* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHAPTER 8
Abuse of notation wikipedia , lookup
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Functional decomposition wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Big O notation wikipedia , lookup
History of the function concept wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard calculus wikipedia , lookup
Recurrence relation wikipedia , lookup
Quadratic reciprocity wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Partial differential equation wikipedia , lookup
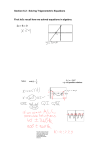
Unpacking the Standards Understanding the standards and the vocabulary terms in the standards will help you know exactly what you are expected to learn in this chapter. What It Means For You Lessons 8-1, 8-2, 8-3, 8-4, 8-5, 8-9, 8-10 Graph … quadratic functions and show intercepts, maxima, and minima. The graph of a quadratic function has key features that are helpful when interpreting a real-world quadratic model: the intercepts and the maximum or minimum value. Key Vocabulary EXAMPLE Graph of y = x 2 + 2x - 3 quadratic function (función cuadrática) A function that can be written in the form f(x)= ax2 + bx + c, where a, b, and c are real numbers and a ≠ 0, or in the form 2 f(x)= a(x - h) + k, where a, h, and k are real numbers and a ≠ 0. x-intercept (intersección con el eje x) The x-coordinate(s) of the point(s) where a graph intersects the x-axis. y-intercept (intersección con el eje y) The y-coordinate(s) of the point(s) where a graph intersects the y-axis. 4 The x-intercepts are -3 and 1. y x 0 (-3, 0) The minimum value is -4. (1, 0) 4 (0, -3) (-1, -4) The y-intercept is -3. maximum/minimum value of a function (máximo/mínimo de una función) The y-value of the highest/ lowest point on the graph of the function. CC.9-12.F.BF.3 Identify the effect on the graph of replacing f(x) by f(x) + k, k f(x), f(kx), and f(x + k) for specific values of k (both positive and negative); … What It Means For You Lessons 8-1, 8-4 You can change a function by adding or multiplying by a constant. The result will be a new function that is a transformation of the original function. EXAMPLE Compression and Stretch/Reflection of f(x) y 4 2 f(x) = x Key Vocabulary function notation (notación de función) If x is the independent variable and y is the dependent variable, then the function notation for y is f(x), read “f of x,” where f names the function. 2 g(x) = 1 x2 2 -4 -2 x 0 2 4 -2 h(x) = -3x2 -4 Chapter 8 408 Quadratic Functions and Equations © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company chapter 8 CC.9-12.F.IF.7a CC.9-12.A.REI.4b Solve quadratic equations by inspection (e.g., for x2 = 49), taking square roots, completing the square, the quadratic formula and factoring, as appropriate to the initial form of the equation. ... Key Vocabulary quadratic equation (ecuación cuadrática) An equation that can be written in the form ax2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are real numbers and a ≠ 0. completing the square (completar el cuadrado) A process used to form a perfect-square trinomial. To complete 2 t he square of x2+ bx, add _ b . 2 Quadratic Formula (fórmula cuadrática) Lessons 8-6, 8-7, 8-8, 8-9, 8-10 Knowing how to solve quadratic equations gives you tools to understand many situations, including the laws of motion. Recognizing the best solution method for a situation allows you to work efficiently. EXAMPLE Solving a Quadratic Equation The height h in feet of a baseball leaving a certain batter’s bat is h(t)= -16t2 + 63t + 4, where t is in seconds. When does the ball hit the ground? -16t2+ 63t + 4 = 0 The ball hits the ground when h = 0. -1(16t + 1)(t - 4)= 0 You can factor the equation. 1 or t = 4 t = - __ 16 The factors give these solutions. The ball hits the ground in 4 seconds. (The negative value is not reasonable in the real-world context.) The formula 2 - 4ac -b ± √ b x = __ 2a which gives solutions, or roots, of equations in the form ax2+ bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are real numbers and a ≠ 0. chapter 8 © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company; Photo credit: © Rim Light/PhotoLink/Photodisc/GettyImages () What It Means For You What It Means For You CC.9-12.A.REI.7 Solve a simple system consisting of a linear equation and a quadratic equation in two variables algebraically and graphically. Key Vocabulary linear equation in two variables (ecuación lineal en dos variables) An equation that can be written in the form Ax + By = C where A, B, and C are constants and A and B are not both 0. Solving a system of equations in two variables involves finding the ordered pair or pairs of values that make both equations true. You can do this algebraically or graphically. EXAMPLE Solving a System of Equations ⎧ y = x2- 2x - 3 ⎨ ⎩ y = -x - 1 x2- 2x - 3 = -x - 1 x2- x - 2 = 0 (x - 2)(x + 1) = 0 Chapter 8 Lessons 8-10 Solutions: (2, -3), (-1, 0) 409 2 y x -2 0 2 4 -2 -4 Quadratic Functions and Equations Key Vocabulary completing the square (completar el cuadrado) A process used to form a perfect-square trinomial. ( ) 2 b To complete the square of x2 + bx, add __ 2 . discriminant (discriminante) The discriminant of the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 2 is b – 4ac. maximum/minimum value of a function (máximo/mínimo de una función) The y-value of the highest/lowest point on the graph of the function. parabola (parábola) The shape of the graph of a quadratic function. 2 quadratic equation (ecuación cuadrática) An equation that can be written in the form ax + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are real numbers and a ≠ 0. 2 √ b - 4ac which gives solutions, or Quadratic Formula (fórmula cuadrática) The formula x = _____________ -b ± 2a roots, of equations in the form ax2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are real numbers and a ≠ 0. chapter 8 quadratic function (función cuadrática) A function that can be written in the form f(x) = ax2 + bx + c, where a, b, and c are real numbers and a ≠ 0, or in the form f(x) = a(x – h)2+ k, where a, h, and k are real numbers and a ≠ 0. vertex of a parabola (vértice de una parábola) The highest or lowest point on the parabola. x-intercept (intersección con el eje x) The x-coordinate(s) of the point(s) where a graph intersects the x-axis. y-intercept (intersección con el eje y) The y-coordinate(s) of the point(s) where a graph intersects the y-axis. Zero Product Property (Propiedad del producto cero) For real numbers p and q, if pq = 0, then p = 0 or q = 0. The Common Core Standards for Mathematical Practice describe varieties of expertise that mathematics educators at all levels should seek to develop in their students. Opportunities to develop these practices are integrated throughout this program. 1. M ake sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. C onstruct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 4. M odel with mathematics. 5. Use appropriate tools strategically. 6. A ttend to precision. 7. L ook for and make use of structure. 8. L ook for and express regularity in repeated reasoning Chapter 8 410 Quadratic Functions and Equations