* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Resources
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
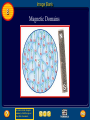
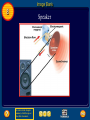
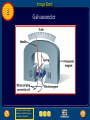
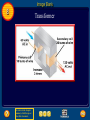
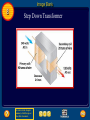
Chapter Resources 8 Click on one of the following icons to go to that resource. gpscience.com Image Bank Foldables Video Clips and Animations Chapter Summary Chapter Review Questions Standardized Test Practice To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Chapter Resources 5 gpscience.com To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Click on individual thumbnail images to view larger versions. Image Bank 8 Transfer Images To transfer images to your own power point follow the following steps: • Open the “Resource” file from the CD-ROM disc – view the file in the “normal view” or “slide sorter view” mode - go to slide #2 – from there you can click through the images and follow these instructions. Click once on the image. • Copy the image • Go to your own power point document • Paste the image. To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Magnetite To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Magnetic Field To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Horseshoe and Disk Magnets To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Compass Needles on a Bar Magnet To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Compass Needle Alignment To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Magnetic Nail To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Magnetic Domains To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Broken Magnetic Poles To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Magnetic Field Current in Wire To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Magnetic Field Wire Loop To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Magnetic Field Wire To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Magnetic Iron Core To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Speaker To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Electromagnet To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Galvanometer To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Fan To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Electric Motor To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Turning Motor To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Current Direction Change To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Motor Forces To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Concept Map-Left To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Concept Map To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Power Plant To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Wind Farm To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Alarm Clock To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Power Lines To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Transformer To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Step Down Transformer To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Image Bank 8 Creating Electricity To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Foldables 8 Using Magnets Many devices you use contain magnets that help convert one form of energy to another. Make the following Foldable to help you understand how magnets are used to transform electrical and mechanical energy. To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Foldables 8 Fold a sheet of paper in half lengthwise. To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Foldables 8 Fold the paper down about 2 cm from the top. To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Foldables 8 Open and draw lines along the top fold. Label as shown. To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Foldables 8 Summarize As you read the chapter, summarize how magnets are used to convert electrical energy to mechanical energy in the left column, and how magnets are used to convert mechanical energy to electrical energy in the right column. To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Video Clips and Animations 8 Click image to play movie To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. To view the next video clip or animation click here. Video Clips and Animations 8 Click image to play movie To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Reviewing Main Ideas 8.1 Magnetism • A magnetic field surrounds a magnet and exerts a magnetic force. • All magnets have two poles: a south pole and a north pole. • Opposite poles of magnets attract; like poles repel. • Groups of atoms with aligned magnetic poles are called magnetic domains. To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Reviewing Main Ideas 8.2 Electricity and Magnetism • An electric current flowing through a wire produces a magnetic field. • An electric current passing through a coil of wire can produce a magnetic field inside the coil. The coil becomes an electromagnet. One end of the coil is the north pole, and the other end is the south pole. To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Reviewing Main Ideas 8.2 Electricity and Magnetism • The magnetic field around an electromagnet depends on the current and the number of coils. • An electric motor contains a rotating electromagnet that converts electrical energy to mechanical energy. To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Reviewing Main Ideas 8.3 Producing Electric Current • By moving a magnet near a wire, you can create an electric current in the wire. This is called electromagnetic induction. • A generator produces electric current by rotating a coil of wire in a magnetic field. To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Reviewing Main Ideas 8.3 Producing Electric Current • Direct current flows in one direction through a wire; alternating current reverses the direction of current flow in a regular pattern. • The number of turns of wire in the primary and secondary coils of a transformer determines whether it increases or decreases voltage. To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Chapter Review 8 Question 1 What do magnetic field lines connect? A. B. C. D. magnetic domains north pole and south pole of a magnet north poles within a magnetic domain south poles within a magnetic domain To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Chapter Review 8 Answer The answer is B. The magnetic field can be represented by lines of force, or magnetic field lines. To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Chapter Review 8 Question 2 What two things are found on all magnets? To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Chapter Review 8 Answer All magnets have two poles: a south pole and a north pole. To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Chapter Review 8 Question 3 Which of these is a single wire wrapped into a cylindrical wire coil? A. B. C. D. domain pole solenoid turbine To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Chapter Review 8 Answer The answer is C. When current flows through a solenoid, the magnetic field inside it is stronger than the magnetic field inside a single loop. To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Chapter Review 8 Question 4 Why are electromagnets temporary magnets? Answer An electromagnet is a temporary magnet because the magnetic field is present only when current is flowing in the solenoid. To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Chapter Review 8 Question 5 Which reverses the direction of current in a regular pattern? A. B. C. D. alternating current direct current electromagnet magnetic domain To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Chapter Review 8 Answer The answer is A. Alternating current reverses the direction of current in a regular pattern. Direct current flows in only one direction through a wire. To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Standardized Test Practice 8 Question 1 Which is best represented by the diagram? A. aluminum foil B. nail in contact with a magnet C. normal iron nail D. glass To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Standardized Test Practice 8 Answer The answer is B. A normal iron nail’s microscopic domains are arranged randomly. Contact with a magnet causes them to become temporarily aligned. To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Standardized Test Practice 8 Question 2 Which is true of a temporary magnet? A. A magnetic field prevents the domains from aligning. B. A magnetic field causes domains to align. C. The domains cannot return to random alignment after a magnetic field is removed. D. Randomly aligned domains cannot be aligned. To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Standardized Test Practice 8 Answer The answer is B. In a temporary magnet, the domains return to random alignment when the field is removed. To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Standardized Test Practice 8 Question 3 A transformer has 50 turns of wire in the primary coil and 250 turns of wire in the secondary coil. The output voltage is 120 V. What is the input voltage? A. 240 V B. 24 V To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. C. 12 V D. 6 V Standardized Test Practice 8 Answer The answer is B. This is a step-up transformer that has 5 times as many turns of wire in the secondary coil as the primary coil has. To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Standardized Test Practice 8 Question 4 What is the output voltage from a transformer if a direct current flows through the primary coil? A. B. C. D. half the input voltage ten times the input voltage twice the input voltage zero To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Standardized Test Practice 8 Answer The answer is D. If direct current flows through the primary coil, the direction of the field does not change. It is the changing magnetic field that induces an alternating current in the secondary coil. To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Standardized Test Practice 8 Question 5 A transformer has 400 turns of wire in the primary coil and 20 turns of wire in the secondary coil. If the input voltage is 440 V, what is the output voltage? A. 440 V B. 220 V To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. A. 120 V B. 22 V Standardized Test Practice 8 Answer The answer is D. In this step-down transformer, the input voltage is twenty times the output voltage. To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. Help 8 To advance to the next item or next page click on any of the following keys: mouse, space bar, enter, down or forward arrow. Click on this icon to return to the table of contents Click on this icon to return to the previous slide Click on this icon to move to the next slide Click on this icon to open the resources file. Click on this icon to go to the end of the presentation. To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document. End of Chapter Resources File To return to the chapter summary click Escape or close this document.