* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PANEL KEGAWAT DARURATAN SISTEM PERNAPASAN
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
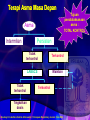
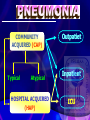
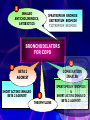
1 PANEL KEGAWAT DARURATAN SISTEM PERNAPASAN (SERANGAN ASMA AKUT, PNEUMONIA DAN COPD) dan EDEMA PARU ASTHMA 2 2 Agonist Bronchodilator Response Anticholinergic Asthma Response Panel A COPD Response Panel B 3 Terapi Asma Masa Depan Tujuan penatalaksanaan asma : TOTAL KONTROL Asma Intermiten Persisten Tidak terkontrol Terkontrol LABACS Maintain Tidak terkontrol Terkontrol Tingkatkan dosis Boushey H. Is Asthma Control Achieveable ?, European Respiratory Journal , Dec 2004 Management of Asthma Exacerbations(Emergency) Inhaled beta2-agonist to provide prompt relief of airflow obstruction Systemic corticosteroids to suppress and reverse airway inflammation For moderate-to-severe exacerbations, or For patients who fail to respond promptly and completely to an inhaled beta2-agonist 5 Risk Factors for Death From Asthma Past history of sudden severe exacerbations Prior intubation or admission to ICU for asthma Two or more hospitalizations for asthma in the past year Three or more ED visits for asthma in the past year 6 Risk Factors for Death From Asthma (continued) Hospitalization or an ED visit for asthma in the past month Use of >2 canisters per month of inhaled shortacting beta2-agonist Current use of systemic corticosteroids or recent withdrawal from systemic corticosteroids PNEUMONIA DEFINITION Inflammation and consolidation of lung tissue due to an infectious agent 9 COMMUNITY ACQUIRED (CAP) Typical Atypical HOSPITAL ACQUIRED (HAP) Outpatiet Inpatient ICU 10 Diagnosis of Pneumonia • Clinical data points – – – – – – – Cough Pleuritic chest pain Purulent sputum, Fever Leukocytosis Abnormal CXR Abnormal ABG • Sputum cultures identify the pathogen Signs of CAP • Patients typically appear short of breath at rest • Vital signs – fever, increased heart rate and increased respiratory rate • Chest exam – crackles over the affected area • Signs of consolidation: vocal and tactile fremitus, dullness to percussion, bronchial breath sounds, whispering egophony Investigations – to establish that a patient has CAP • CXR – Characteristically abnormal in CAP (some early disease may be an exception) • White blood cell count - WBC with left shift (if bacterial) • Sputum – Gram stain Treatment of CAP 14 Diagnosa HAP/Hospital Acquired Pneumonia)(Emergency) ATS (American thoracic Society, 1996). Bila gejala pneumonia, terjadi 48-72 jam penderita masuk rumah sakit, disebut HAP (dan diperkuat)dengan: Infiltrat baru atau perubahan infiltrat selagi terjadi onset baru Hipo/hipertermi Produksi sputum Lekositosis/lekopenia (Staufler, 1996) 15 MANAGEMENT Antibiotic therapy is the cornerstone of treatment for both CAP and HAP. Initial therapy should be instituted rapidly. Patients should initially be treated empirically, based on the severity of disease and the likely pathogens. 16 COPD 17 COPD - SIGNS HYPERINFLATION DECREASED EXPANSION CHEST PROLONGED EXPIRATION/±WHEEZE SIGNS PULMONARY HYPERTENSION AND/OR RVH (± CARDIAC FAILURE) CYANOSIS HYPERCAPNIA - ASTERIXUS, (PRE)COMA 18 MANAGING EXACERBATIONS(Emergency) ANTIBIOTICS CONTROLLED OXYGEN BRONCHODILATOR - BETA AGONIST ANTICHOLINERGIC, ±THEOPHYLLINE STEROIDS INTUBATION/VENTILATION TREAT HEART FAILURE IF PRESENT (RESPIRATORY STIMULANTS?) 19 1 INHALED ANTICHOLINERGICS, ANTIBIOTICS IPRATROPIUM BROMIDE OXITROPIUM BROMIDE TIOTROPIUM BROMIDE BRONCHODILATORS FOR COPD 3 2 COMBINATION INHALER BETA 2 AGONIST SHORT ACTING INHALED BETA 2 AGONIST 4 THEOPHYLLINE IPRATOPRIUM BROMIDE & SHORT ACTING INHALED BETA 2 AGONIST Manage Exacerbations Key Points • Inhaled bronchodilators (beta2-agonists and/or anticholinergics), theophylline, and systemic, preferably oral, glucocortico-steroids are effective for the treatment of COPD exacerbations (Evidence A). Manage Exacerbations Key Points • Patients experiencing COPD exacerbations with clinical signs of airway infection (e.g., increased volume and change of color of sputum, and/or fever) may benefit from antibiotic treatment (Evidence B). pulmonary edema 24 Cause of acute pulmonary edema ? Cardiogenic pulmonary edema Hydrostatic or Hemodynamic edema Non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema Increased-permeability pulmonary edema, acute lung injury or acute respiratory distress syndrome Difficult to distinguish because of similar clinical manifestations 25 Pulmonary Edema Management THE END 26 Thanks for your attention!! 27