* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stress Fracture of the Leg
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
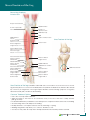
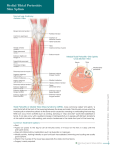
Stress Fracture of the Leg Normal Leg Anatomy: Anterior View Biceps femoris tendon Patellar tendon Common peroneal nerve Insertion of sartorius muscle Tibial tuberosity Tibialis anterior muscle Deep peroneal nerve Tibia Gastrocnemius muscle Stress Fracture of the Leg Soleus muscle Extensor digitorum longus muscle Superficial peroneal nerve Peroneus longus muscle Peroneus brevis muscle Inferior extensor retinaculum Peroneus tertius tendon Extensor digitorum brevis muscle Extensor digitorum longus tendon Extensor digitorum brevis tendon Extensor hallucis longus muscle Medial malleolus Tibialis anterior tendon Deep peroneal nerve Tibial stress fracture Extensor hallucis brevis tendon Extensor hallucis longus tendon Stress Fracture of the Leg is a hairline crack that can occur in either one of the two bones of lower leg, but they are more common in the tibia (shin bone) than in the fibula. Stress fractures are caused by overuse or prolonged use of the leg in impact activities such as running. Symptoms of leg stress fractures include pain, tenderness and swelling. Common Treatment Options • Rest is the most important treatment. • Apply ice packs to the knee for 20 - 30 minutes every 3 - 4 hours for the first 2 - 3 days until the pain goes away. • Avoid anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen or naproxen which can slow bone healing. • Avoid smoking which can delay bone healing. • Modify activities to low impact exercise such as swimming or cycling. • Wearing a leg brace may allow you to return to activities sooner. • Your doctor may order an X-ray which will help determine when activity can be resumed. © 2 0 1 0 L i p p i n c o t t W i l l i a m s & W i l k i n s | Wo l t e r s K l u w e r H e a l t h Superior extensor retinaculum Lateral malleolus Contact information © 2 0 1 0 L i p p i n c o t t W i l l i a m s & W i l k i n s | Wo l t e r s K l u w e r H e a l t h Notes: