* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cdma450 Core Network - CDMA Development Group
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
SIP extensions for the IP Multimedia Subsystem wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
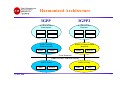
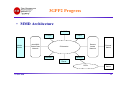
cdma450 Core Network Betsy Kidwell Chair, 3GPP2 TSG-X Lucent Technologies [email protected] CDMA450 Evolution Seminar Hosted by 3GPP2, CDG, and IA450 Warsaw, Poland 15 June 2004 Presentation Overview • Network Evolution Drivers – End User Needs – Operator/Vendor Needs • Network Evolution Goals – IP Core Network – Worldwide Roaming – Security • 3GPP2 Progress – – – – Harmonization Efforts MMD CDMA/GSM Roaming Services • Conclusion 15 June 2004 1 Network Evolution Drivers • End User Needs – – – – – – – – 15 June 2004 Voice Services High Speed Data Easy Operation Low Cost High Quality Bandwidth as appropriate Worldwide roaming Small/Multifunction device 2 Network Evolution Drivers • Operator/Vendor Needs – – – – Low cost of operation Protection against theft of service Profitable business Worldwide access for their customers – via roaming or actual network – Simple billing and collection – More spectrum 15 June 2004 3 Network Evolution Goals • IP Core Network – Voice and data services • VoIP • High speed data transfer • Internet access – – – – 15 June 2004 Ease of service introduction Lower maintenance Standard protocols and services Cross-technology interoperability 4 Network Evolution Goals • Worldwide Roaming – – – – CDMA/GSM circuit and packet roaming IP cdma2000®1/UMTS roaming Cross-technology roaming (wireless/WLAN) Backwards compatible with legacy network (TIA-41, LMSD) 1 cdma2000® is the trademark for the technical nomenclature for certain specifications and standards of the Organizational Partners (OPs) of 3GPP2. Geographically (and as of the date of publication), cdma2000® is a registered trademark of the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA- USA) in the United States.” 15 June 2004 5 3GPP2 Progress • Harmonization Efforts with 3GPP – – – – – Decided to harmonize IP Core Network in April 2002 Core network now virtually identical X.S0013-0 v1.0 aligned with 3GPP Release 5 X.S0013-A v1.0 will align with 3GPP Release 6 Harmonization applies to services as well as core network • • • • 15 June 2004 MMS Push to Talk Presence Etc. 6 Harmonized Architecture 3GPP 3GPP2 IP Multimedia Subsystem IP Multimedia Domain P-CSCF S-CSCF P-CSCF S-CSCF I-CSCF HSS I-CSCF HSS 3GPP GPRS Core Network SGSN 3GPP2 Packet Data Network GGSN PDSN MIP HA Core Network Radio Access Network (RAN) 3GPP RAN RNC 15 June 2004 Node-B 3GPP 2 RAN BSC BTS 7 3GPP2 Progress • 3GPP2/3GPP Differences 3GPP2 3GPP Allows IPv4 Mandates IPv6 Allows home P-CSCF address on MS (e.g. SIP URI, IP address) or use DHCP Special GPRS Procedure Allows PDSN and P-CSCF to be located in different networks (e.g., PDSN in visited network, P-CSCF in home network) Requires GGSN and P-CSCF to be in the same network Smart cards optional Smart cards required Allows HTTP digest authentication Other minor differences… 15 June 2004 8 3GPP2 Progress • Harmonization Efforts with IETF – Why • Leveraging Internet products • Easy to interwork with Internet services • Flexible service creation – How • Close coordination with IETF on ID/RFC development – 3GPP2/IETF Liaison – IETF Dependency List – Members actively participate in IETF • Use of SIP, DIAMETER, IPv4, IPv6 15 June 2004 9 3GPP2 Progress • Harmonization Efforts with OMA – Proposal to transfer network independent aspects of MMS to OMA • On hold pending OMA IPR issue resolution • Coordinated with similar transfer proposal from 3GPP – Ongoing coordination on • Presence • Push to Talk • IP based Location Services 15 June 2004 10 3GPP2 Progress • MMD Functional Entities – Authentication, Authorization, Accounting (AAA) – extension of the HLR to include user data for the IP Multimedia Subsystem • Access from the CSCF uses IETF protocols (DIAMETER) – Call Session Control Function (CSCF) – provides call control functions • Proxy CSCF – SIP proxy server for the mobile, acting on behalf of the UE within IMS – Forward messages between mobile and other SIP servers • Serving CSCF – SIP registrar, with cooperation from AAA (location server) – Session control call state machine for the registered end-point – Interaction with service platforms for service control, provides service triggers • Interrogating CSCF – Entry point from other networks – Allocate or determine the S-CSCF – May hide network topology 15 June 2004 11 3GPP2 Progress • MMD Architecture S-CSCF P-CSCF Mobile Station cdma2000 Packet Data Network I-CSCF Remote Access Network IP Networks HSS/AAA Remote Station Gateway Application Server PSTN 15 June 2004 Remote Station 12 3GPP2 Progress • MMD Protocol Stack Applications SIP RTP HTTP IP Multimedia signaling and payload traffic HTTP UDP/TCP SIP RTP UDP/TCP IP IP PPP IP PPP RLP RLP MAC MAC Physical Layer Phys. Layer Mobile Station Cdma2000 RAN 15 June 2004 Applications Lower Layer Protocols PDSN Lower Layer Protocols Far-End System 13 3GPP2 Progress • MMD High Level Call Flow Mobile BSC/PCF MSC PDSN AAA HA P-CSCF Traffic Channel PPP setup and authentication Mobile IP Registration P-CSCF Discovery and MMD SIP Registration MMD SIP Call Setup MMD Media Bearer Setup 15 June 2004 14 3GPP2 Progress • Release A Features – Harmonization across different access technologies (e.g., 3GPP, WLAN) – Interworking between MMD and Internet – Interworking between MMD and PSTN – Presence – Instant Messaging – Conferencing – Group management – Interface between mobile and application server for service data management 15 June 2004 15 3GPP2 Progress • Evolution path to MMD – Legacy MS Domain Support provides a step by step evolution path from existing circuit networks to All IP networks • LMSD Step 1 (X.S0012-0 v2.0) published March 2004 • LMSD Step 2 (X.P0025-0 v1.0) planned for publication 3Q04 • MMD Release A (X.P0013-A v1.0) provides support for circuit/packet handoff with LMSD 15 June 2004 16 3GPP2 Progress • CDMA/GSM Roaming – Approved X.S0023, Network Interworking between GSM MAP and TIA-41Networking, for publication in June 2004 • One way and two way circuit based service roaming • SIM based operations – X.P0003, TIA/EIA-41-D Network Enhancements to Support CDMA SIM Roaming to GSM, approved for V&V in June 2004 • TIA-41 specific enhancements for one way and two way roaming – New project X.P0023-A, CDMA/GPRS Data Roaming, planned for publication 1Q05 • Enhances current roaming capabilities to include packet data as well as circuit service 15 June 2004 17 3GPP2 Services • Presence – 3GPP/3GPP2/OMA focused on SIP/SIMPLE for Presence and Instant Messaging – SIP Subscribe/Notify and Message methods – Watcher subscribes to presence events – Work in progress • SIP Publish to declare presence information • XCAP to manage user data 15 June 2004 18 3GPP2 Services • Presence Architecture – CSCFs serve as watcher/presentity proxies – Network may update presentity (via AAA interface or presence user agent) – IM Server and applications connect to CSCF proxies (non-IMS/MMD implementations currently in use: Wireless Village SMS transport of AOL/Yahoo IM etc.) 15 June 2004 19 3GPP2 Services • Push to Talk (PTT) – Several vendors have PTT solutions over cdma2000 1x networks • • • • • • • ZTE (Gota) Huawei Kodiak (RTX) Motorola HP/Togabi (PocketCHAT) Qualcomm (QCHAT) Ericsson – Push to Talk over Cellular (PoC) being addressed in OMA • With 3GPP2 review and comment 15 June 2004 20 3GPP2 Services • Broadcast/Multicast Service (BCMCS) – Supported for both 3G1X and HRPD systems – Efficient use of radio resources when transmitting to multiple end users – Operator has control over: • • • • Which programs are delivered to which part(s) of the network Billing of user/content provider Encryption of IP flows Service offerings – Pay per view movies – Sporting events – Streaming data (e.g., stock values, traffic 15 June 2004 21 3GPP2 Services • BCMCS (continued) – End user • • • • • 15 June 2004 Needs a BCMCS capable device Subscription for/ad hoc access to BCMCS service Selects BCMCS programming (may be menu driven from device) Receives BCMCS programming Receives billing for BCMCS services 22 3GPP2 Services • Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) – X.S0016-0 v1.0 (parts 000, 200, 310, 311, 340, 370) published May 2003 – Aligned with 3GPP Release 5 MMS – Supports Stage 3’s using • OMA-WAP • Inter-carrier Interworking • VASP Interworking 15 June 2004 23 3GPP2 Services • High Level MMS Architecture Fixed Network 2 1 4 Cellular Network Internet MMSE 3 5 Cellular Network 15 June 2004 Cellular Network rd 3 Party Service Provider 24 3GPP2 Services • MMS Architectural Elements Message store MMS User Agent Mobile Network MMS Server User Databases e.g. profiles, subscription, HLR/ AAA MMS Relay MMS VAS Applications External Server Internet / IP Network MMSE Mobile Network Mobile Network B MMS User Agent Wired EMail Client Roaming MMS User Agent 15 June 2004 25 Conclusion • Benefits of 3GPP2 Specifications – Evolution path from circuit (TIA-41) networks to IP networks – Standard service offerings – Interoperability with other networks (e.g., GSM/UMTS, WLAN) – Economy of scale with common platforms and protocols – Support for inter-technology roaming (allows worldwide roaming) 15 June 2004 26 ACRONYMS • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • 3GPP/2: 3rd Generation Partnership Project/2 AAA: Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting AKA: Authentication and Key Agreement AMR: Adaptive Multi-Rate AS: Application Server BCMCS: Broadcast Multicast Service BGCF: Breakout Gateway Control Function BSC: Base Station Controller BTS: Base Transceiver Subsystem CDMA: Code Division Multiple Access CS: Circuit Switched CSCF: Call/Session Control Function GGSN: Gateway GPRS Support Node GSM: Global System Mobile GSN: GPRS Support Node GPRS: General Packet Radio Service HSS: Home Subscriber Server I-CSCF: Interrogating CSCF IMS: IP Multimedia Subsystem IM: Instant Messaging IP: Internet Protocol MAP: Mobile Application Part MGCF: Media Gateway Control Function MGW: Media Gateway 15 June 2004 • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • MMD: IP Multi-Media Domain MMS: Multimedia Messaging Service MRF: Multimedia Resource Function MS: Mobile Station MSC: Mobile Switching Center OMA: Open Mobile Alliance PCF: Packet Control Function P-CSCF: Proxy CSCF PDSN: Packet Data Serving Node PoC: Push-to-Talk over Cellular PS: Packet Switched PTT: Push-to-Talk QoS: Quality of Service RAN: Radio Access Network RLP: Radio Link Protocol RTP: Real-time Transmission Protocol S-CSCF: Serving CSCF SDP: Session Description Protocol SGSN: Serving GPRS Support Node SIP: Session Initiation Protocol UE: User Equipment UMTS: Universal Mobile Telecommunications System WCDMA: Wideband CDMA 27 Supplementary Slides • WLAN • Security 15 June 2004 28 Wireless LAN Interworking Capability • Four scenarios have been identified for the WLAN Interworking capability. – Scenario 1: Common Billing and Customer Care – Scenario 2: 3GPP2 System Based Access Control – Scenario 3: Access to 3GPP2 Packet Data Services via the WLAN System – Scenario 4: Session Continuity 15 June 2004 29 Wireless LAN Interworking Capability • Phase 1 Efforts in 3GPP2 will focus on Scenarios 1 and 2. • WLAN Interworking Requirements Document S.P0087 is under review and comment • Stage 2 and Stage 3 text (X.P0028)is under development in 3GPP2 TSG-X WG3.1 with a scheduled completion of 2Q04. 15 June 2004 30 Wireless LAN Interworking Reference Model 3GPP2 Home Netw ork Broker Netw ork (0 or more) Database 2 H-AAA 2 B-AAA MS 1 W-AAA Internet WLAN 15 June 2004 3GPP2-WLAN Interworking Architecture for Scenario 2 31 Wireless LAN Interworking Reference Model • H-AAA: AAA in a home 3GPP2 Network. Authenticates and Authorizes the MS for access to the 3GPP2-WLAN interworking service. • B-AAA: AAA in a broker network. An intermediate network between the WLAN and 3GPP2 home network. May be 0, 1 or more. • W-AAA: The AAA in the WLAN, if available, interacts with the MS’s HAAA server to authenticate and authorize the MS for WLAN access. • Database - The database is in the MS’s 3GPP2 home network where authentication and subscriber service profile information is stored. • WLAN: The Wireless Local Area Network supports 802.11 types of accesses. It may support 802.1x and/or 802.11i. The topology of the WLAN is outside the scope of a 3GPP2 specification. 15 June 2004 32 Wireless LAN Interworking Capability • Work is currently focused on choosing an Authentication and Key bootstrapping method for Authentication of a mobile accessing a WLAN and authenticated by a 3GPP2 system. • Several authentication methods using EAP are under consideration as well as several keying methods. 15 June 2004 33 Network Security • MMD Security Architecture – Several Layers of Security • • • • • Access Network Packet Data Network Mobile IP (if used) MMD Security Association MS to P-CSCF (TLS, Digest, IPSec) End-to-end Security (optional, not specified) – MMD Security also includes network interfaces (CSCF-AAA) 15 June 2004 34 Network Security • MMD Security Architecture End-to-End Security Association (optional) IMS Security Association IMPU NAI MIP MN-HA Authentication (Mobile IP) CHAP (Simple IP) / MIP FAC (Mobile IP) NAI AAA AAA CAVE / AKA Auth. Center IMSI Mobile Station 15 June 2004 BSC/PCF PDSN Home Agent CSCF Far-End Terminal 35