data Bank, Alliance for Cell Signaling, Joint Center for Structural Genomics • Cal(IT)2 High Tech Coast GIS EarthScope CSIT Workshop, March 25-27, 2002 Database Integration & Application Integration • Federate data from distributed databases and applications • Need not bring data to single location • Data is up to date • Can deal with “non-cooperating” sources • Database integration—employs database technology (data models and query languages) • Application integration—employs object-oriented programming technology (Java) • The SDSC/Cal-(IT)2 Information Integration Testbed EarthScope CSIT Workshop, March 25-27, 2002 SDSC/Cal-(IT)2 Information Integration Testbed Industry partners: Enosys ESRI IBM DiscoveryLinks Blue Titan Application Polexis Integration (ad hoc integration) Clients I2T Mediator Spatial mediator XML queries XML (GML) Technology to automate creation of Web services (“Query Set Specification”) WSDL SOAP Sociology Workbench Survey data WSDL SOAP WSDL SOAP WSDL SOAP ICPSR Univ. of Michiga n Stats Package ArcIMS ArcSDE EarthScope CSIT Workshop, March 25-27, 2002 Database Integration Spatial mediation: • Dealing with differences in resolution, scale • Plug-in conflation routines • Web workflows and Service “orchestration” Semantic Integration • Data about the “same” high-level concept, but uses different ontologies and metadata • E.g., Human brains and mouse brains • E.g., Geologic, geophysics, geochemistry, geochronologic information about plutons • • Knowledge representation, rule-based, logic-based approaches for integration Biomedical Informatics Research Network (BIRN). Funded by NIH. Integrate neuroscience brain data from multiple labs • Human, mouse, rat brains • Structural data and functional data • RDF, DAML+OIL, SDSC KIND Mediator—Semantic Web EarthScope CSIT Workshop, March 25-27, 2002 A Geoscientist’s Information Integration Problem What is the distribution and U/ Pb zircon ages of A-type plutons in VA? How about their 3-D geometry ? How does it relate to host rock structures? ? Information Integration Geologic Map (Virginia) GeoChemical “Complex Multiple-Worlds” Mediation GeoPhysical GeoChronologic (gravity contours) (Concordia) Foliation Map (structure DB) Model-Based Integration • Use of domain models, statistical models, probabilistic techniques (data mining) to integrate information • Integrate across scale in biology • Molecular, genetic, protein, cell, tissue, organ… • Encyclopedia of Life project at SDSC • Annotate genes with protein information • 17-step pipeline • Will read and generate many TB’s of data • Possible applications to geosciences… EarthScope CSIT Workshop, March 25-27, 2002 Model-based Integration in Astronomy 2MASS SDSS Skyserver Data analysis Database queries, data mining Load into DBMS Image Analysis Digital images Result Sky Catalogs Correlate across Catalogs Catalog A Data mining Cross-Match Service Data mining via Web services EarthScope CSIT Workshop, March 25-27, 2002 Catalog B The SDSS Skyserver Project • Sloan Digital Sky Survey, SDSS • 5-year survey (2001-05) • Northern cap of universe, 10,000 square degrees (1/2 arcsecond resolution) • ~200 million objects in 5 optical bands, and spectrograms of a million objects • Software pipeline at Fermilab • About 400 attributes for each object + image of object • 1st year, 80GB, 14 million objects, 50K spectra • At end, 40TB of images, 3TB processed data • Parallel database implementation using IBM DB2 AIX/Linux clusters • Parallel data mining using parallel databases EarthScope CSIT Workshop, March 25-27, 2002 GSA Special Paper on Geoinformatics • • • • Co-edited by K. Sinha and C. Baru 11 articles from geoscience authors 6 articles from IT authors To be published early 2003 EarthScope CSIT Workshop, March 25-27, 2002