* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Objectives ACLS Medications
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
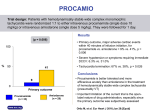
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
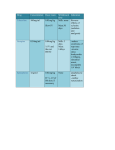
LT Kenneth Stearns PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident Claremore Indian Hospital 1 Objectives • To list the medications administered within ACLS protocol • To differentiate which arrhythmias require medication administration • To review ACLS protocol 2 ACLS Medications Medications used during an ACLS code include: • • • • • • Epinephrine Amiodarone Lidocaine Magnesium Sulfate Atropine Dopamine 3 Epinephrine Alpha-adrenergic effects • Vasoconstrictor • cerebral and coronary blood flow • Mean Arterial Pressure • aortic diastolic pressure • ACLS dose: 1 mg 4 Amiodarone • Used for its anti-arrhythmic activity • ACLS dose: 300mg bolus • An additional 150mg dose may be considered 5 Lidocaine • May be used if amiodarone is not available • Administered at 5 to 10 minute intervals • First dose: 1 – 1.5mg/kg • Subsequent dose: 0.5 – 0.75mg/kg • Max dose: 3mg/kg 6 Magnesium Sulfate • Used only in torsades de pointes • Loading dose: 1 – 2 g • Diluted in 10mL D5W or Normal Saline • Administer over 5 – 20 minutes 7 Atropine • 1st line in symptomatic bradycardia • Not effective for 2nd or 3rd degree AV block • Bradycardia dose: 0.5 mg IV every 3 – 5 minutes as needed • Max total dose is 0.04mg/kg 8 Dopamine • 2nd line for symptomatic bradycardia • Useful in hypotension (Systolic 70 to 100mm hg) with signs of shock • Dose: infused at 2 – 20 mcg/kg/min • Titrated to response 9 ACLS Cases • Bradycardia • Stable and Unstable Tachycardia • Cardiac Arrest 10 Bradycardia Types: • Sinus bradycardia • First-degree AV block • Second-degree AV block • Type I (Wenchebach/Mobitz I) • Type II (Mobitz II) • Third-degree AV block 11 Bradycardia If bradycardia is symptomatic = treatment • Atropine – 1st line • If no response to atropine: • Transcutaneous pacing • Dopamine infusion (2 – 10 mcg/kg/min) • Epinephrine infusion (2 – 10 mcg/kg/min) • Do not use atropine for 2nd or 3rd degree heart block 12 Tachycardia Types: • • • • • • • Sinus tachycardia Atrial fibrillation Atrial flutter Reentry supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) Monomorphic VT Polymorphic VT Wide-complex tachycardia of uncertain type 13 Tachycardia • Treated by synchronized cardioversion (50 – 200 J) • Wide QRS 0.12 second • Adenosine if regular narrow complex • First dose: 6mg IV push, then 12mg if needed 14 Cardiac Arrest Cardiac arrest is caused by four rhythms: • • • • Ventricular fibrillation (VF) Pulseless ventricular tachycardia (VT) Pulseless electrical activity (PEA) Asystole 15 Ventricular Fibrillation Once VF is identified: • • • • CPR Shock Epinephrine Amiodarone 16 Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia Once VT is identified: • • • • CPR Shock Epinephrine Amiodarone 17 Pulseless Electrical Activity • No shock in pulseless electrical activity • Epinephrine 18 Asystole • No shock in asystole • Epinephrine 19 Self-Assessment 1 A patient arrived into the ER and has been diagnosed with pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia. Which of the following would be appropriate to administer according to the 2015 ACLS guidelines? A. Vasopressin B. Dopamine C. Atropine D. Epinephrine 20 Self-Assessment 2 Another patient arrives into the ER and has no pulse. After an EKG is obtained, it is determined that this patient is in asystole. Which of the following would be the appropriate action according to the 2015 ACLS guidelines? A. Administer vasopressin, then epinephrine B. Start a dopamine drip C. Administer Epinephrine IV D. Shock the patient with 150J 21 Self-Assessment 3 Which of the following would be the appropriate treatment for a patient who is experiencing altered mental status with a heartrate of 160 (monomorphic ventricular tachycardia). A. Adenosine IV push B. Lidocaine C. Magnesium Sulfate D. Vasopressin 22 References In Sinz, E., In Navarro, K., In Soderberg, E. S., Callaway, C. W., & American Heart Association. (2011). Advanced cardiovascular life support. Link MS, Berkow LC, Kudenchuk PJ, et al. Part 7: Adult Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support: 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines Update for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Circulation 2015; 132:S444. 23 LT Kenneth Stearns PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident Claremore Indian Hospital 24