* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download www.apjor.com Page 26 MUSCULAR VARIATION ON THE
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
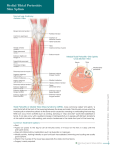
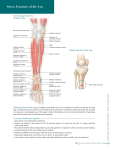
Asia Pacific Journal of Research Vol: I. Issue XXV, March 2015 ISSN: 2320-5504, E-ISSN-2347-4793 MUSCULAR VARIATION ON THE DORSUM OF THE FOOT AND ALTERATION OF STRUCTURES PASSING UNDER COVER OF THE EXTENSOR RETINACULA OF THE LOWER LIMB – A CASE REPORT 1 1 Huban Thomas. R*,2Prasanna, LC,3Suhani S, 4Sneha G, 5PrakashBabu B Senior Grade Lecturer and Corresponding Author, 2 Associate Professor, 3Senior Grade Lecturer,4 Associate Professor, 5Additional Professor. Department of Anatomy, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal University, Manipal. Karnataka State, India. ABSTRACT Extensor digitorum longus is one of the muscle of the anterior crural region of the leg, arises from the upper part of the medial surface of the shaft of fibula, a small area of lateral tibial condyle, interosseous membrane and anterior intermuscular septum of the leg. The tendon of the extensor digitorum longus lies on the lower part of the tibia passes beneath the superior and inferior extensor retinaculum, finally split into four digital slips and joins with the lateral three slips of extensor digitorum brevis to form the dorsal digital expansion. Anterior tibial artery is the main artery of the anterior crural region which lies between the extensor halluces longus and extensor digitorum longus in the lower third of the leg and appears on the dorsum of the foot as dorsalis pedis artery. During routine dissection for undergraduate medical students,in a middle aged male cadaver an additional tendon was observed in theextensor digitorum longusand is attached to the middle of the shaft of the fifth metatarsal bone.Anterior tibial artery lies lateral to the peroneus tertius muscle in the lower third of the leg, then it passes medially deep to the peroneus tertius and extensor digitorum longus muscles. Lateral tarsal artery arises from the dorsalis pedis artery and lies lateral to the deep peroneal nerve while the main trunk lies medial to the nerve beneath the inferior extensor retinaculum of the lower limb. Awareness of presence of an additional tendon in the dorsum of the foot and variation in the course of the anterior tibial artery is crucial while treating the compartment syndrome. Key Words: Extensor digitorum longus, anterior tibial artery, compartment syndrome www.apjor.com Page 26 Asia Pacific Journal of Research Vol: I. Issue XXV, March 2015 ISSN: 2320-5504, E-ISSN-2347-4793 Introduction The retinacula of the ankle are distinct structures defined as regions of localized thickening of the superficial aponeurosis covering the deep structures of the distal portion of the leg, ankle, and foot. These retinacula are sites of reinforcement of the superficial aponeurosis, maintaining approximation of tendons to the underlying bone. The retinacula act as a pulleylike mechanism that appears to represent an adaptation of the body to provide both a smooth gliding surface and the mechanical strength to prevent tendon bowstringing[1]. The superior extensor retinaculum is a transverse, roughly rectangular band located above the tibiotalar joint. It attaches laterally on the lateral crest of the lower fibula and the lateral surface of the lateral malleolus and medially on the anterior crest of the tibia and the medial malleolus. The structures that pass deep in relation to this retinaculum include the tibialis anterior muscle, extensor hallucis Longus muscle, anterior tibial blood vessels, deep peroneal nerve, extensor digitorum longus muscle, and peroneus tertius muscle. [2]. Case Presentation During routine dissection for undergraduate medical students in middle aged male cadaver, an additional tendon was observed in the extensor digitorum longus and is attached to the middle of the shaft of the fifth metatarsal bone. Anterior tibial artery lies lateral to the peroneus tertius muscle in the lower third of the leg and deep to the superior extensor retinaculum, then it passes medially deep to the peroneus tertius and extensor digitorum longus muscles. Lateral tarsal artery arises from the dorsalispedis artery and lies lateral to the deep peroneal nerve while the main trunk lies medial to the nerve beneath the inferior extensor retinaculum of the lower limb. Arrangement of structures beneath the superior extensor retinaculum also altered;from medio laterally these are tibialis anterior muscle, extensor hallucis Longus muscle, deep peroneal nerve, extensor digitorumlongus muscle, peroneus tertius muscle, anterior tibial blood vessels. Figure – Anterior view of the left leg TA – tibialisanterior , EHL – extensor hallucis Longus, DPA – dorsalispedis artery, DPN– deep peroneal nerve, EDL- extensor digitorumlongus , ATA- anterior tibial artery, PT- peroneus tertius www.apjor.com Page 27 Asia Pacific Journal of Research Vol: I. Issue XXV, March 2015 ISSN: 2320-5504, E-ISSN-2347-4793 Discussion The extensor digitorum longus muscle frequently shows variation in the arrangement and insertion of its tendons. It may give an additional slip to the base of the proximal phalanx of the second toe, the first interosseous muscle and the anterior end of the fifth metatarsal bone. Sometimes, it may be connected to the extensor hallucislongus by a slip, extensor digitorumbrev is by a cross band and peroneus tertius by a slip. Further, the digital tendon to each toe may be doubled or rarely tendon to the second and little toes alone may be doubled. [3] Presence of an additional tendon in extensor digitorumlongus muscle is seldomly reported in the past andcan be used for tendon transfer surgeries. Course of the anterior tibial artery is deep to the peroneus tertius and extensor digitorum longus muscles. This may cause transient compression of the anterior tibial artery leading to ischemia of the muscles of the anteriortibial compartment of the leg causing anterior tibial compartment syndrome. Conclusion Knowledge of these variations is necessary for the surgeon to perform tendon transfer surgeries. Furthermore, Knowledge of vascular anatomy of foot is essential for arterial reconstruction flap surgeries of the foot. This can avoid amputation of foot in cases of arterial trauma like thromboangitisobliterans, industrial automobile accidents, diabetes and severe ischaemia of lower limb.[4] References 1. Numkarunarunrote, N., Malik, A., Aguiar, RO., Trudell,DJ.,Resnick, D,.(2007) ‘Retinacula of the Foot and Ankle:MRI with Anatomic Correlation in Cadavers’. American Journal of Roentgenology. Vol 188, pp 348-354. 2. Sarrafian SK. Anatomy of the foot and ankle: descriptive, topographic, functional,2nd ed. (1993)Philadelphia,PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins,:113–158 3. Jetti, R., Sirasanagandla, S R., Nayak, B S., Gorantla, V R., Shetty, A S,.(2014) ‘Higher division of the extensor digitorum longus muscle: A cadaveric case report;.OA Case Reports Vol 25, pp:12. 4. Kulkarni, J., Paranjpe, V., Vatsalaswamy.(2012) ‘Anterior Tibial Artery Terminating as Tarsal arteries). IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (JDMS) Vol 1, Issue 2, PP 21-22 www.apjor.com Page 28