* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kuliah 32 -Pendidikan Bersepadu
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
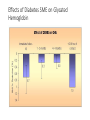
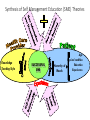
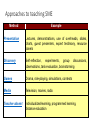
PENGURUSAN SESI PENDIDIKAN KESIHATAN ANJURAN : BAHAGIAN KAWALAN PENYAKIT BAHAGIAN PEMBANGUNAN KESIHATAN KELUARGA Modul Latihan Pegendalian NCD Untuk Paramedik KKM 1 Pendidikan kesihatan adalah usaha untuk menimbulkan perubahan tingkah laku hidup sihat, baik lingkungan masyarakat dan sosial. Pendidikan kesihatan adalah proses perubahan perilaku yang: • Dinamik di mana perubahan tersebut bukan sekadar proses transfer teori dari seseorang ke orang lain tetapi perubahan tersebut terjadi kerana adanya kesedaran dari dalam diri individu, kelompok, atau masyarakat sendiri ( Wafid Iqbal Mubarak & Nurul C,2009: 9-10) Modul Latihan Pegendalian NCD Untuk Paramedik 2 Objektif: • Komponen yang penting dalam memberikan perkhidmatan kesihatan yang komprehensif • Membantu pesakit untuk mencapai tahap kawalan penyakit yang baik • Membantu menggalakkan pesakit mematuhi perawatan sendiri seperti diet, senaman dan intervensi lain Juga dikenali sebagai ‘Behavioral Modification’ Definisi Pendidikan kesihatan mengenai penyakit tidak berjangkit (NCD) yang diberikan kepada pesakit (& keluarga) yang merangkumi pelbagai disiplin Anggota kesihatan yang terlibat: • Perubatan • Doktor • Diabetic Educator/paramedic • Pegawai Pemakanan • Pegawai Farmasi • Instruktor kecergasan • Kaunselor Modul Latihan Pegendalian NCD Untuk Paramedik 4 Self management Education (SME) • Adalah satu proses : • Kollaborasi • Interaktif • Berkembang • Melibatkan pesakit (& keluarga) serta Pendidik • Mengajar pesakit supaya boleh mengendalikan penyakit kronik mereka sendiri dengan baik Modul Latihan Pegendalian NCD Untuk Paramedik 5 Change in clinical data, QOL Scores, & diabetes knowledge 5 HDL PQS 0 A1C DBP -5 SBP MQS KS A1C Fasting blood glucose LDL cholesterol HDL cholesterol -10 Tiglycerides LDL -15 TC -20 -25 FBS -30 -35 TG Total cholesterol Diastolic blood pressure Systolic blood pressure Physical QOL score Mental QOL score Knowledge score Pre- to Post-Program Change in Clinical Data, QOL Scores, and Diabetes Knowledge (All sites) Hogue V, et al. Diabetes Spectrum 2003 Components of Self Management Education Assessment of the individual’s specific education needs Identification of the individual’s specific diabetes selfmanagement goals Educational and behavioral intervention directed toward helping the individual achieve identified selfmanagement goals Effects of Diabetes SME on Glycated Hemoglobin Stages of SME/Behavior Modification The Transtheoretical Model of Behavioral Change, University of Rhode Islands, 2001. Kumpulan sasaran 1.Pesakit yang baru didiagnosa dengan penyakit NCD 2.Pesakit NCD yang tidak mencapai tahap kawalan penyakit yang disarankan 3.Pesakit dengan komplikasi penyakit tertentu e.g Chronic Kidney Disease, Stroke dan lain-lain 4.Pesakit dengan masalah psikososial e.g Depression, Stress Turut melibatkan ahli keluarga dan penjaga pesakit NCD Modul Latihan Pegendalian NCD Untuk Paramedik 10 Bahan • Buku • CD-rom • Flipcharts • Model kaki dan makanan • Presentasi Power Point • Buku rekod pemakanan • LCD • Komputer Modul Latihan Pegendalian NCD Untuk Paramedik 11 Buku dan CD Modul Latihan Pegendalian NCD Untuk Paramedik 12 Flipcharts Modul Latihan Pegendalian NCD Untuk Paramedik 13 Model Kaki Modul Latihan Pegendalian NCD Untuk Paramedik 14 Penyampaian • Pilih topik • Tempoh masa • Satu jam • Separuh hari • 10-15 minit setiap pagi • Kekerapan • Sekerap mungkin • 10-15 minit setiap pagi • 1 jam setiap minggu • ½ hari setiap bulan Modul Latihan Pegendalian NCD Untuk Paramedik 15 Penyampaian • Di ruang menunggu • Bilik Konsultasi • Pusat Sumber • Bilik seminar Modul Latihan Pegendalian NCD Untuk Paramedik 16 Synthesis of Self Management Education (SME) Theories Knowledge Teaching Style SUCCESSFUL SME Age Physical condition Education Hierarchy of Experiences Needs Approaches to teaching SME Method Example Presentation Lectures, demonstrations, use of overheads, slides, charts, guest presenters, expert testimony, resource panels Discovery Self-reflection, experiments, group discussions, observations, task evaluation, brainstorming Games Drama, role-playing, simulations, contests Media Television, movies, radio Teacher-absent Individualized-learning, programmed learning, distance education Methods…Presentation •Benefits • Efficient delivery of large quantities of information • Good means of establishing interest SME Methods…Discovery • Benefits • Self-understanding through experience • Allows learners to find in themselves what they already know or have the ability to know SME Methods…Games • Benefits • Affective learning; psychological/physical stimuli, making learning enjoyable • Facilitates group learning • Uses the concepts of cooperation/competition • Knowledge/skill transfer SME Methods…Media • Benefits • Provides accessibility to prominent people who could otherwise not present and give a personal appearance • Tangible documentation • Sensory experiences • First-person views of history, geography, and nature SME Methods…Teacher-absent •Efficient delivery of information to a dispersed population •Each interaction with the patient is an opportunity for the doctor and the other HCPs to teach, encourage, and reinforce chronic disease care. •To make the collaboration between health care practitioner (HCP) and the patient possible, there should be “shared responsibility” in their respective tasks AACE Medical Guidelines • Emphasizes the different tasks of both the health care professional and the patient in maintenance of an intensive diabetes self-management PROACTIVE Patient + SUPPORTIVE Health Care Practitioner Successful Intensive = Disease Self-Management A PROACTIVE Patient P-performs blood glucose, blood pressure monitoring consistently R-records and tracks activities and diet O-overcomes psychological barriers like stigma, feeling of impending doom and others A-adherent to medications, diet, exercise program and avoidance of smoking C-consistent with appointments with health care professionals T-targets in treatment are being achieved I-interacts, communicate with health care team on possible barriers to therapy V-values the clinical parameter that should be achieved E- evaluates eye, feet and other possible organs that might be affected SUPPORTIVE Health Care Provider processes and programs to evaluate the patient’s U Utilizes adherence to treatment and effectiveness of self-care P Prevents complications through emphasis of preventive measures P Promotes adherence to guidelines adherence of the patient outcome measurements and determines patient satisfaction and O Observes quality of life by use of questionnaires appropriately to patient needs after thoroughly evaluating the R Responds patient’s concern every 3 months in a utilizable data format Trains the patient to do the procedures properly, utilizing skill evaluation T Supervises the patient’s education on diabetes programs and objectively doing this semiannually I V E Identifies errors and misconceptions in the knowledge, self-care behavior and skills of the patients Verifies any difficulties that the patient may have in any area of the Intensive Disease Self-Management System Establishes and maintain a regular follow-up schedule, defining the frequency of the visits and assessing the patient’s ability to adhere to it Patient Care Plan •Prerequisites to initiation •Assess the patient’s education needs •Determine prerequisite knowledge for the accomplishment of patient education •Determine patient’s baseline knowledge •Relevance of knowledge and skills to be discussed Patient Assessment • Personal and socioeconomic information • Baseline Diabetes Information • Other medical information • Lifestyle factors • Nutrition information • Education factors Educational Patient Care Plan •Important Points •Preventing complications •Self-monitoring and relapse prevention •Preventing Psychologic Morbidities •Reasons for developing psychologic morbidities •% for each psychologic morbidity Preventing Complications • How risks of NCDs are recognized • How the risks of NCDs may be effectively communicated • How to promote healthy eating, weight loss, physical activity and appropriate medication • How to reduce socioeconomic and cultural disparities in all these areas • How to maximize benefits and minimize psychological and other risks of screening Self-monitoring and Relapse Prevention • Blood glucose self monitoring • HbA1c testing (2-4 times/year) • Patient education in NCDs management • Medical nutrition therapy and education • Annual eye exam • Annual foot exam • Blood pressure measurement • Other related annual blood test • Annual screening for disease complications Reasons for Developing Psychologic Morbidities • Adverse effects of the medications being used • The escalating cost of treatment • The onset of chronic disease complications • A change and limitation in the functional abilities • Lack of support from the family • Fluctuations in physical well-being • Mood associated with changes in blood glucose etc Goals of SME •To optimize metabolic control •Prevent acute and chronic complications associated with NCDs •Optimize quality of life while keeping costs acceptable Qualities of a Good Regimen •Adaptable to meet the patient’s lifestyle and needs •Balances the risks and benefits of therapy •Allows frequent evaluation and modification Factors that facilitate Compliance • Inclusion of patient’s support network in the treatment team • Definition and agreement on treatment goals and self-care behavior • Correct choice of regimen for the patient and its adaptation to his lifestyle • Allowing patient to practice self-care behaviors • Monitoring the efficacy and outcomes of the behaviors that have been agreed to • Redefining goals as necessary • Renegotiating care plans if current plan has not been successful Through regular follow-ups, changes can be made and the patient’s decision-making and problem-solving skills will be enhanced, promoting a greater sense of control over their chronic diseases. TAKE HOME MESSAGES: Pendidikan kesihatan kepada pesakit NCD penting untuk memperkasakan pesakit Gunakan masa semasa pesakit menunggu giliran rawatan Guna bahasa ringkas dan mudah Kaedah pendidikan kesihatan yang bersesuaian dengan pesakit Tempoh masa yg pendek tapi kerap Buat perancangan awal & jadual pendidikan kesihatan Penglibatan semua anggota kesihatan secara bergilir Doktor, Paramedik ,Pegawai Pemakanan, Pegawai Kerja Sosial, Pegawai Farmasi dan Jurupulih anggota/ Fisioterapis Modul Latihan Pegendalian NCD Untuk Paramedik 39 Modul Latihan Pegendalian NCD Untuk Paramedik 40