* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CONDUCTIVE KERATOPLASTY(CK)
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension wikipedia , lookup
Corrective lens wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment wikipedia , lookup
Near-sightedness wikipedia , lookup
Contact lens wikipedia , lookup
Vision therapy wikipedia , lookup
Diabetic retinopathy wikipedia , lookup
Dry eye syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Keratoconus wikipedia , lookup
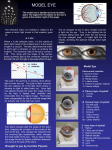
Normal Eye Focusing Lens Retina Focal Length CLEAR Focused Image Cornea CK is designed for people ages 40 and over who use glasses or contacts for hyperopia or presbyopia, but who have otherwise healthy eyes and stable vision. With today’s technology, most refractive vision problems can be corrected. You and the doctor will discuss which procedure (or combination of procedures) is right for you and your specific needs. Pre-surgery testing and discussions with the doctor will help determine if you should consider CK, monovision or other refractive techniques. Hyperopia or Farsightedness Objects close up and in the distance tend to be blurred. Hyperopia occurs when the eyeball is too short or the cornea is too flat, causing light to focus behind the retina rather than on the retina. Presbyopia Farsighted Eye Focal Length BLURRED Image Through the natural aging process, the lens of the eye loses its effective ability to change shape and accommodate focus changes from distant objects to near objects. Good near or reading vision is lost. People with presbyopia usually wear bifocals, magnifying reading glasses, or use monovision (which corrects one eye for close vision and the other for distance vision) with contact lenses. Adults over age 40 are most likely to develop presbyopia. © 2003, ApaGrafix, Inc., CON003-30203-752 • 1-800-521-5361 • 770-591-4474 • www.apagrafix.com • email: [email protected] • All rights reserved. Are you a candidate? PERSONALIZE THESE CONDUCTIVE KERATOPLASTY (CK) BROCHURES WITH For Mild to Moderate Hyperopia and Presbyopia YOUR LOGO NAME PERSONAL MESSAGE B/W PHOTOGRAPH MAP ADDRESS PHONE ETC. ApaGrafix 1148 JVL Court, Suite 100 Marietta, GA 30066 USA 800-521-5361 770-591-4474 email: [email protected] www.apagrafix.com Note If this is a fax the document has been reduced to 68% of its original size to fit on a standard 8.5” X 11” fax sheet. The actual size of the brochure is 9” X 16” folded to 4” X 9”. Reduce or eliminate the need for glasses, contact lenses or bifocals without invasive surgery YOUR LOGO NAME PHONE WEB SITE Both eyes are usually corrected for people with hyperopia; however, a technique called ‘blended vision’ is usually used for people with presbyopia. Blended vision corrects farsightedness in only one eye, leaving the other eye unadjusted. The patient can then use one eye for reading and the other for driving and viewing objects in the distance. F or the first time, doctors can treat farsightedness (hyperopia) and presbyopia without a laser or scalpel. A new, noninvasive technique called Conductive Keratoplasty (CK) can correct patients’ vision quickly, safely and effectively. Unlike LASIK, PRK and other refractive vision correction techniques which cut and remove tissue, CK uses radiofrequency energy to gently reshape the eye. Advantages of CK • Noninvasive Before Conductive Keratoplasty • No cutting or removal of tissue After CK • Little pain or discomfort • Quick recovery • Most patients no longer need glasses or contact lenses following the procedure • Can be used for patients with dry eyes Refractive Errors In normal vision, images both close up and in the distance are clear. Light enters the eye through the cornea and is focused at a single point on the retina in the back of the eye. Refractive errors such as nearsightedness, farsightedness, astigmatism and presbyopia occur when light misses the retina, causing the eye to lose its ability to focus clearly. The Procedure The entire CK procedure takes less than three minutes per eye to complete, and can be done right in the doctor’s office. First, the doctor numbs the eye with local anesthetic drops. Once the eye is numb, a special holder is placed between the eyelids to keep the eye open. The doctor marks the cornea with tiny dots of rinse-away dye. Then, a thin pen-shaped instrument is used to apply dots of energy in a circle around the edge of the cornea. The CK procedure itself is painless, although some patients experience a scratchiness or ‘foreign-object’ feeling in their eyes for a day or two that can be relieved with over-the-counter pain medications. After Conductive Keratoplasty Conductive Keratoplasty During a quick in-office procedure, CK uses a probe as thin as a human hair to apply controlled dots of radiofrequency energy (8–32 points depending on the correction required) in a circle around the edge of the cornea. Where the points of energy are placed, small areas of corneal tissue shrink. The combined effect of all applications produces a constricting ring around the cornea, which pulls like a belt to steepen its curvature. The new sharper curve to the cornea bends light rays a little more than before CK to bring objects into focus directly on the retina, improving the patient’s vision. The only medication required during the short healing period is eye drops. Most people can resume their normal activities, including working and driving, within 24 hours after CK. The doctor will probably recommend that you avoid rubbing your eyes or getting unclean water (i.e. from a lake or swimming pool) in them for at least two weeks. Usually, vision will begin to improve immediately after CK and will continue to improve for several weeks. During that period, your eyesight may fluctuate. Because CK treats the area outside the optical zone (the area you see through) and does not cut or remove tissue, it is considered a very safe vision correction procedure. A few patients may experience non-sight-threatening side effects like light sensitivity, a slight ‘foreign body’ sensation or astigmatism. These side effects are usually temporary and diminish over time. With some patients, the effect of the procedure may moderate and they may desire re-treatment.