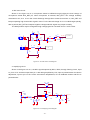
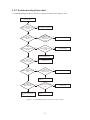
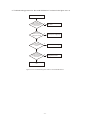
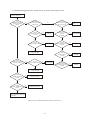
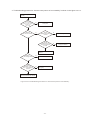
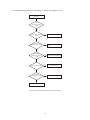
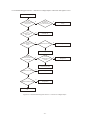
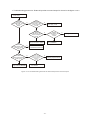
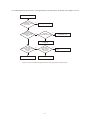
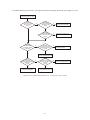
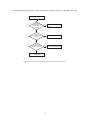
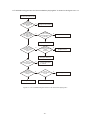
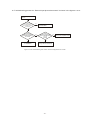
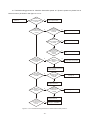
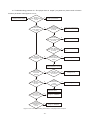
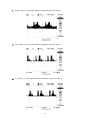
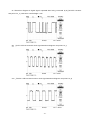
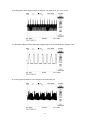
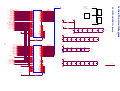
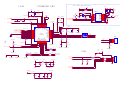
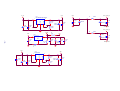
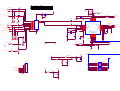
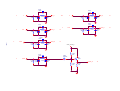
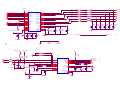
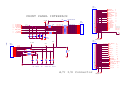
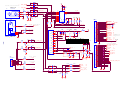
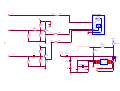
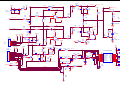
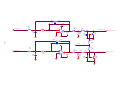
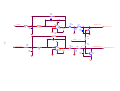
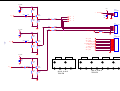
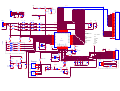
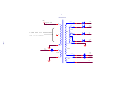
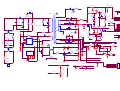
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
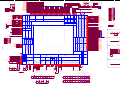
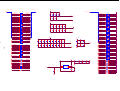
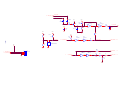
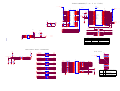
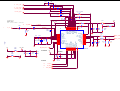
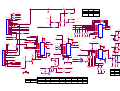
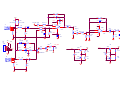
Download service manual DW9918K
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Phone connector (audio) wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic range compression wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Videocassette recorder wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
DW9918K service manual Catalog Chapter One About Maintenance 1.1 Safety precautions 1 1 1.1.1 Power supply 1 1.1.2 Precautions for antistatic 1 1.1.3 Precautions for laser head 1 1.1.4 About placement position 2 1.2 Maintenance method 2 1.2.1 Visualized method 2 1.2.2 Electric resistance method 2 1.2.3 Voltage method 2 1.2.4 Current method 2 1.2.5 Cutting method 2 1.2.6 Element substitution method 3 1.2.7 Comparison method 3 1.3 Required device for maintenance Chapter Two Functions and Operation Instructions 3 4 2.1 Features 4 2.2 BASIC INFORMATION 4 2.2.1 Illustration of the Front Panel 4 2.2.2 Illustration of the Rear Panel 5 2.2.3 Illustration of the VFD 5 2.2.4 Illustration of the Remote Control 6 2.2.5 Accessorles 6 2.3 SYSTEM SETUP 7 2.3.1 Operation Interiace and General Steps 7 2.3.2 General Setup 7 2.3.3 Screen Saver Setup 7 2.3.4 Porgressive /Interlaced Setup 7 2.3.5 SCART Output Setup 8 2.3.6 Video Output Format Setup 8 2.3.7 Restore Factory Settings 8 2.3.8 Playback Settings 8 2.3.9 TV Aspect Ratio 9 2.3.10 Rating Level Setup 9 2.3.11 Digital Audio Output Setup 9 2.3.12 Analog Audio Output Setup 10 2.3.13 Record Setup 10 2.3.14 Auto Chapter Marker Setup 10 2.3.15 Default Input Signal 10 2.3.16 Default Recording Quality Selection 11 2.3.17 Language Setup 11 2.3.18 OSD Language Setup 11 2.3.19 DVD Menu Language Setup 11 2.3.20 DVD Subtitle Language Setup 11 2.3.21 DVD AUDIO Language Setup 12 2.3.22 Channel Tuning 12 2.3.23 Auto Scan Channels 12 2.3.24 Modify channel Information 12 2.3.25 M o d i f y C h a n n e l Information (CONTINUED) 12 2.3.26 Modify Channel Information(CONTINUED) 13 2.3.27 Sort Channel Order 14 2.3.28 System Clock Setup 14 2.3.29 System Clock Setup (CONTINUED) 14 2.4 RECORDING MODE 15 2.4.1 Summarization 15 2.4.2 How to Receive the TV Program 15 2.4.3 Viewing the Input Source 15 2.4.4 Manual Recording 15 2.4.5 Manual Recording (CONTINUED) 16 2.4.6 One Touch Recording (OTR) 17 2.4.7 To Control the DV Camera system will cancel the OTR. 17 2.5 TIMER TASK SETTING 17 2.5.1 Summarization 17 2.5.2 Operation Steps (CONTINUED) 18 2.5.3 Operation Steps (CONTINUED) 19 2.5.4 To Browse the Contents of the Disc and Select one Title to Play 20 2.5.5 Erasing Title 20 2.5.6 Edit Title 20 2.5.7 Rename Title 20 2.5.8 Overwrite Title / Append Title / Overwrite Disc 21 2.6 EDITING MODE 21 2.6.1 Summarization 21 2.6.2 Entering the Editing Mode 21 2.6.3 Menu Explanation 21 2.6.4 Operation Steps 21 2.6.5 Selecting the Title /Chapter to be Edited (CONTINUED) 21 2.6.6 Insert Chapter Marker 22 2.6.7 Hiding / Unhiding Chapter 22 2.6.8 Changing the Index Picture 22 2.6.9 Split Title 22 2.6.10 Exiting the Editing Mode 22 2.7 DISC OPERATION MODE 22 2.7.1 Summarization 22 2.7.2 Entering the Disc Operation Mode 23 2.7.3 Operations 23 2.7.4 Exiting the Disc Operation Mode 23 2.8 PLAYBACK MODE 23 2.8.1 Entering the Playback Mode 23 2.8.2 Playback from the Menu Displayed 24 2.8.3 Playback from the Titles Displayed 24 2.8.4 Ending Playback 24 2.8.5 Playing Mode Control 24 2.8.6 Playing Mode Control (CONTINUED) 25 2.8.7 Playback Process Control 25 2.8.8 Title/Chapter/Track Selection 26 2.8.9 Audio / Subtitle Selection 26 2.8.10 Angle Selection 26 2.8.11 PBC ON/OFF 26 2.8.12 T-Time/Tr-Time Display 26 2.8.13 The Operations of Function Buttons 27 2.8.14 Playing JPEG/MP3/CD/DivX Disc 27 2.8.15 Playback Control Menu 28 2.8.16 Control Wipe Mode when Playing JPEG Disc 28 2.8.17 Control Zoom Mode when Playing JPEG Disc 29 2.8.18 Picture Rotating when Playing JPEG Disc 29 2.9 USB MODE 29 2.9.1 Summarization 29 2.9.2 Operations 29 2.9.3 Exiting the USB mode 29 2.10 SPECIFICATIONS Chapter Three Unit Circuit Principle Section One Principle of the Player 31 33 33 3.1.1 PCB board composition figure and video signal figure 34 3.1.2 Block diagram of the player 35 3.1.3 Introduction to IC used by this player 36 Section Two Unit Circuit Principle 37 3.2.1 System control and code, decode circuit 37 3.2.2 Audio output circuit 39 3.2.3 Video output circuit 42 3.2.4 Audio input circuit 43 3.2.5 Video input circuit 45 3.2.6 Reset circuit 48 3.2.7 IIC bus control circuit 49 3.2.8 Voltage regulating circuit 50 3.2.9 USB jack circuit 52 3.2.10 DV jack circuit 52 3.2.11 Loader jack circuit 53 3.2.12 Control panel 53 3.2.13 AV circuit 55 3.2.14 MIC circuit 60 3.2.15 Power circuit 62 Section Three Servicing Cases 64 3.3.1 Servicing cases 64 3.3.2 Troubleshooting flow chart 70 Section Four Servicing Parameters 84 3.4.1 Signal waveform diagram 84 3.4.2 Key point voltage 97 Section Five Function Introduction to IC 99 3.5.1 function introduction to MT 8602 99 3.5.2 Function introduction to Cd4053 104 3.5.3 function introduction to TSB41AB1 105 3.5.4 function introduction to M13S128168A 110 3.5.5 Function introduction to CD4052 113 3.5.6 function introduction to TVP5150A 114 3.5.7 function introduction to 16316-52 107 3.5.8 function introduction to SN74LVC16373 109 3.5.9 function introduction to MSP 34x5G 121 3.5.10 function introduction to TPS2041A 123 3.5.11 function introduction to Lp2995 125 3.5.12 function introduction to FSDM0565R 125 3.5.13 Function introduction to M41T80 126 3.5.14 function introduction to Em6353 127 3.5.15 function introduction to KA5H0380R 128 3.5.16 function introduction to 74HC/HCT14 129 Chapter Four Disassembly and Assembly Process 130 Chapter Cinque PCB board & Circuit diagram 131 Section One PCB board 131 5.1.1 Surface layer of AV OUT Board 131 5.1.2 Bottom layer of AV OUT Board 132 5.1.3 Surface layer of DECODE&DECODE &SERVO Board 133 5.1.4 Bottom layer of DECODE&SERVO Board 134 5.1.5 Surface layer of KEY SCAN Board 135 5.1.6 Bottom layer of KEY SCAN Board 136 5.1.7 MIC Board 137 5.1.8 POWER Board 138 Section Two circuit diagram 139 5.2.1 MPEG&SERVO Board 139 5.2.2 AV Board 150 5.2.3 DV Board 158 5.2.4 USB Board 159 5.2.5 MIC Board 160 5.2.6 KEY SCAN Board 161 5.2.7 POWER Board 162 Chapter six BOM List 164 Chapter One About Maintenance 1.1 Safety precautions 1.1.1 Power supply When maintenance personnel are repairing DVD players, he should pay special attention to the power board with 220V AC and 330V DC which will cause hurt and damage to persons! 1.1.2 Precautions for antistatic Movement and friction will both bring static electricity which causes serious damages to integrated IC. Though static charge is little, when a limited quantity of electric charge is added to largescaleintegrated IC, as the capacitance is very small in the meantime, now the integrated IC is very much easy to be struck through by static electricity or the performance will decrease. Thus static electricity prevention is of extraordinary importance. The following are several measures to prevent static electricity: 1. Use a piece of electric conduction metal with the length of about 2 metres to insert into the earth, and Fetch the lead wire from the top of the surplus metal and connect to the required static electricity device. The length and depth of the metal embedded under the earth should be determined according to the wettability of the local soil. For humid places, it may be shorter, and longer and deeper for dry places. If possible, it can be distributed and layed in terms of “#” shape. 2. On operating table-board, the antistatic table cushion should be covered and grounded. 3. All devices and equipments should be placed on the antistatic table cushion and grounded. 4. Maintenance personnel should wear antistatic wrist ring which should be grounded. 5. Places around the operating position should also be covered with electric conduction cushion or Painted with antistatic paint. 1.1.3 Precautions for laser head 1. Do not stare at laser head directly, for laser emission will occur when laser head is working, which will Hurt your eyes! 2. Do not use wiping water or alcohol to clean laser head, and you may use cotton swab. -1- 1.1.4 About placement position 1. Never place DVD player in positions with high temperature and humidity. 2. Avoid placing near high magnetic fields, such as loudspeaker or magnet. 3. Positions for placement should be stable and secure. 1.2 Maintenance method 1.2.1 Visualized method Directly view whether abnormalities of collision, lack of element, joint welding, shedding welding, rosin joint, copper foil turning up, lead wire disconnection and elements burning up among pins of elements appear. Check power supply of the machine and then use hands to touch the casing of part of elements and check whether they are hot to judge the trouble spot. You should pay more attention when using this method to check in high voltage parts. 1.2.2 Electric resistance method Set the multimeter in resistance position and test whether the numerical value of resistance of each point in the circuit has difference from the normal value to judge the trouble spot. But in the circuit the tested numerical value of resistance is not accurate, and the tested numerical value of integrated IC's pins can only be used for reference, so the elements should be broken down for test. 1.2.3 Voltage method Voltage method is relatively convenient, quick and accurate. Set the multimeter in voltage position and test power supply voltage of the player and voltage of a certain point to judge the trouble spot according to the tested voltage variation. 1.2.4 Current method Set the multimeter in current position and test current of the player of a certain point to judge the trouble spot. But when testing in current method, the multimeter should be series connected in the circuit, which makes this method too trivial and troublesome, so it is less frequently used in reality. 1.2.5 Cutting method Cutting method should be combined with electric resistance method and voltage method to use. This method is mainly used in phenomena of short circuit and current leakage of the circuit. When cutting the input terminal voltage of a certain level, if voltage of the player rises again, it means that the trouble lies in this level. -2- 1.2.6 Element substitution method When some elements cannot be judged good or bad, substitution method may de adopted directly. 1.2.7 Comparison method A same good PC board is usually used to test the correct voltage and waveform. Compared these data with those tested through fault PC board, the cause of troubles may be found. Through the above maintenance method, theoretical knowledge and maintenance experience, all difficulties and troubles will be readily solved. 1.3 Required device for maintenance Digital oscillograph ( 100MHE) TV set SMD rework station Multimeter Soldering iron Pointed-month pincers Cutting nippers Forceps Electric screw driver Terminals connecting cord Headphone Microphone -3- Chapter Two Functions and Operation Instructions 2.1 Features # Utilizes MPEG- Real-Time encoding and decoding technology, capable of directly recording TV and external program sources on to DVD+R, DVD+ RW discs # Capable of recording your favorite video tapes into DVD # Built-in DV (i. LINK/IEEE1394) input jack enables high fidelity digital recording of digital video camera signals # Progressive scan capable of producing stable and clear pictures without flickering, # Built-in 5.1CH Dolby Digital surround decoder, separate 5.1CH outputs, 2CH Dolby outputs, optical and coaxial outputs for digital audio # 24bit audio DAC capable of producing perfect acoustic fidelity # With normal DVD playback function, capable of playing DVD, SVCD, VCD, CD, MP3, JPEG, DivX DVD+R and DVD+RW discs # Recorded discs playable on normal DVD players # Capable of recording up to 6 hours of video on single-sided discs DVD+R/DVD+RW (4.7GB) # Supports 4 recording modes: HQ, SP, EP, SLP # OTR function enables one-touch recording, convenient to select the length of recording time # Manual/automatic insertion of chapter mark # Features chapter hiding, disc locking to the recorded discs (DVD+RW) and titles renaming # Title index pictures of recorded disc (DVD+RW) are freely selectable # Multi-dubbing, multi-angle, multi-subtitle for selection # Built-in TV tuner with automatic channel scanning # AV input S-Video, DV (i. LINK/IEEE1394) and antenna input conveniently located on both the front and rear panels, to record various program sources # Supports composite video, component/progressive-scan video output terminals and TV antenna output terminals # Built-in USB jack, capable of playing JPEG, MP3 file # Intelligent preset timer recording function makes you won't miss any wonderful programs # Recording and output system supports both PAL/NTSC systems # Wide range of operating power supply: ~100V 240V, 50/60Hz, standby power consumption 3W # Intelligent software upgrading capability # Dual SCART: one for input, another for output # Dual Kara OK function 2.2 BASIC INFORMATION 2.2.1 lllustration of the Front Panel -4- 1 18 19 20 3 2 5 4 6 7 8 16 15 17 9 14 13 12 11 10 1 STANDBY indicator 8 Infrared remote sensor 15 CH+button 2 STANDBY/ON button 9 VFD display window 16 CH- button 3 MICPHONE 1 10 PLAY button 17 USB input terminal 4 MICPHONE 2 11 PAUSE button 18 DV input terminal 5 VOL KNOB 12 STOP button 19 Front AV input terminal 6 Disc tray 13 REC button 20 Open the terminal 7 OPEN/CLOSE button 14 SOURCE button protection cover here # The function of buttons on the front panel is the same with that of the corresponding ones on the remote control. # The input terminals on the front panel can only be seen when the protection cover is opened 2.2.2 Illustration of the Rear Panel . 1 1 2 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 TV TUNER input terminal 7 L/R channel audio output terminal # The antenna cable plug is inserted here 8 COMPOSITE VIDEO out terminal TV TUNER output terminal 9 S-VIDEO output terminal # This terminal is directly connected with the 10 COMPONENT VIDEO output terminal TV TUNER Input Terminal inside this unit 11 COAXIAL output terminal 3 Rear COMPOSITE Video input terminal 12 OPTICAL output terminal 4 Rear S-Video input terminal 13 CVBS/ RGB and audio output terminal 5 L/R channel audio input terminals 14 CVBS and audio input terminal 6 5.1CH output terminals 2.2.3 Illustration of the VFD The look of VFD is shown as the following figure: D REC SVCD MP3 PBC -5- SYSTEM SETUP - GENERAL Screen saver ON Progressive/Interlaced Interlaced SCART output RGB Video output format PAL Restore factory settings General OK Setup General Setup Menu SYSTEM SETUP - GENERAL 1 Screen saver ON 2 Progressive/Interlaced Interlaced SCART output RGB Video output format PAL 3 4 Restore factory settings OK 5 6 General Setup System Setup Menu SYSTEM SETUP - GENERAL Screen saver SCART output ON ON Interlace OFF RGB Video output format PAL Progressive/Interlaced Restore factory settings General Setup OK 4.You can also keep on pressing [IS/PS] button for 3 seconds to perform the Progressive / Interlaced switching. # The value of this setting must accord with the scanning mode of the TV, otherwise the TV screen will display Nothing. # If nothing is shown on the TV screen, you may try to keep on pressing [IS/PS] button for 3 seconds. # To avoid instability of output signal, please don't perform Progressive/Interlace function by component(Y,Cb/Pb, Cr/Pr) terminal on the rear panel when "SCART output" item is RGB. requirements. 3.Press [SELECT] button, and then the system will switch the output format to what you select right now. # You can switch the TV output format by pressing the [PAL/NTSC] button too. # Changing the output format may cause no picture on the TV screen. If this happens, you can press [PAL/NTSC] button to restore the output format. SYSTEM SETUP - GENERAL Screen saver ON Progressive/Interlaced Interlaced SCART output RGB Video output format PAL NTSC PAL Restore factory settings SYSTEM SETUP - GENERAL General Screen saver ON Progressive/Interlaced Interlaced Progressive YCbCr Interlaced PAL SCART output Video output format Restore factory settings 2.3.7 Restore Factory Settings OK 1.Select "Restore factory setting" by [5], [6]buttons in the general setup menu, then press[SELECT] button, and the TV screen displays: 2.Highlight "OK" in the menu by [3], [4] buttons. 3.Press [SELECT] button to make all setup items restore the factory settings. # When your unit is in abnormal working mode, it is probably caused by your wrong setup. Please try the "Restore Factory Settings" operation to make it work normally. 2.3.5 SCART Output Setup 1.In general setup menu, highlight "SCART output ", and press [SELECT] button, and then a list will appear. 2.Select "YCbCr" or "RGB" in the list. # When using component video output, please select "YCbCr". # When using SCART output, you may select according to the fact .But you had better select the "RGB". # This setup does not affect the composite video output. 3.Press [SELECT] button to confirm. ! Restore factory settings System will reset all the setup items to the default values, OK to confirm, Cancel to exit. Ok Interlaced SCART output RGB YCbCr Germany France RGB Restore factory settings 1.Display the system setup control menu. 2.Move the cursor by [5],[6] buttons to select “ " item . 3.Press [SELECT] button to enter the playback setup mode. The right figure is the main menu of playback setup. ON Progressive/Interlaced Video output format Cancel 2.3.8 Playback Settings SYSTEM SETUP - GENERAL Screen saver Setup OK 2.3.6 Video Output Format Setup SYSTEM SETUP - PLAYBACK This unit has two video output systems: PAL and NTSC . You can select one of them according to your TV set specs. 1.Highlight "Video output format" in the general setup menu and press [SELECT] button. A pop-up menu will appear. 2.Select the proper option according to factual TV aspect ratio Letter Box Rating level OFF Digital audio output RAW Analog audio output 5.1 CH the main menu of playback setup -8- 2.Input the password and press [SELECT] button.If the password is right, the TV screen displays the window shown as the right figure.The super password is 3308. 2.3.9 TV Aspect Ratio 1.In the playback setup menu, select item "TV aspect ratio" by[5], [6] buttons, press [SELECT] button and then the value list will appear, which is shown as the right figure. 2.Select the suitable value by using [5], [6] buttons, and then press [SELECT] button. # The meaning of each value to be selected of this item is as follows: # 16 : 9: Applicable to wide screen TV set. # Pan Scan: Suitable for the common size TV set. When playing wide screen pictures, left and right edges of the original pictures are cut off. The picture will be displayed to full screen. # Letter Box: Suitable for the common size TV set. When playing wide screen pictures, black banners will appear on the top and bottom of the TV set. 3.Press [RETURN] button to return to the previous menu and proceed other settings. Set Rating Level OFF New password Digital audio output Letter Box 16:9 Pan Scan Letter Box RAW Analog audio output 5.1 CH Rating level NEW 3.Select "Set rating level" , and press [SELECT] button to display the pop-up list which is shown Set Rating Level OFF OK OFF English 8: Adult NEW 4.Select the rating level by [5], [6] buttons and press [SELECT] button to confirm. 5.If you do not want to change the original password, highlight the "OK" in the menu through cursor buttons and then press [SELECT] button. 6.To change the password, please highlight the "New" in the above figure and press [SELECT] button. Now the TV screen will display: SYSTEM SETUP - PLAYBACK TV aspect ratio OK New Password Notes New password OK Confirm password # The playback effect is related to the playing disc.If a disc is recorded in the aspect ratio of 4:3, the ratio can only be 4:3, no matter which screen setting you select. # This setting should conform to the aspect ratio of the TV set. 7.Select "New password" by the cursor buttons and input the new password by number buttons. 8.Select "Confirm password" by the cursor buttons and input this password again by number buttons. # The input password in the "New password " must accord with that in the "Confirm password". 9.Highlight "OK" by cursor buttons and then press [SELECT] button. # After setting the rating level, when playing the disc with the rating level higher than what you have set, you must input the password. # If you forget the password, you may input the super password. 2.3.10 Rating Level Setup By setting this unit's authorization rating and password, some discs with control grade cannot be played without inputting the password. In this way, you can confine the children to watch the disc unsuitable to them. 1.In the playback setup menu, move the cursor upand down by [5] , [6] buttons to select the item "Rating level", and then press [SELECT] button. The TV screen displays: 2.3.11 Digital Audio Output Setup Enter Password OK Cancel This unit has digital audio output jacks. So you can enjoy the higher quality audio with an amplifier with digital audio decoders. Cancel -9- 1.Access the playback setup menu. Select item “Digital audio output" by [5], [6]buttons, and then press [SELECT] button. A list will pop up: 2.Select the proper value by [5], [6] # RAW :This unit doesn't perform # LPCM: This unit performs decoding # If the TV screen displays " ", when pressing [5]/[6]button, it may indicate that the current activated menu will not be the system setup control menu. Please press [RETURN] button once or more to activate the system setup control menu. 2.3.14 Auto Chapter Marker Setup SYSTEM SETUP - PLAYBACK TV aspect ratio Letter Box Rating level OFF Digital audio output RAW RAW OFF LPCM Analog audio output 2.3.12 Setup 1.In the record setup menu, select item "Auto chapter marker" by [5], [6] buttons, press [SELECT] button, and then a pop-up menu will appear: 2.Select the proper value by [5], [6] buttons, and then press [SELECT] button to confirm. # This setup is used to make sure whether insert the chapter marker automatically when recording. # If you don't set this item to "OFF", the recorded contents will be automatically divided into some chapters with the same length according to the interval time you`ve selected. Analog Audio Output This setting is used to select an analog audio output format between 2CH analog mix audio output and Dolby 5.1 CH analog output. 1.Select "Analog audio output" item by [5], [6] buttons, and press [SELECT] button, then a pop-up list will appear: 2.Select the desired value by [5], [6] buttons then press [SELECT] button to confirm. SYSTEM SETUP - RECORD Auto chapter marker Default source 5 minutes 5 minutes Tuner 10 minutes Default quality SP SYSTEM SETUP - PLAYBACK TV aspect ratio Letter Box Rating level OFF Digital audio output RAW Analog audio output 5.1 CH 5.1 CH 2 CH 2.3.15 Default Input Signal Sources Selection 1.In the record setup menu, select "Default source" by [5], [6] buttons and press [SELECT] button, then a pop-up menu will appear: 2.Select the desired value by [5], [6] buttons and then press [SELECT] button. 2.3.13 Record Setup After finishing the settings introduced in this chapter, when recording, the values you set will become the default values of the correlative items. 1.In the system setup control menu, select item " " by [5], [6] buttons and then press [SELECT] button to enter record setup menu. The screen displays: SYSTEM SETUP - RECORD Auto chapter marker 5 minutes Default source Tuner Default quality DV SP SCART Tuner SYSTEM SETUP - RECORD Auto chapter marker 5 minutes Default source Tuner Default quality SP # There are several groups of input source ports. Please refer to the "Basic Information Illustration of the Front/Rear Panel " for their position on the unit. # Front CVBS: Front panel composite video and audio inputs. the record setup menu Note - 10 - # Rear CVBS: Rear panel composite video and audio inputs. # Rear S-VIDEO: Rear panel S-video and audio inputs. # DV: Front panel DV input. # SCART: Rear panel CVBS and audio inputs. # TUNER: Rear panel TV tuner input. 2.3.16 Default Recording Quality Selection 1.In the record setup menu, select item "Default quality" by [5], [6] buttons, press [SELECT] button, and then a list menu will appear. 2.Select the desired value by [5], [6] buttons, and then press [SELECT] button. # Please refer to the "TERMS" for the four different recording qualities: SP, SLP, EP, HQ. SYSTEM SETUP - LANGUAGE OSD language Menu language Audio language 5 minutes Default source Tuner Default quality SP English 2.3.19 DVD Menu Language Setup 1.In language setup menu, select item "Menu language" by [5], [6] buttons, press [SELECT] button, and then a list will pop up, which is shown as the following figure. 2.Select your desired language by [5],[6] buttons, and then press [SELECT]button. # If you play the DVD discs that support the selected language, the system will adopt this language as the DVD menu Language. # If the disc does not support the selected language, the system will use the language supported by the disc. SYSTEM SETUP - RECORD Auto chapter marker English English Russian Subtitle language HQ SP EP SLP SYSTEM SETUP - LANGUAGE OSD language English Menu language English Subtitle language English OFF Audio language D anish English Chinese 2.3.17 Language Setup To meet the needs of consumers in different regions, this unit is equipped with many kinds of operation interface languages for your selection. 1.Enter the system setup mode. 2.In the system setup control bar, move the cursor by [5], [6] buttons. Select item “ ", and then press [SELECT] button to enter the language setup menu. The screen displays: 2.3.20 Setup Some DVD discs have many kinds of subtitle languages and this setup is used to set the default DVD subtitle language. 1.In the language setup menu, select item "Subtitle language" by [5], [6] buttons, press [SELECT] button, and then a list will pop up, which is shown as the following figure: 2.Select your desired language by [5], [6] buttons, and then press [SELECT] . # "OFF" means closing the subtitle output. # The system will select this setup language as the DVD subtitle language preferentially. If the DVD discs you select do not support this language, this setup is invalid. # You may change the subtitle language at random when playing. Please refer to "Playback mode" for details. SYSTEM SETUP - LANGUAGE OSD language English Menu language English Subtitle language OFF Audio language English DVD Subtitle Language the language setup menu 2.3.18 OSD Language Setup 1.In the language setup menu, select item "OSD language" by [5], [6] buttons, press [SELECT] button, and then a list will pop up, which is shown as the following figure: 2.Select your desired language by [5], [6] buttons, press [SELECT] button to confirm, and then the OSD language will change correspondingly. SYSTEM SETUP - LANGUAGE OSD language English Menu language English Subtitle language OFF OFF English English Chinese Audio language - 11 - 2.3.21 Setup DVD AUDIO Language 2.3.23 Auto Scan Channels 1.Highlight item "Scan channels", and press [SELECT] button to start channel scanning. # You can press [STOP] button to stop the scanning during the operation. If do so, the channel information having been obtained during scanning can also be saved. # When scanning a channel, the TV will show the image of this channel's program. 1.In the language setup menu, select item "Audio language" by [5], [6] buttons, press [SELECT] button, and then a list menu will pop up, which is shown as the following figure. 2.Select your desired language by [5], [6] buttons, and then press [SELECT] button. # The system will use the setup language as the D V D o u t p u t l a n g u a g e p r e f e r e n t i a l l y. If the disc dose not support this setup,the setup is invalid. # When playing DVD discs, you may change the output language at random. Please refer to "Playback Mode" for details. Note # Before the channel scan operation, you must connect the system properly to ensure the TV signals can enter the system through the "TV TUNER input" jack. Please refer to "System Connection-System Connection of Recording External Signals" for the connection illustration. SYSTEM SETUP - LANGUAGE OSD language English Menu language English Subtitle language OFF Audio language English English Chinese Danish 2.3.24 Modify channel Information Here, you can name the channel after the corresponding program's name or any other name you like, sort the channel order to access the special channel easily, tune the channel finely, and scan the channel manually. You can manage the channels more easily, and make this unit receive the TV signal better by these operations introduced in this section. 1.Highlight item "Modify channel information" in "SYSTEM SETUP-CHANNEL SCAN"menu, and press [SELECT] button, then the "Channel Edit" menu will appear, as shown in the right figure: this unit have not scanned some # If programs,the "Channel Edit"menu can not be displayed. 2.Select the desired channel to modify by pressing [CH+] / [CH-] button. Notes # About the DVD language setup introduced in this chapter, some discs have not the language you set, so the setup will be invalid. When playing, the relative languages are the corresponding ones provided by the discs. # For some DVD discs, when playing, it will display the language selection menu. If you perform the selection in it, the corresponding setup of this unit will be invalid, and the relative languages are the ones you select. 2.3.22 Channel Tuning This unit is equipped with a TV tuner, by which you can receive TV signals. Before receiving TV signals, you must proceed tuning operation . The result of the operation will be saved and will not be lost after this unit is switched off.This operation can tune this unit automatically to receive the TV programs. 1.In the System Setup Control menu , highlight item " " by [5], [6] buttons . 2.Press [SELECT] button, then the SYSTEM SETUP-CHANNEL SCAN menu will appear, as shown in the following figure. CHANNEL EDIT Name Frequency TV system NICAM Audio Skip Scan channels OK EDIT SORT Cancel 2.3.25 Modify Channel Information (CONTINUED) SCAN Sort channel order 328.27MHz PAL I ON DUAL A NO Fine tune SYSTEM SETUP - CHANNEL SCAN Modify channel information P001/Ch001 3.Change the Channel name: Highlight the "Name"item, press [SELECT] button, and then the right window of the same line will become input status shown as the following figure. - 12 - Move the cursor toa character by [3], [4] buttons, and then change the character by [5], [6] buttons. When finishing changing all the characters, press [SELECT] button to confirm. TV program, press [SELECT] button, then the TV program signal shall be correlated with the current channel number & name, that is the current channel number & name represents this TV program. 6.Skip a channel: Highlight the item "skip", and press [SELECT] button to display the drop down list. Select" YES" or "NO", and then press [SELECT] button to confirm. # If you select "YES", and when receiving TV programs, this channel can not be received, as if it does not exist. 7.Channel Fine Tuning: Highlight item "Fine tune" in the "Channel Edit" menu. Then you can start fine tuning the channel. # After finishing the channel scanning, maybe some channels' frequency is not adjusted to right value. In this way, when watching these channels, the image and sound will be misty. Then you should perform channel fine tuning to right adjust these channels' frequency. CHANNEL EDIT Name Ch001 Frequency TV system NICAM Audio 328.27MHz PAL I ON DUAL A NO Skip Fine tune Cancel OK # The changing sequence of the character when pressing [5] button is as following: 0,1,2, 9 A,B,C, Z a,b,c, z # When pressing [6] button the sequence is reverse. 4.Change TV system: Highlight the item "TV system",and press [SELECT] button to display the drop down list. Select proper value , and then press [SELECT] button to confirm. # The value of the TV system must match the received TV signal. If it is not right, the system will not receive the program's sound signal. So you should select the right value. 5.Manual Scan Channels: A.Select a channel number by pressing [CH+], [CH-] buttons. B.According to the demands of the local TV system, set items "TV system" by the methods described in step 4 . C.Highlight "Frequency" item in the "Channel Edit" menu by [5],[6] buttons, and press [3]/[4] button, then the system shall start scanning channels. # If you press [4] button, the system shall forward scan channels from the current frequency. # If you press [3] button, the system shall backward scan channels from the current frequency. # When encountering a channel with TV program, the scanning will stop. 2.3.26 Modify Channel Information(CONTINUED) # Pressing [3] button once can decrease the frequency. # Pressing [4] button once can increase the frequency. # When changing the frequency, the definition of the image or sound will be changed correspondingly, then from this, you can know the effect of the fine tuning. 8.Close/Open NICAM functions: Highlight the item "NICAM" , and press [SELECT] button to display the drop down list. Select "ON" or "OFF" from the list, and then press [SELECT] button to confirm. # The so-called NICAM functions include stereo function and dual dubbings function. When "NICAM" item is "ON", if the received TV program supports stereo function, this unit will output the stereo dubbing; on the other hand, if the received TV program supports dual dubbings function, you can select one of the two dubbings as output by item "System Setup-Channel Scan- Channel audio language" . Of course , if you set "NICAM" to "OFF"or receive TV program without NICAM function, the above functions are invalid. 9.Switch channel audio language:when receiving the TV programs supporting dual dubbings functions, you can select one of the two dubbings as output by this item. CHANNEL EDIT Name Frequency TV system NICAM Audio Skip Fine tune OK P001/Ch001 328.27MHz PAL I ON DUAL A NO Cancel D.When the scanning ending ,that is, encountering a channel with - 13 - A.Highlight item "Audio"in the "Channel Edit"menu, and then press [SELECT] button to pop up a submenu list. B.Select "DUAL A" or "DUAL B " in the list, and then press [SELECT] button to confirm. button to select the right position where you want to insert this channel. 4.Press [SELECT] button to insert the channel name to the selected position in the left list window, as shown in the right figure. 5.Press [RETURN] button to return to the previous menu and proceed other settings. CHANNEL EDIT Name Frequency TV system NICAM Audio Skip Fine tune OK P001/Ch001 328.27MHz PAL I ON DUAL A DUAL A OFF DUAL B NO CHANNEL SORT P010 P011 P012 P013 P014 P006 P015 P016 P017 Cancel # You must open the NICAM function first, otherwise this function will be invalid. Please refer to step 8 in section " Modify Channel Information " to open the NICAM function. # The value "DUAL A" or "DUAL B"stands for one of the two dubbings. If the received TV program can not support dual dubbing function, the above operations shall not influence the output dubbing. # You can select "DUAL A" or "DUAL B" by [AUDIO] button in the remote control when not in "CHANNEL EDIT" menu. Ch010 Ch011 Ch012 Ch013 Ch014 Ch006 Ch015 Ch016 Ch017 Unskip Unskip Unskip Unskip Unskip Unskip Unskip Unskip Unskip After pressing the [SELECT] button, this channel name is moved to this position. P006 Ch006 Unskip Before pressing the [SELECT] button, the channel name is in here. 2.3.28 System Clock Setup 1.Enter the system setup mode. 2.In the system setup control menu, move the cursor to select item " " by [5], [6] buttons, and then press [SELECT] button, so the TV screen will display the time setup window, which is shown as the right figure. SYSTEM SETUP - CLOCK Date(dd/mm/yy) 01/01/01 Time(hh:mm:ss) 12:17:14 2.3.27 Sort Channel Order 1.Highlight item "Sort channel order",and press [SELECT] button, then a corresponding menu will appear, as shown in the right figure. this unit has not scanned some # If programs,the "Sort channel order"menu can not beDisplayed. 2.3.29 System Clock Setup (CONTINUED) 3.Select item "Date (dd /mm / yy)" and make it in input mode. Highlight a number by [3], [4] buttons, and change it by [5],[6]buttons. After inputting the date by sequence of "date/ month/year",press [SELECT] to confirm. CHANNEL SORT P000 P001 P002 P003 P004 P005 P006 P007 P008 Ch000 Ch001 Ch002 Ch003 Ch004 Ch005 Ch006 Ch007 Ch008 Unskip Unskip Unskip Unskip Unskip Unskip Unskip Unskip Unskip SYSTEM SETUP - CLOCK 2.Highlight the desired channel in the left list window by cursor buttons, and press [SELECT] button, then the channel name will appear in the right list window, shown as the right figure. Ch000 Ch001 Ch002 Ch003 Ch004 Ch005 Ch006 Ch007 Ch008 Unskip Unskip Unskip Unskip Unskip Unskip Unskip Unskip Unskip 01/01/01 Time(hh:mm:ss) 12:17:14 4.Select item "Time (hh: mm: ss)" and make it in input mode. Highlight a number by [3],[ 4] buttons, and change it by [5],[6]buttons. After inputting the time by sequence of "hh:mm:ss",press [SELECT] to confirm. CHANNEL SORT P000 P001 P002 P003 P004 P005 P006 P007 P008 Date(dd/mm/yy) SYSTEM SETUP - CLOCK P006 Ch006 Unskip 3.Move the channel name up and down by [5],[6] - 14 - Date(dd/mm/yy) 01/01/01 Time(hh:mm:ss) 12:17:14 # The correct setup of system clock is the precondition of time recording. Make the source equipment work properly, and let it output the signal intended for recording. 2.There are three ways for selecting the signal to view. A.Pressing [SOURCE] button can directly view the external signals one by one. The sequence of viewing the external signal is shown in the following. 2.4 RECORDING MODE 2.4.1 Summarization This unit has various external input signal terminals including S-video input, composite video input, TV tuner input, DV input , SCART input and stereo audio input. You can record any group of these video and audio input signals. The recordable discs of this unit are DVD+RW and DVD+R. There are four recording qualities to be selected,including SLP (about 6 hours), EP (about 4 hours), SP (about 2 hours) and HQ (about 1 hour). This unit also incorporates time recording function with which you can prepare a record schedule before-hand and it will record your desired programs according to the schedule on time. 2.4.2 Program Playback MODE Front CVBS TV INPUT Rear CVBS Rear S-VIDEO DV SCART B.When this unit is playing a title of a DVD+RW disc, after pressing [SOURCE] button, a warning message window will appear as shown in the following figure . Please press [SELECT] button, and then select the signal you want by method in point a OverWrite!!! Overwriting from current point if you select Overwrite mode to record! How to Receive the TV 1.Connect the system according to the figure shown in section "System Connections Connecting to the TV set". 2.Connect the power plugs of the TV and this unit to the outlet. 3.Switch the TV set to AV mode, and turn on this unit by pressing the [STANDBY/ON] button . 4.Press the [SETUP] button to enter the System Setup mode, and then perform the Channel Scanning and Channel Fine Tuning according to the steps introduced in chapter" System Setup - Channel Tuning" .After finishing, please press [SETUP] button to exit setup mode. # Before receiving TV programs for the first time, you must do this step, this unit will save corresponding information after you have done it . 5.According to the method described in section "Viewing the Input Source",select the TV input source to view. 6.Press [CH+]/[CH-] to switch the TV program. C.Press [NAVIGATION] button once or twice to display the record control menu. Select "SOURCE" item by [5], [6] button , then press [SELECT] button to display the source drop down list as shown in the following figure . Select the desired source from the list, and press [SELECT] button, then the TV screen will show the corresponding picture. RECORD (DVD+RW) MODE New Title SOURCE Front CVBS Front CVBS QUALITY SP Rear CVBS TRICK Stop TITLE 01/01 CHAPTER 01 TIME Rear S-VIDEO DV SCART The source drop down list 0:01:55/1:24:21 Record control menu Notes # In the above three ways , if the system displays " " , it means viewing the input source can not be realized in the current mode , so please press [RETURN] button once or more times to quit the current mode, then perform the corresponding operations again. # When the unit is recording ,if you want to view the external signals , you must stop the recording first. 2.4.3 Viewing the Input Source You can let the input source signal be shown directly on the TV screen. By this function you can get a preview of the external signals for more rightly selecting the desired signal. 1.Please connect the system according to "System Connections-System Connection of Recording External Signals" . 2.4.4 Manual Recording The following figure shows the construction of the menu in recording mode. - 15 - The last three items can not be controlled in this mode, but you can learn some information by them. Please follow the following steps to finish a recording task. Button before the recording stops automatically, the remanent part of the current title will turn into another new title. Overwrite disc:When you perform this order by method a as follow , this unit will overwrite the disc from current point as a new title. In this situation , the recording won't stop until you press [STOP] button. If an existed title doesn't be overwritten totally after you press [STOP] button, the remanent of the current title will turn into another new title .When you perform this order by method b as follow, this unit will overwrite the disc from the beginning of the current title. In this situation , the recording won't stop until you press [STOP] button. If an existed title doesn't be overwritten totally after you press [STOP] button , the remanent of the current title will turn into another new title . New Title Append title RECORD (DVD+RW) MODE New Title SOURCE Front CVBS QUALITY SP TRICK Stop TITLE 01/01 CHAPTER 01 TIME 0:01:55/1:24:21 Overwrite title Overwrite disc mode list of recording Front CVBS Rear CVBS Rear S-VIDEO DV SCART Tuner source list HQ SP EP SLP recording quality list Stop Pause Record recording process control item list the menu construction in recording mode 1.Make sure an unfinalized DVD+R or DVD+RW disc has been in the disc tray. 2.Select the desired external signal source to be recorded according to the way in section "Viewing the Input Source". 3.Press [NAVIGATION] button to display the record control menu . 4.Refer to the menu construction figure, rightly set the values of "MODE" and "QUALITY". You can refer to following contents to realize this step. # Highlight the desired menu item by [5], [6] buttons, pop out the submenu by [4] or [SELECT] button, and confirm by [SELECT] button. # Meanings of some values in the submenu are as follow: Notes # In some situations , "Overwrite title" and "Overwrite disc" may be invalid . To make it valid , there are two ways as follow: A.When selecting the desired external signal 5 source in step 2 described above , make sure that the Step b in section "Viewing the Input Source" has been done. Then please perform steps 3 , 4 and 5 . B.After the unit has read an unempty DVD+RW disc , select an unempty title by [5],[6] button then press [4] button to display the control menu . From it ,select "Overwrite title "or "Overwrite disc " item by [5],[6] button and press [SELECT] button to confirm. Then please perform steps 3 , 4 and 5 SOURCE Front CVBS : Front panel composite Videoand audio inputs Rear CVBS : Rear panel composite video And audio inputs Rear S-VIDEO : Rear panel S-video and audio Inputs DV : Front panel DV input SCART : Rear panel CVBS and audio Inputs Tuner : Rear panel TV turner input, please select the TV program By [CH+],[CH-] buttons. 2.4.5 Manual Recording (CONTINUED) MODE New title: Add a new title when recording. Append title: Append the recording content to the last title, and does not add a new title. Overwrite title: When you perform this order by method as follow , this unit will overwrite the current title from current point as a new title .In this situation, the recording will stop automatically when meeting the end of the current title .If you press [STOP] button before the recording stops automatically, the remanent part of the current title will turn into another new title.When you perform this order by method as follow, this unit will overwrite the current title from the beginning of the current title , and the recording will stop automatically when meeting the end of the current title. If you press [STOP] Notes # The source value must match the port through which the external source signal is inputted. - 16 - QUALITY HQ: perfect quality, a single-side DVD disc can record about one hour program. SP: standard play, a single-side DVD disc can record about two hours program. EP: extend play, a single-side DVD disc can record about four hours program. SLP: standard long play, a single-side DVD disc can record about six hours program. YRICK Stop : Stop the recording Pause : Pause the recording Record : Start recording 5.After finishing the steps described above, please set item "TRICK" to "Record" ,then press [SELECT]button to start recording . While recording , you can pause or stop recording by setting item "TRICK" to the corresponding value. Certainly , you can more conveniently realize these control by pressing [RECORD], [PAUSE] and [STOP] buttons. hand , if the unit is not in recording mode, this unit can not be influenced and the DV will stop. # This operation can make the recording control bar disappear. 3.Pressing the [PLAY] button doesn't influence this unit, but can make the DV switch to normal playback.When pressing [PAUSE / STEP] button, if this unit is in recording mode, the recording will pause and the DV can not be influenced; on the other hand, if the unit is not in recording mode, it can not be influenced and the DV will pause. # This operation can make the recording control bar disappear. 5.When pressing the [REW] button, the DV will play fast backward. If this unit is in recording mode, the recording will pause. # This operation can make the recording control bar disappear. 6.When pressing the [FWD] button, the DV will play fast forward. If this unit is in recording mode, the recording will pause. # his operation can make the recording control bar disappear. 2.4.6 One Touch Recording (OTR) This function can make you set the end time of the recording.When the time is up,the recording will stop automatically. 1.Enter the recording mode and start recording. 2.According to the desired time, press the [RECORD] button once or more. # Pressing [RECORD] button once, the length of the recording time will extend for 15 minutes ( 60minutes)or 30 minutes(>60minutes). If it exceeds the disc recordable time, the system will cancel OTR function and switch to normal recording mode. # If the OTR process is paused or stopped, the system will cancel the OTR. Notes # Do not shake this unit or unplug it when recording. # A finalized DVD+R disc cannot be used to record. # If you want to play the recorded disc in normal player, you should perform the operation of Finalizing or Making Compatible. Please refer to "Disc Operation" for details. 2.5 MODE 2.4.7 To Control the DV Camera Recorder by this Unit TIMER TASK SETTING 2.5.1 Summarization This function can make this unit record automatically according to the preset requirements when the preset timeis coming. And it will resume the original mode after finishing the recording.To carry out this function. You should set down a record schedule first and then finish the configuring of the system according to the requirements on the schedule. If you are busy and unwilling to miss any wonderful program, this unit can satisfy your requirements. Operation Steps 1.Press the [TIMER] button to display the record scheduler menu shown as the following figure. This unit may control the DV camera recorder through the 1394 serial interface, that is, when using DV as input source, you may fulfill the operations of playback ,pause, etc. to the DV through the remote control of this unit. 1.Properly connect the DV (Please refer to "System Connection of Recording External Signals" for details) and make it work normally. Then set the "Source" item in the control menu bar of this unit to "DV". 2.When pressing the [STOP] button, if this unit is in recording mode, the recording will stop and the DV can not be influenced, on the other - 17 - # Highlighting any non-empty note by cursor buttons, and then pressing [ADD/CLEAR] button, can delete it. 5.Setting recording date You can perform this setting at the third row in the "Item Editor". Move the cursor to select this rowand press [SELECT] button, then a list will pop up. It is shown as follows: # From this illustration, we can learn that this pop up list has six options. Their meanings are as follows: # ONCE: record at a certain time # DAILY: record once per day # WEEKLY: record once per week # Mon~Fri: record once per day from Monday to Friday # Mon~Sat: record once per day from Monday to Saturday # Sat~Sun: record once per day from Saturday to Sunday Record scheduler Quality Source Date Start End 1 2 3 4 5 6 2.Press [SELECT] button ,then the TV screen will display the Item Editor window as shown in the following figure. # Performing the relative setting in this Item Editor window can make a record Scheduler. Item Editor Source Front CVBS Quality SP Mode Once Date 02/09/04 Start 01:48 02:18 End OK Item Editor Cancel the Item Editor window 3.Setting the input source:Press [SELECT] button to display the drop down list, then select the right item from the list by [5],[6] buttons. At last, press [SELECT] button to confirm. # Please refer to "System Setup -Record Settings - Default Input Signal Sources Selection " for the values of the " Source" Item. # For example, if you want to record the Ch003 TV program, you may set the value of the Source item to Ch003. Front CVBS Quality Front CVBS Rear CVBS Rear S-VIDEO SCART Mode Date Start End SP Mode Once Date Once Start 0 1/01/04 Daily 0 2:18 End Weekly 02:18 End OK Cancel A.If you select "ONCE", after confirming by [SELECT] button, move cursor by[6] button and press[SELECT] button to make the next row into input mode, then input the date in sequence of "date/month/year" . Finally press [SELECT] button to Confirm. # When the date input window is in input mode, you can select a number by [3], [4]buttons ,then press [5]/[6] button to change it . Item Editor 01:48 02:18 OK Front CVBS Quality Start Item Editor Source Source Cancel Source Front CVBS Quality SP Mode 2.5.2 Operation Steps (CONTINUED) Once Date 0 1/01/04 Start 01:48 02:18 End OK Highlight "Quality" item by [5],[6]buttons, and press [SELECT] button to display the drop down list, select the right value from the list, and then press [SELECT] button to confirm. # As for the recording quality, please refer to "Basic Information -Terms" for details. Cancel B.If you select "DAILY"/"Mon~Fri"/"Mon~Sat"/ “Sat~Sun", you only need to press [SELECT] button to confirm. And then the TV screen will display the following figure. Item Editor Item Editor Source Front CVBS Front CVBS Quality SP Quality SP Mode Mode HQ Once SP 0 1/01/04 EP 02:18 SLP Date Everday Start 01:48 Source Date Start OK 02:18 End 02:18 End OK Cancel - 18 - Daily Cancel C.If you select "WEEKLY", after confirming by [SELECT] button, move cursor by [6] button and press [SELECT] button to display the weekday list, then select what you need from the list. well set, please highlight the "OK" button in the "Item Editor" , and press [SELECT] button to finish the setup. 9.Set another timer recording task or press [TIMER] button to quit the record schedule menu. 10.After finishing setting the recording schedule, collocate the system according to the requirements in the recording schedule and make this unit in standby or working mode. # In 3 minutes before recording, if the unit is working normally, a message dialogue will appear to require whether it starts to record. If the recording conditions are satisfied, please highlight the "OK" button on the dialogue and press [SELECT] button to confirm. # If this dialogue is not managed, the system will think you are agree to record. After a moment, it will start recording. # If the system is in standby mode, it will automatically switch on and enter the recording mode in about 1 minutes before recording, and then start recording. # After the recording is finished, the system automatically enters the standby mode. Item Editor Source Quality Front CVBS SP Mode Weekly Date Saturday Start Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday OFF End OK 2.5.3 Operation Steps (CONTINUED) 6.Setting the start time of recording.Select the "Start" item by [5], [6] buttons in the "Item Editor" and press [SELECT] button to make it in input mode, as shown in the right figure. Input the time between 00:00~23:59 by number buttons, then press [SELECT] button to confirm. # Highlighting a number by [3], [4] buttons, and then pressing[5], [6] buttons can change the number. Item Editor Source Front CVBS Quality SP Mode Once Date 02/09/04 Start 01:48 02:18 End OK Notes # This unit can't perform two or more timer record tasks at the same time. # Before timer recording, you must set the system time & date (refer to "System SetupSystem Clock Setup" for details) properly, otherwise, this function introduced in this chapter will not be implemented. # The system must be properly collocated to fulfill the schedule recording task. # Do not use the finalized DVD+R disc. After finishing recording a DVD+RW/ DVD +R disc, you may play it in this unit, then you can do some operations on it to make it more easy to use. When loading this disc, the TV screen will display the following picture. Each little icon in the picture stands for a title, the right words and numbers indicate some information of the title. Their meanings are as follows: a.Title name, and "Title" is the default name. b.The date of recording this title. c.The time of recording this title D.The record quality and length of the title The following descriptions will tell you how to do when meeting this picture. Cancel 7.Setting the end time of recording. The operation is similar to that in step 6 . # The meaning of this setting is that when the finish time is up, the recording will be over and the unit will resume to the original mode before recording. # If the record time (from the start time to the End time) is too long,an error message window will appear on the button of the screen, and you can not perform the following steps. And then you need to set the "Start" time and "End" time again. Item Editor Source Front CVBS Quality SP Mode Once Date 02/09/04 Start 01:48 02:18 End OK Cancel 8.After every parameter of the time recording is - 19 - Play title Edit title 1.TITLE 01/01/2000 03:25:02 SP 00:01:04 Rename title Erase title Overwrite title 2.TITLE 01/01/2000 03:25:02 SP 00:03:42 Overwrite disc Append title 3.TITLE 01/01/2000 03:25:02 SP 01:28:28 2.5.7 Rename Title 1.Highlight a title icon you want to rename in the Title List and press [4] button, then a menu will pop up as shown in the right figure. The start picture when playing DVD+R/RW disc recorded by this unit (Title list ) 2.5.4 To Browse the Contents of the Disc and Select one Title to Play Play title 1.Roll up and down the title list picture by [5], [6] buttons to browse all the titles. 2.Highlight a title icon you desire to play by [5], [6] buttons, then press [SELECT] button to play it. 3.During playing, you can press [TITLE] button to switch the TV screen picture to Title List to select another title to play. Erase title Edit title Rename title Overwrite title Overwrite disc Append title 2.Highlight "Rename title" item, and press [SELECT] button, then a key board menu will pop up. Title name: 2.5.5 Erasing Title TITLE _ 1.Highlight a title icon you want to delete in the Title List picture and press [4] button, then a menu will pop up as shown in the right figure. 2.Highlight "Erase title" item, and press [SELECT] button, then the system will erase this title. A B C D E F G H I J K 0 1 2 L M N O P Q R S T U V 3 4 5 W X Y Z ( ) - : ? . 6 7 8 Space Caps BkSp Delete Clear Exit 9 OK the key board menu The meanings and operations of the controller in the key board menu are as follows: # Title Name Editing window # Characters area: select a certain key in this area by using cursor buttons, and then press the [SELECT] button. The letter on the key will appear in the Title Name Editing window. # Space: blank button by which you can insert a blank to title name. # Caps: selecting this key and pressing the [SELECT] button can make the letters in the Characters area switch between the capitalization and the common letterform. # BkSp: selecting this key and pressing the [SELECT] button can cancel the letter before the cursor in the Title Name Editing window, meanwhile the cursor backs a space. # Delete: selecting this key and pressing the [SELECT] button can cancel the letter after the cursor in the Title Name Editing window. # Clear: selecting this key and pressing the [SELECT] button can clear all the letters in the Title Name Editing window. # Exit: selecting this key and pressing the [SELECT] button can exit this menu and keep Play title Edit title Rename title Erase title Overwrite title Overwrite disc Append title 2.5.6 Edit Title This operation can switch the system to edit mode.The functions and operations for edit mode are described at the next chapter. 1.Highlight a title icon you want to edit in the title List picture and press [4] button, then a menu will pop up as shown in the right figure. 2.Highlight "Edit title" item, and press [SELECT]button, then the system will enter edit mode. 3.Then, refer to chapter "Editing Mode"to perform corresponding operations. 4.To exit, please press [EDIT] button first and wait a few seconds until system operation is finished. - 20 - the Title Index name unchanged. # OK: selecting this key and pressing the [SELECT] button can exit this menu, meanwhile change the Title Index to the one in title Name Editing window. 3.Type a new title name in the Title Name Editing window by the keyboard in the menu. 4.Select the "OK" key and press the [SELECT] button to fulfill the naming to the title. 2.6.2 Entering the Editing Mode When the disc in the loader is DVD+R/RW and the system is not in the mode of writing or erasing ,pressing the [EDIT] button can enter the edit mode and display the control menu. Notes # When" " appears while you press the [EDIT] button, it mayindicate that the DVD+RW disc in the loader has been write protected, or the system in current mode can not enter the editing mode. You can perform the disc operation to cancel the write-protect or exit current mode. 2.5.8 Overwrite Title / Append Title / Overwrite Disc "Overwrite title", "Append title" and "Overwrite disc" are three kinds of record mode. The meaning about them is introduced in section "RECORDING MODE --Manual Recording-MODE". If youhave connected the external signal to this unit, you can select one of them to perform recording. 1.Highlight a title icon you want to overwrite and press [4] button to display the menu. 2.Highlight "Overwrite title" item, " Append title" item or "Overwrite disc" item, then press [SELECT] button to confirm.please note that 1 you can see "Append title" item only in menu of the last title. 2.6.3 Menu Explanation The editing control menu is shown in the EDIT MODE Title: 01/05 1 Chapter: 01/01 2 PLAY 3 Chapter marker 4 Hide chapter 5 Index picture 6 Split title T-Elapsed: 0:01:05 7 8 1.Title : the left of the number beside the icon is the current title number, and the right is the total of the titles in the disc. 2.Chapter : the left of the number beside the icon is the current chapter number, and the right is the total of the chapters in the disc. 3.Play : this item can perform the following functions: Play, Pause, Fast forward, Slow forward, and Step. 4.Chapter marker : separate or combine the chapters. 5.Hide/Unhide chapter: display or skip the chapter when playing it. 6.Index picture : change the index icon . 7.Split title : divide current title to 2 titles at current point. 8.T-Elapsed: can not be controlled, showing the elapsed time. Play title Edit title Rename title Erase title Overwrite title Overwrite disc Append title Highlighting the "overwrite title" item Play title Edit title Rename title Erase title Overwrite title Overwrite disc Append title Highlighting the "overwrite disc" item Play title Edit title Rename title Erase title Overwrite title Overwrite disc Append title Highlighting the "Append title" item 2.6 EDITING MODE 2.6.4 Operation Steps 2.6.1 Summarization Selecting the Title/Chapter to be Edited 1.Enter the editing mode 2.Select the Title/Chapter item by using [5], [6] buttons in the editing control menu. For the recorded disc, the dividing of the title and chapter can't match your fancy. The index icon and name of each title are confirmed by the system, which are not striking, not beautiful, not convenient to skim over the disc, and not possible to meet your personalized enjoyment either. The edit function is set for getting over the above limitations. 2.6.5 Selecting the Title /Chapter to be Edited (CONTINUED) 3.Press [SELECT] button to make the Title/ Chapter item in input mode. - 21 - 4.Input the number of the Title/Chapter to be edited by using number buttons,and press [SELECT] button, then the system starts to play the selectedtitle or the one which the selected chapter belongs to repeatedly. Notes # This operation is invalid to DVD+R. 2.6.8 Changing the Index Picture EDIT MODE Title: 01/05 Chapter: 01/01 PLAY Chapter marker Hide chapter Index picture Split title T-Elapsed: 0:01:05 2.6.6 Insert Chapter Marker 1.In the edit control menu, move the cursor by [5], [6] buttons to highlight the "Chapter marker" item, then press [4] / [SELECT] button to display the value list shown as the following figure. When entering the DVD title menu(Press the [TITLE] button when playing), the title index will be shown on the screen as a little icon, standing for a title (Please refer to "Playback Mode").The method of changing the title index is introduced in the following. 1.In the edit control menu, move the cursor by [5], [6] buttons to select the "Index picture" item. 2.Now, please watch the playing picture carefully, when meeting a picture you like, you can press [SELECT] button to replace that title icon by that picture. EDIT MODE Title: 01/05 Chapter: 01/01 EDIT MODE Title: 01/05 PLAY Chapter: 01/01 Chapter marker PLAY Chapter marker Hide chapter Index picture Split title Hide chapter Insert marker Delete marker Delete all markers Index picture Split title the value list of the "Chapter marker" item T-Elapsed: 0:01:05 T-Elapsed: 0:01:05 2.6.9 Split Title 2.Select proper value from the list by [5], [6] buttons, and press [SELECT] button to confirm, then the system will start separating or combining the current chapter. # If you select "Delete marker", this chapter and the former chapter will be combined to one chapter. # If you select "Insert marker", this chapter will be separated into two at the current location. # If you select "Delete all markers", all chapters of this title will be combined into one chapter. 1.Highlight the "Split title" item in edit control menu, shown as the following figure, then 1 press [SELECT] button. # The operation will divide current title to 2 titles at current point, and it will occupy many time, please wait for a moment. EDIT MODE Title: 01/05 Chapter: 01/01 PLAY Chapter marker 2.6.7 Hiding / Unhiding Chapter Hide chapter Index picture 1.In the edit control menu, move the cursor by [5], [6] buttons to select the Chapter Hide/Unhide item. 2.Press the [SELECT] button to switch the value of this item. # If the value is "Hide chapter", this chapter will be played when playing in normal mode. # If the value is "Unhide chapter", this chapter will be skipped when playing in normal mode. Split title T-Elapsed: 0:01:05 Notes # This operation is invalid to DVD+R disc. 2.6.10 Exiting the Editing Mode 1.Press [EDIT] button to exit this mode. # When exiting, the system will write some information into the disc, so the unit will stop responding for a while. EDIT MODE Title: 01/05 Chapter: 01/01 2.7 DISC OPERATION MODE PLAY 2.7.1 Summarization Chapter marker The disc operations refer to some operations about the disc in the loader , including viewing the disc information, finalizing Hide chapter Index picture Split title T-Elapsed: 0:01:05 - 22 - a disc, erasing the disc content, erasing the title, lock/unlock the disc and so on. # "Make compatible" can appear if you make "Insert Maker" operation according to the method in section "EDIT MODE -Insert Chapter Maker". 2.7.2 Entering the Disc Operation Mode If you load unfinalizing DVD+R or DVD+RW disc, you can enter this mode. There are two ways to enter this mode. 1.During playing, you can enter this mode by [DISC OPER] button. After entering the mode, pleas press [4] button to display the control main menu, as shown in the following figures. Play PAL Rename disc PAL DVD Finalize disc DVD EDIT Record a new title Play Rename disc Erase disc Record a new title Overwrite disc Make compatible Lock disc EDIT When playing unfinalizing DVD+R Finalize disc Warning: this operation will finalize the DVD+R disc in loader. If finalized, it can not record new content any more. Are you sure to continue? Yes # Lock disc: " Lock disc" is valid for DVD+RW. This operation can protect the recorded contents frombeing deleted. If you want to record new contents in the disc, you must unlock the disc. You can highlight item "Lock disc" and press [SELECT] button to lock or unlock the disc. If the disc is locked, this operationwill unlock the disc, otherwise it will lock it. # Erase disc: This operation is only available for DVD+RW disc.Highlight item "Erase disc" and press [SELECT] button, then the system will start erasing disc contents. This operation will occupy many time. When erasing, any other operations can not be proceeded, including standby. Once the operation starts, it cannot be cancelled midway. Please do not unplug the unit midway. Otherwise, the disc will be probably damaged. # Record a new title / Overwrite disc: These operations can perform recording function. "Record a new title " can add a new title when recording , and "overwrite disc"can overwrite all the contents in the disc as new one. You can highlight "Record a new title" or "Overwrite disc" item, and press [SELECT] button to start recording. Play Unlock disc PAL DVD EDIT When playing DVD+RW When playing locked DVD+RW 2.Display Title List picture by the methods introduced at chapter "Playing and Processing the Disc Recorded by this Unit", and press [5] button continuously until the icon appears, then press [4] button. PAL DVD EDIT 2.7.3 Operations # Play: Highlight item "Play" in the menu, and then press [SELECT] button. # Rename disc: Highlight item "Rename disc", and press [SELECT] button, then a keyboard menu will appear. By the keyboard, you can rename the disc through the methods introduced in chapter"Playing and Processing the Disc Recorded by this Unit". # Finalize disc/Make compatible : Disc name: MY DVDA B C D E F G H I J K 0 1 2 L M N O P Q R S T U V 3 4 5 W X Y Z ( ) - : ? . 6 7 8 Space Caps BkSp Delete Clear Exit No 2.7.4 Exiting the Disc Operation Mode 9 OK the key board menu by which you can rename the disc 1.Press [DISC OPER] again to exit. # "Finalize disc" is valid for DVD+R disc. If do this, the disc can be played in normal DVD player, but can't record new contents. "Make compatible" is valid for DVD+RW disc. These operations can make the disc able to be played in normal player. Highlight item "Finalize disc" and press [SELECT] button, then a dialogue will open shown as the right figure, please highlight "Ok" key in the dialogue, then press [SELECT] button to start this operation. These operations will occupy some time, Please wait for a few minutes. 2.8 PLAYBACK MODE 2.8.1 Entering the Playback Mode In the playback mode, this unit is totally the same as a high quality DVD player. The way to enter the playback mode is as follows: 1.Connect this unit with the TV set (Refer to "System Connection" for details), turn on the TV set and switch it to the AV input mode. RW - 23 - 2.Plug in the unit, then press [STANDBY / ON] button to turn it on. 3.Press [OPEN / CLOSE] button to open the disc tray. 4.Load the disc correctly as shown in the illustration. 5.Press [OPEN / CLOSE] button to close the disc tray, then the system starts playing. # According to different discs, the system will probably enter the Title Selecting Playback mode or Menu Playback mode. If this condition appears , the disc will not be continued playing (please refer to the following text). 6.If system is in other working mode, please press [PLAY] button to enter the playback mode. 7.If you press [PLAY] button, the TV screen displays " " . Please exit current working mode first, and then press [PLAY] button again. # When writing or erasing, pressing [PLAY] button will be invalid. # If there is no disc in the loader or load the disc that this unit doesn't support or has been damaged badly, pressing [PLAY] button will be invalid. as the right figure. You can highlight an icon you like, then press [SELECT] button to play it. 1 2 3 4 Notes # The title menu of different DVD discs may be different. # Not all DVD discs have title menu. For some DVD discs without title menu, pressing [TITLE] button is invalid. 2.8.4 Ending Playback # This unit enters the pre-stop mode. # In this pre-stop mode, this unit automatically memorizes the pre-stop point. If you press [PLAY] button ,this unit will resume the playback from the pre-stop point (Playback starts from the beginning of the pre-stopped track for MP3). If you press [STOP] button twice, this unit will enter stop mode and the memory is cleared. 2.Press [OPEN/CLOSE] button to eject the tray. 3.Take the disc out. 4.Press [OPEN/CLOSE] button to retract the disc tray. 5.Press [STANDBY/ON] button to end the operation. 2.8.2 Playback from the Menu Displayed 1.When playing a DVD disc, it will enter menu playing mode.The menus of different discs are different. In general, you can select the playing language, set the subtitle language and so on by that menu. To perform some operations,you only need to highlight the corresponding item by cursor buttons and confirm by [SELECT] button. 2.When playing some VCD disc, these menus will be a list of tracks. You can select a track by number or cursor buttons,then press [SELECT] button to play the selected track. 3.During playing, you can open the disc menu by pressing [MENU] button. Of course, all the functions about the disc menu can be fulfilled by the corresponding control menu based on this unit. Note # If the disc is badly damaged or loaded incorrectly, the OSD will display "NO DISC". 2.8.5 Playing Mode Control 1.Press [NAVIGATION] button twice to open the main control menu. 2.Highlight "MODE" item by [5], [6] buttons, and press [SELECT]/[4] button to display the drop down list window shown as the right figure. 3.Select one value in the list, then press [SELECT] button to confirm.The meanings of the values are as the following: 1.BIRNAK Sequence Playback 2.A-B A-B Playback 3.C-RPT Segment Repeat Playback 4.T-RPT Title Repeat Playback 5.D-RPT Disc Repeat Playback 6.TR-RPT Track Repeat Playback 2.8.3 Playback from the Titles Displayed This operation is only available for the DVD disc.During playing, if you want to select some title to play, you can press [TITLE] button. Then the screen will display the title icons list, shown - 24 - 7.PROG 8.RANDOM Program Playback Random Playback pressing [ADD/CLEAR] button can add the item to right list window. # Highlighting an item in right window, then pressing [ADD/CLEAR] button can delete the item # If the items of the left window is title, you can expand item by pressing [SELECT] button, shown as the following figure: DVD MODE Normal TRICK Play TITLE 03/06 CHAPTER 04/19 AUDIO 01/01-ENG SUBTITLE 01/03-ENG ANGLE 01/01 T-TIME 00:13:02/01:15:17 Normal A-B Repeat Chapter Repeat Title-Repeat Disc Repeat mode value list Main control menu The list values are different when playing different discs. For most operations, if you perform step 3 , things are over, but if you select "A-B Repeat" and "Program",you shall perform the following steps. TITLE TITLE TITLE TITLE TITLE TITLE TITLE TITLE TITLE TITLE TITLE Set A- TRICK Play TITLE 03/06 CHAPTER 04/19 AUDIO 01/01- ENG SUBTITLE 01/03- ENG ANGLE 01/01 T-TIME 00:13:02/01:15:17 Press the [SELECT] button Unfold the content of "TITLE 01" CHAPTER CHAPTER CHAPTER CHAPTER CHAPTER CHAPTER CHAPTER CHAPTER CHAPTER 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 Press the [SELECT] button Go back to the previous window 6.Add your favorite contents to right window in your desired sequence according to theabove description, then move the cursor to the right window and press [SELECT] button to start program playback. DVD MODE CHAPTER OF TITLE 01 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 2.8.7 Playback Process Control 4.If you select "A-B Repeat", when pressing [SELECT] button, the menu becomes the style shown as the right figure. You need to set the B point. Press [SELECT] button to display Mode value list again and select"A-B Repeat ".Now, please wait, and when meeting your desired point,you can press [SELECT] button to set the B point. # During your waiting, the main control menu will disappear. You also can press [NAVIGATION] button to hide the menu. 5.If you select "Program" in step 3 , the following list windows will pop up. 1.Press [NAVIGATION] button twice to open the main control menu. 2.Highlight "TRICK " item by [5], [6] buttons, and press [SELECT]/[4] button to pop out the drop down list window shown as the right figure. 3.Select one value in the list, then press [SELECT] button to confirm. DVD MODE Normal TRICK Play TITLE 03/06 CHAPTER 04/19 AUDIO 01/01-ENG SUBTITLE 01/03-ENG ANGLE 01/01 T-TIME 00:13:02/01:15:17 Play STOP PreSTOP PAUSE FastForward*2 Edit program play list TITLE TITLE TITLE TITLE TITLE TITLE TITLE 01 02 03 04 05 06 The means of the List values are as following: 1 PLAY playback 2 STOP stop 3 PreSTOP prestop 4 PAUSE pause 5 FastForward2~32 fast playback, the number shows the speed of the playback 6 FastBackward2~32 fast backward playback, the number shows the speed of the backward Playback 7 SlowForward1/2~1/16 slow playback, the fraction shows the degree of slow Playback Favorite/Program By this menu you can select your favorite contents from the disc to play in your pointed sequence. 2.8.6 Playing Mode Control (CONTINUED) You can control the two list windows by the following points. # Move the cursor between left window and right window by [3], [4] buttons. # Move the cursor up and down in one of the windows by [5], [6] buttons. # Highlighting an item in left window, then - 25 - # The list values are different when playing different disc. 2.8.10 Angle Selection 1.Press [NAVIGATION] button twice to open the main control menu. 2.Highlight "ANGLE" item by [5], [6] buttons, and press[SELECT]button to make it in input mode. # The right side of the numbers beside the icon is the total angle number of this disc ; the left is the current angle number. 3.Input the ANGLE number you need by number buttons, and press [SELECT] button to confirm. 2.8.8 Title/Chapter/Track Selection 1.Press [NAVIGATION] button twice to open the main control menu. 2.Highlight "Title"/"Chapter"/"Track" (for VCD/ SVCD) item, and press [SELECT] button to make it in input mode. 3.Enter your desired number by number buttons, and press [SELECT] button, then the system will start playing the selected Title/ Chapter/Track. # The left part of the item value is the number of current playingcontent; the right one is the tota l number. DVD DVD VCD MODE Normal MODE Normal MODE Normal TRICK Play TRICK Play TRICK Play TITLE 03/06 TITLE 03/06 TRACK 01/15 CHAPTER 04/19 CHAPTER 04/19 AUDIO STEREO AUDIO 01/01-ENG AUDIO 01/01-ENG PBC PBC ON SUBTITLE 01/03-ENG SUBTITLE 01/03-ENG TR-TIME ANGLE 01/01 ANGLE 01/01 T-TIME 00:13:02/01:15:17 T-TIME 00:13:02/-01:15:17 Highlight title item DVD Highlight chapter item Highlight track item when playing VCD/SVCD. Normal TITLE 03/06 CHAPTER 04/19 AUDIO 01/01- ENG SUBTITLE 01/03- ENG ANGLE 01/01 T-TIME 00:13:02/01:15:17 2.ENG DTS Play TITLE 03/06 CHAPTER 04/19 AUDIO 01/01- ENG SUBTITLE 01/03- ENG ANGLE 01/01 T-TIME 00:13:02/01:15:17 MODE Normal TRICK Play 01/15 AUDIO STEREO PBC PBC ON 00:01:25-00:02:28 PBC ON PBC OFF # The PBC function refers to the menu playback function of the VCD 2.0 disc. When the PBC is on, the TV screen displays a list of all the tracks. You can select any track by number buttons on theremote control, and press [SELECT] button to play from the selected track. During the playing, if you want to play the other track , you need to press [MENU] button to display the track list, and select another track by number buttons then press [SELECT] button to confirm. When the PBC is off, the system plays the disc contents in sequence. # Not all the VCD discs can proceed PBC playback. DVD Normal 01/01- ENG SUBTITLE Notes 1.CHI DOLBY 3.Select one value in the list, and then press [SELECT] button to confirm. # The values of the lists are based on the played disc # For DVD disc, the values of audio list will be DOLBY, DTS and so on. # For VCD/SVCD, the values of audio list will be STEREO, LEFT and RIGHT. # The settings of these items also can be done in DVD menus.The initial value of the two items can be set in System Setup. TRICK 04/19 AUDIO TRACK TR-TIME Highlight "AUDIO" item MODE 03/06 CHAPTER VCD DVD Play Play TITLE 1.Press [NAVIGATION] button twice to display the main control menu. 2.Highlight "PBC" item by [5], [6] buttons, and then press [SELECT]/[4] button to display the drop down list window shown as the right figure. 3.Select "ON" or "OFF" from the list, and then press [SELECT] button. 4.Pressing [MENU] button also can make the PBC on or off. 00:01:25-00:02:28 2.8.9 Audio / Subtitle Selection TRICK Normal TRICK 2.8.11 PBC ON/OFF 1.Press [NAVIGATION] button twice to open the main control menu. 2.Highlight "AUDIO"/"SUBTITLE" item by [5], [6] buttons,then press [SELECT]/[4] button to open the drop down list shown as the right figure. MODE MODE 2.8.12 T-Time/Tr-Time Display 01/03- ENG 0.OFF ANGLE 01/01 1.CHI T-TIME 00:13:02/01:15:17 2.ENG 1.Press [NAVIGATION] button twice to display the main control menu. Highlight "SUBTITLE" item - 26 - 2.Highlight "T-Time" (For DVD) or "Tr-Time"(For VCD/SVCD) item by [5], [6] buttons, and then press [SELECT] button to open the drop down list shown as the right figure. 3.Select your desired item by [5], [6] buttons, then press [SELECT] button to confirm. # In DVD playing mode, it includes "TITLE" and "CHAPTER" , in VCD/SVCD playing mode, it includes "DISC" and "TRACK". # The left part of the item values is the elapsed time of the title/track, the right one is the remain time. DVD MODE Normal TRICK Play TITLE 03/06 CHAPTER 04/19 AUDIO 01/01-ENG SUBTITLE 01/03-ENG ANGLE 01/01 T-TIME 00:13:02/01:15:17 CHAPTER TITLE 2.8.13 The Operations of Function Buttons Most of the operations in playing mode can be done by menu or function buttons, some operations only can be done by menu, and other operations only can be done by function buttons. 1.REPEAT button - Repeat playback Press [REPEAT] button repeatedly, and the playing mode will be circularly switched in the following sequence: normal mode repeat chapter repeat title repeat disc 5.PAUSE/STEP button - Pause playback & playing frame by frame. A.When playing the valid disc , if you press [PAUSE/STEP] button, the playback will pause. B.If you press [PAUSE/STEP] button again, the picture goes forward a frame. C.If you press [PLAY] button, the system will enter normal playback. # Pressing the [PAUSE] button the second time means normal playback when playing CD-DA and MP3 discs. 6.VOL+/VOL-/MUTE button - Volume control A.If you press [MUTE] button, the system has or hasn't audio output. B.If you press the [VOL+] button, the volume increases. C.If you press the [VOL-] button, the volume decreases. 7.GOTO button - Switching the mode of selection playing A.In the playback mode, you can press [GOTO] button to highlight different select item circularly in the playback control menu. You can input the corresponding values by using the remote control with the method aforesaid. # The illustration below is the example of playing the DVD disc. It is similar to other discs. TITLE : _ _ Title 01/04 Selection 2.FWD button - Forward playback Press [FWD] button repeatedly, and the playing speed will be changed in the following sequence: Normal Speed Playback FF*2 FF*4 ...... FF*32 3.REW button - backward playback Press [REW] button repeatedly, and the backward playing speed will be changed in the following sequence: Normal Speed Playback FB*2 FB*4 ...... FB*32 4.SKIP button A.If you press the [ ] button on the remote control, the system goes forward into the next chapter (to DVD) or track (to VCD) and begins playback B.If you press the [ ] button on the remote control, the system goes backward into the previous chapter (to DVD) or track (to VCD) and begins playback. CHAPTER : _ _ Chapter Selection 11/27 TIME : _ :_ _ :_ _ Time Selection # Pressing [GOTO] button is invalid to some discs. B.When play disc (as JPEG/MP3/DivX disc) with directory structure, you must press [GOTO] button toconfirm instead of pressing [SELECT] button. # In directory structure, to go to corresponding directory, you need press [GOTO] button once and input the number of the directory then press [GOTO] button again to confirm. Press [SELECT]button to open it. # In file structure, to go to corresponding file and start playing it, please operate according to the method in directory structure . # In playing MP3/DivX file, to go to some time position of current file and start playing, at first press [GOTO] button twice and input the number your desired then press [GOTO] button again to confirm. 2.8.14 Playing JPEG/MP3/CD/ DivX Disc Operation When loading disc with directory structure, the TV screen will display the disc content list and favourite/programlist windows as shown in the following figure. From this you can do selection playback or program playback. 1.Highlight your desired file or directory by [5], [6] buttons, and then press [SELECT] button. # If the highlight item is file, the system will start playing it. # If the highlight item is directory, the system will expand its contents. # To return to previous menu, please press [RETURN] button. If you press [ADD/CLEAR] button, the highlighted file itemwill be added to the right list window, then you can do program playback by the following steps. PIC - playing JPEG VIDEO - playing DivX 2.MODE: please refer to Playback Mode Playing Mode Control for submenu content. 3.TRICK: please refer to Playback Mode Playback Process Control for submenu content 4.AUDIO: you can select different audio channel output (stereo/left/right),you can also do it by press [AUDIO] button repeatedly. 5.TIME: you can select displaying elapsed time or remain time. 6.WIPE: please refer to Playback Mode Control Wipe Mode when Playing JPEG Disc . 7.ZOOM: please refer to Playback Mode Control Zoom Mode when Playing JPEG Disc . 8.ROTATE: please refer to Picture Rotating when Playing JPEG Disc . 9.LANG: if the disc include several kinds of language, you can select desired language from this item. File Play-Stop 0:00:00-0:00:00 FILES&DIRECTORY ..\ Car butterfly cat city fish forien katong FAVORITE/PROGRAM 2.Select your desired content from left list window by [5], [6] buttons and add it to right list windowby pressing [ADD/CLEAR] buttons. 3.Move the cursorto the right list window by [4 ] button and press[SELECT] button,then the system starts playing the contents of the right list window one by one. # Highlighting the item in right list window by [5], [6] buttons and pressing[ADD/CLEAR] button can delete it. 4.When you play JPEG/DivX file, please press [<] button to return to previous menu. Notes # Some discs labelled with MPEG4 on the market actually are *.rm/*.ra/*.ram/*.rmm others,withwhich are incompatible. Please take care when buying discs. 2.8.16 Control Wipe Mode when Playing JPEG Disc In general, many pictures will be saved in the disc as the JPEG file format. When playing this disc, the pictures will be shown on the screen one by one. You can select the mode of the picture switching. 1.Playing a JPEG file, press [NAVIGATION ] button twice to display the playback control menu. 2.In the playback control menu, select the Control Wipe Mode item by[5], [6] buttons, and then press [SELECT] button to display thewipe mode list shown as the right figure. 3.Select the desired mode of the picture switching from the list by [5], [6] buttons and then press [SELECT] button. 4.Press [NAVIGATION] button to return to the previous menu. 2.8.15 Playback Control Menu Loaded a disc with directory structure or playing a file like JPEG/MP3/CD/DivX, your can display the playback control menu by pressing [NAVIGATION] button once or twice. You can do some operation to current file by the playback control menu. The playback control menu will be different when playing different type disc. File Play File Play File Play TYPE AUDIO TYPE PIC TYPE VIDEO MODE NORMAL MODE NORMAL MODE NORMAL TRICK PLAY TRICK PLAY TRICK PLAY AUDIO STEREO WIPE Top to bottom AUDIO STEREO 0:00:00/0:00:00 ZOOM FITSCREEN TIME 0:00:00/0:00:00 CLOCKWISE 0 LANG LANGUAGE 1 TIME ROTATE When playing MP3/CD When playing JPEG When playing DivX The means of the list values are as following: 1.Type: display current playback type AUDIO Playing MP3/CD File Play TYPE PIC MODE NORMAL TRICK PLAY WIPE Top to bottom ZOOM FITSCREEN ROTATE - 28 - CLOCKWISE 0 Top to bottom Down to top Left to right Right to left Extend V 2.8.17 Control Zoom Mode when Playing JPEG Disc This function can zoom in or zoom out the picture to facilitate your watching. 1.Playing a JPEG file, press [NAVIGATION ] button twice to display the playback control menu. 2.In the playback control menu, select the Control Zoom Mode item by [5], [6] buttons, and then press [SELECT] button to display the zoom mode list shown as the right figure. 3.Select the percentage of zoom from the list by [5], [6]buttons, and then press [SELECT] button. # The value of "FITSCREEN" means the full screen display. 4.Press [NAVIGATION] button to return to the previous menu. File Play TYPE PIC MODE NORMAL TRICK PLAY WIPE Top to bottom ZOOM FITSCREEN ROTATE CLOCKWISE 0 200% 400% FITSCREEN 2.8.18 Picture Rotating when Playing JPEG Disc This function can change the angle of the placement of the picture on the screen to facilitate your enjoying. 1.Playing a JPEG file, press [NAVIGATION ] button twice to display the playback control menu. 2.Select the Picture Rotating Select item in the playback control menu by [5], [6] buttons, and then press [SELECT] button to display the rotating value list shown as the right figure. # There are four kinds of rotating angles: 0o, 90o , 180o , 270o 3.Select the desired angle from the list by [5], [6] buttons and then press [SELECT] button. 4.Press [NAVIGATION] button to return to the previous menu. File Play TYPE PIC MODE NORMAL TRICK PLAY WIPE Top to bottom ZOOM FITSCREEN ROTATE CLOCKWISE 0 CLOCKWISE 0 CLOCKWISE 90 2.9 USB MODE 2.9.1 Summarization This unit is equipped with an USB socket, then the equipment with USB socket(e.g.DV,DC,Mp3 Player, Flash Driver, USB Hub, USB Card reader) can be connected to this unit. # This unit only supports such file formats in USB device: JPEG,MP3 and WMA. # Only when the other file format is translated to one supported by this unit , can it be played. 2.9.2 Operations 1.Insert the USB device to the USB socket in this unit . 2.Plug in this unit , and then turn it on by button [STANDBY/ON]. 3.Press button [USB/DVD] to enter the mode of reading USB. 4.When playing the files in USB, please perform the corresponding operations according to chapters: "Playback Mode - Playing JPEG/ MP3/CD Disc", "Control Wipe Mode when playing JPEG Disc", "Control Zoom Mode when Playing JPEG Disc" and "Picture Rotating when Playing JPEG Disc". 2.9.3 Exiting the USB mode Press button [SOURCE] or [USB/DVD] to exit the USB mode. Note: This unit can not support all the USB devices of DV DC MP3 Player Flash Driver USB Hub and USB Card reader in the market. We list some USB devices passing the test in this unit for your use reference. Table 1 - 29 - CF MD (micro Drive) SD MMC MS XD SM USB 2.0(NEQ ND3260) PASS PASS PASS PASS PASS PASS PASS Zynet 8 in 1 USB 2.0(NEQ ND3260) PASS PASS PASS PASS PASS X PASS PQl 7 IN 1,USB flash 1.1(Sl) PASS PASS PASS PASS PASS X PASS No branch 8 in 1,USB 1.1(ALCOR Au9632) PASS N/A PASS PASS N/A PASS PASS Cyberhome 5 in 1,(ALIM5635) PASS X N/A N/A PASS N/A PASS BBK 8 in 1,(ALCOR Au9632) PASS N/A PASS PASS PASS N/A PASS Neodio 8 in 1,(ND3060-LB) PASS PASS PASS PASS PASS N/A PASS CARD model USB card reader model # cells marked "PASS" means these card are supported on this unit. # cells marked "N/A" means these card are not recognized on this unit. # cells marked " “ means the card reader have not corresponding slot. Table 2: Name Equipment Model/Character Details/Remarke SQA Comments (updated on Build042) Sony DCR-T RV 18 120×digital zoom Can detect and play Sony DCR-PC1 01 E 120×digital zoom Can detect and play JVC GR- D70 U 700×dingital zoom Can detect and play CA NON ZR65 MCA 400×digtal zoom Not support CA NON IXUS S430 4M Pixels,3X,CF card Can detect and play SONY DSC-F717,Milpitas pref er 5M Pixels,7X,MS card Can detecct and play Niko n Coolpic 5000 CF Car d Can detect and play Olympus ì300 3M Pixel,3X,XD card Can detect and play FUJIFILM FinePix F420 3M Pixels,3X,XD card Can detect and play APPLE iPod 15G MP3(CBR/VBR)/WAV/AAC,) Can detect and play SAMSUNG Yepp Y P-55V,USB 1.1 MP3/WMA Can detect and play ZARVA CA-128M MP3/WMA Can detect and play MSC MSN HA-128F MP3/WMA,USB interfac e Can detect and play Sony(MD) N10 MP3/WAV/WMA/ATRAC3 Not support Apac er 128M 128M,USB 1.1 Can detect and play Aigo Mini king 128M,USB 1.1 Can detect and play SanDisk Cruzer Mini USB 2.0 128M 128M,USB 2.0 Can detect and play Putian U-571 128M,USB 1.1,USB 2.0 Can detect and play NETAC U215 64M,USB 1.1 Can detect and play 32M,USB 1.1 Can detect and play 128M,USB 2.0 Can detect and play DV DC MP3 player Flas h Driver Longview SONY 128M MV - 30 - USB Hub 1 to 4,USB 1.1 Sprinters DX-174BP USB SLIM HUB Can detect and play w hen connect more than one USB devices Note # USB refers to Universal Serial Bus. Most of USB devices on the market are USB1.1 or USB2.0.There are some types USB 1.1 devices:Monitors, Communication devices,Audio, Human input, Mass storage. # Most FLASH MEMORY,MP3 PLayer ,USB HDD ect. belong to MASS storage Class . Mass storage Class include 2 transport manners: 1. USB 1.1 Mass Storage Class Control/Bulk/Interrupt (CBI) Transport 2. USB 1.1 Mass Storage Class Bulk-Only Transport # This unit support USB 1.1 Mass Storage Class Bulk-Only Transport, we are not sure that other USB devices can be supported !So please find out about the features of USB equipments before buy. # When use USB 1.1 Mass Storage Class Bulk-Only Transport devices,please notice the file operation system support Windows FAT ,not support FAT32 and NTFS ect. file system. 2.10 SPECIFICATIONS Playable discs DVD,DV D+R/RW,SV CD,V CD,CD- DA,Mix ed CD-DA ,MP3,JPEG,DivX Recordable discs DVD+R,DVD+RW Recording formats DVD(MPEG 11) Recording quality SLP(Standard Long Play),SP(Standard play) EP(Extend play),HQ(Perf ect Quality) Input Composite video input S-video input(Y /C) DV camera jack input(IEE1394,I-Link) USB input RF input Analog audio input SCART input MIC input Output Composite video output S-video output(Y /C) Component video output(Y Pb/Cb Pr/Cr) SCART output 2CH analog mix audio output 5.1CH aalog output Digital audio coaxial output Digital audio optical output Composite video: output Video charac teristics Composite video: Input Audio charac teristics S-video: S-video: NTSC/PAL sys tem Video amplitude 1.0±0.2V(p- p),75Ù Y ioutput amplitude 1.0V(p- p),75Ù C output amplitude 0.286V(p-p) ,75Ù NTSC/PAL sys tem Video amplitude 1.0±0.2V(p- p),75Ù Y input amplitude 1.0V(p- p),75Ù C input amplitude 0.286V(p-p) ,75Ù Output Audio amplitude 2.0 Vrms,10kÙ AF respons e 20Hz~20kHz(±1dB) Signal/noise ratio 85dB Audio distortion+noise -65dB(1kHz) Input Audio amplitude 2.0Vrms Impedance 10kÙ - 31 - General Specific ation Power supply: ~100V-240V ,50/60Hz Power consumption: 35W Standby pow er cons umption: 3W Operating temperature 5 ~35 Operation humidity Relative humidity 15%~75%(No condensation) Dimension: 430mm×296mm×48mm - 32 - Weight: Net w eight: 3.4kg ross w eight: 4.5kg Chapter Three Unit Circuit Principle Section One Principle of the Player DW9918K is a DVD disc playing and recording player that integrates playing and recording together, which supports DVD-R DVD-RW DVD+R DVD+RW format record disc, and plays DVD/CD/MP3 format discs. This player is composed by decode board, loader, AV board, power board and main panel. Decode board: it is the main part of the player, which includes decode chip, audio/video D/A conversion and FLASH/SDRAM module, etc. The main function is fulfil the decompression of data during the course of playing to reconvert signals conveyed by loader into analog audio/video signals; and responsible to converse analog audio/video signals to digital signal and perform decoding to send to the player during the course of recording; and also control the system of the working of the player. Loader components: includes loader laser head, frame and servo board. This loader adopts ATAPI jack, with strong applicability, which may read DVD, CD format discs and support the write function of DVD-R DVD-RW DVD+R DVD+RW discs at the same time. AV board: includes input/output amplifying circuit of multi-channel audio/video, input/output channel selection, switch circuit, Nicam decode circuit, output terminal and tuner. Power board: provides power required by each circuit of the player. The main output voltage has 12V, +3.3V, +2.5V, +5V, STB5V and -25V, etc. In special conditions, STB5V and panel VFD drive voltage are only provided. Main panel: includes panel function control, VFD display control, remote control and decode function, and is mainly composed by VFD and D16316. - 33 - +5V GND -25V GND F- F+ Main panel (4DW9916-3) CN2 4 CN6 CN1 GND 6/7 Decode board +5V ATN_FM +2.5V Front AV board CN3 CDW9916 -4 2 GND TPBTPB+ GND TPATPA+ JP2 9/10 +12V 2DW9916-6 Loader components CN4 VCC GND USB_BDM0 USB_BDP0 GND USB_OC0 USB_PO0 USB jack board KEY-04 KEY-C GND STB_LED Subsidiary panel - 34 - Figure 3.1.1.1 PCB board composition figure OPTICAL SPDIF_OUT GND SUBWOOFER MUTE CENTER RST_AUDIO REAR_R GND REAR_L GND A_R_OUT GND A_L_OUT E5_GPIOX5 E5_GPIO1 E5_GPIOX2 E5_GPIOX4 E5_GPIO4 E5_GPIO5 SDA SCL E5_GPIOX35 5V_STB CN3 D_HOST Power board 5 P_CTL_PSW CN5 +5V RST_HOST_LED CN3 3 5V_STB +3.3V 1 MUTE 5VSTB VFD_STB CN4 P_CTL VFD_CLK NC VFD_DIO 59918K-2 GND CN2 E5_GPIOX1 S_Y_OUT GND S_C_OUT GND V_OUT GND R_V_OUT GND G_Y_OUT GND B_U_OUT GND R_C_IN GND R_Y_IN F_Y_IN V3_IN GND R_SC2_SC1_CVBS_IN V4_IN V1_IN GND A_L_IN GND A_R_IN PCB board composition diagram is shown as in the following figure 3.1.1.1: 3.1.1 PCB board composition figure and video signal figure -12v GND +12V +5V AV board 7DW9918K-2 A-12V GND A+12V OK MIC_DET MIC board AINLF AINRF JP1 GND FCVBS MIC 1, 2 input Keyboard U1 UPD16316 Rear audio input VFD SCART1 audio input U17 (CS5360) U17 CS4360 4558 Rear audio output U6 (MSP3415G) L-OUT, R-OUT Block diagram of the player is shown in the figure 3.1.2.1: 3.1.2 Block diagram of the player U8 4053 SCART2 audio output Reset circuit USB jack DV jack U1 U10 U8 (FLASH) DMN8602 TSB41AB1 U5 74AHCT14 Front video input S-video input Loader U18 4052 Tuner video input Rear video input U10 4052 Optical output U14 TVP5150 S-video output U3 4 SDRAM Rear video output SCART1 composite video input SCART1 video RGB input Coaxial cable output U8 U7 4053 4053 SCART2 composite video output Video RGB output SCART2 video RGB output - 35 - Tuner audio input U1 (4052) Figure 3.1.2.1 Block diagram of the player Front audio input 3.1.3 Introduction to IC used by this player Introduction to IC used by this player is shown in the following table: Board Number Decode board 2DW9916-6 4DW9916-3 SN Material code 1 0881935 DMN-8602 BGA U1 main chip 2 0882839 EM6353BX2SP3B-2.9V SOT23-3L U6 reset IC 3 0881814 LP2995 SOP U2 DDR final linear voltage regulator (1.25V ) 4 0881815 M13S128168A-6T TSOP U3,U4 5 0881816 SN74HCT14PWR TSSOP U5 rever ter 6 0881818 SN74ALVCH16373 TSSOP U7 memorizer 7 0881819 TSB41AB1PHP QFP U10 DV jack IC (1394) 8 0881820 PQ018EZ02ZP U11 1.8V v oltage regulating IC 9 0881693 TL 74HC4052D SOP U18 video input sw itch IC 10 0881821 PQ025EZ01ZP U13 2.5V v oltage regulating IC 11 0882873 TVP5150 U14 video A/D conv erter 12 0881057 CS4360 SSOP U15 audio D/A conver sion 13 0882353 CS5340 TSSOP U17 audio A/D conver sion 14 0881236 39VF160-70 U8 FLA SH 1 0881013 D16316 QFP U1 panel VFD drive, button coding 1 08805819 TL431C TO-226AA( LP) IC3 precis e voltage regulator 2 0882462 AZ431A Z-A TO-92 IC4,IC5 precis e voltage regulator 3 0880765 5L0380R YDTU IC6 pow er sw itch module 4 1080032 @HS817 VDE IC2 photoelectric c oupler 1 0881226 RC4558D SOP U1 operational amplifier 1 0881080 PCF8563T SO8 U2 clock IC 2 0881693 TL 74HC4052D SOP U1,U10 (channel s election) electronic sw itch 3 0881965 MAX4052A SOP U1,U10 (channel s election) electronic sw itch 4 0881226 RC4558D SOP 5 0881842 MSP3415G QFP 6 0881992 HC4053M SOIC Model Location Function explanation SDRAM(128M) 59918K-2 69918K-3 79918K-2 U3,U4,U5 operational amplifier (audio amplifying) U6 NICAM IC U7,U8,U9 electronic s w itch (c hannel selection) - 36 - Section Two Unit Circuit Principle 3.2.1 System control and code, decode circuit 1. This layer adopts the single-chip processor DMN-8602 of recordable DVD products used for single drive of the second generation of LSI Logic Company. The single chip includes a 2nd-generation DV coder, 5th-generqtion coder, USB controller, shown in the figure 3.2.1.1, NTSC/PAL TV coder and 14.31818M VFD U14 5M U18 4052 Video input mode selection TVP5150 Panel buttons D16316 Video A/D conversion IR_FMUTE ATNFM D_HOST VFD_DIO VFD_CLK VFD_STB VI_D[7:0] Y/C Y/G PR/R PB/B USB_DO+ USB_DOUSB_OC0 USB_PO0 USB jack Loader jack CVBS HDAT[0:15] AO_MCLKO AO_SCLK AO_FSYNC AO_D3 AO_D2 AO_D1 DMN-8602 DV terminal R_Y_IN R_C_IN F_Y_IN F_C_IN F_CVBS_IN TV_CVBS_IN R_SC2_SC1_CVBS_IN TPB+ TPBTPA+ TPA- AV output board Video signal output filtering, clamping U15 CS4360 Audio D/A conversion Video signal amplifying B_Cr R_Cr G_Cr v_out S_Y_OUT S_C_OUT R_OUT L_OUT REAR_R_OUT REAR_L_OUT CENTER_OUT SUBWOOFER_OUT U3 U4 U5 4558 Audio amplifying U5 74AHCT14 SPDIF_OUT OPTICAL U10 SDRAM_A[0:16 TSB41AB1 HD0~HD15 SDRAM DQ[0:31] BA[1:22] AI_MCLKO AI_SCLK AI_FSYNC AI_D0 U17 CS5340 Audio A/D conversion U1 4052 AV input switch BTSC_AINR BTSC_AINL 13.5M 24.576M U8 U6 MSP3415G U3 U4 FLASH(16M) U7 74LVC16373 EXT_AUDIO_IN_L EXT_AUDIO_IN_R F_AUDIO_IN_R F_AUDIO_IN_L SDRAM (8M*16DDR) NICAM processing 1.8V 2.5V 3.3V U11 U12 U13 1.8V 2.5V 3.3V Voltage regulating circuit 18.432M Figure 3.2.1.1 System control and code, decode circuit block diagram - 37 - SC1_L_IN SC1_R_IN SC2_L_IN SC2_R_IN TV_IF TV_MONO DoMiNoFX Technique. Single-chip design supports all recordable DVD formats, ensures the ample features of recordable DVD; compared with the system with the similar level, the cost has been reduced greatly, and the complexity of electronic communication manufacturer is reduced at the same time. DMN-8602 provides advanced product features, for instance, the direct digital dubbing technology makes personal digital contents convert from portable video camera to DVD simplification; a single small contact control and re-playable MPEG-4 video format can make general audio, video signal adopt MPEG-2 format to record into high quality DVD discs, and also can make DV signal of some machines, such as video camera, realize DVD format with higher quality image. At the same time, this machine is also a high-performance DVD player, which may record DV signal and normal audio, video signal to MPEG-2 format in DVD+RW , DVD+R discs. Input audio/video signal, DV signal and TV TUNER signal, manual and timing record function, with playback function of DVD player, which may play DVD, VCD, SVCD, CD-DA; compatible with DVD-RW, DVD-R, DVCD, Mp3, JPEG format discs. DV (IEEE 1394) jack may realize Hi-Fi digital record, front and back multi-channel AV, S-VIDEO input and TV tuner input. Progressive scanning output and component video output makes picture more perfect. 24 bit DAC audio output high quality sound is adopted. Single-sided disc DVD+RW, DVD+R has 6-hour recordable time at most (stream 1.7 M bit/S), and 1-hour high quality image (stream 9.72 M bit/S). 2. Function realization explanation (1) System control circuit: fulfilled by U1 DMN-8602, the basic core to fulfill the ordered working of the player, through the control to each function circuit by the bus, the player works ib an orderly way according to the requirements designed by program. After switching the internal working mode through software, the system selects input signal, DV, jack, external input signal (external audio signal, external video signal and TV signal), DVD signal, USB signal. The working principle is as follows: (2) External input: the system sends the externally-inputtedvideo signals to decode board, through U18 4052 video input selection, sends to video decoder U14 TVP5150 for video decode, TVP5150 converses NTSC, PAL and SECAM video signal into digital component video signal, and sends the digital component video signal after being decoded to DMN-8602 for MPEG coding processing and then send to DVD recorder driver to fulfill disc record storage after coding, at the same time outputs from DMN-8602 analog video output jack directly and makes analog video signal output after being filtering, clamping and amplifying to realize the simultaneous output in the course of recording and the appearance will not be affected. The externally-inputted audio signals, after being NICAM processed on AV board through U15 MSP3415, are sent to U1 4052 for channel selection, and audio signals after selecting are sent to AD converter U17 CS5340 of decode board to converse analog signals to digital audio signals, then send to AIN jack of DMN-8602, through DMN-8602 processing, output from AOUT jack of DMN-8602, the outputted digital audio signals are sent to DA converter U15 CS4360 to convert to analog signal and then send to output terminal for output after amplifying analog signal, at the same time AO_IEC958 of DMN-8602 outputs digital audio signal. - 38 - (3) DV input means: DV signal is inputted through DV jack, then sent to U10 TSB41AB1 cable transceiver of decode board for decoding to send the data after being decoded to 1394 jack of DMN8602 directly for code processing and then send to DVD recorder driver to realize disc record storage or output signals after being coded from DMN-8602 analog video output jack (VDENC) and AVOUT analog audio output jack, or output at the same time of recording. (4) DVD signal output: DMN-8602 communicates with DVD|Recorder through ATAP jack, the disc information achieved by DVD Recorder is sent to DMN-8602 for decoding through ATAP jack, and the decoded data is send to analog video output jack (VDENC) and digital audio output jack AOUT for output. (5) USB signal: DMN-8602 has a USB1.1 jack, which supports low speed and full speed transmission modes. USB data is sent to the USB jack of decode board DMN-8602 through jack for format conversion, and then encodes different format according to user’s requirements to send to DVD recorder driver to realize disc record storage, or output from DMN-8602 analog video output jack and audio output jack directly. The working principle of audio, video output is the same with that of DVD player. After loader reads data, it is sent to U1 DMN-8602 ATAPI jack through ATAPI bus then to decode chip DMN-8602 for audio, video decode and then save the data after being decoded inside SDRAM temporarily, when uses need to play, decode chip calls the data saved in SDRAM for replay, audio data performs D/A conversion through U15 CS4360 and outputs analog audio signal, video signals are kept inside decode chip for video decode and then output analog video signal, after filtering and amplifying, the output is completed. 3.2.2 Audio output circuit 1. Audio signal output flow chart is shown in the following figure 3.2.2.1: AO_MCLKO AO_SCLK U1 DMN8602 AO_FSYNC AO_D1 AO_D2 AO_D3 CENTER 7 5 U415 6 CS4360 2 Audio D/A 3 converter 4 SUBWOOFER REAR_L REAR_R A_L_OUT A_R_OUT CENTER 6 SUBWOOFER 4 REAR_L 10 CN3 8 CN1 REAR_R 2 6 6 2 U5 4558 U4 4558 1 7 7 1 A_L_OUT 14 A_R_OUT R160 SUBWOOFER_OUT REAR_L_OUT Audio output terminal S5 REAR_R_OUT L_OUT 2 12 CENTER_OUT 6 U3 4558 R159 1 7 R_OUT SC1_L_OUT SCART OUTPUT SC1_R_OUT 14 4 12 5 U8 74HC4053 OK CN6 Figure 3.2.2.1 Audio signal output flow chart When the player is playing again, decode chip U1 DMN-8602 reverts the disc information conveyed from loader, digital audio signal outputs through the pin of decode chip AOUT module to D/A converter, audio data performs D/A conversion through CS4360 and outputs analog 5.1CH audio signal, after - 39 - Capacitor C253~C258 coupling and filtering capacitor C259~C264 filtering, audio signals are sent to CN3 to send audio signal to AV board through CN3. Because DMN-8602 is BGA packaging, we cannot test IC pin, as for the chip about BGA packaging in future, the pin will not be noted and the output signal definition is as follows: E5_GPIO3: the pin that decode chip performs reset to CS4630. AO_MCLKOS: MASTERCLOCK signal. AO_SCLK: SERIAL CLOCK signal. AO_FSYNC: LEFT/RIGHT CLOCK signal. AO_D1, AO_D1, AO_D2: digital audio signal serial data jack. AO_IEC958: digital audio output (optical, coaxial). 2. Audio amplifying circuit (this part lies in AV board) The 6-channel audio analog signals transmitted from decode board are sent to U3, U4 and U5 through CN1 for amplifying, in which, A_R_OUT A_L_OUT is sent to U3 for amplifying, MIC board, through the MIC signal conveyed from CN6, is overlayed to the input end of U3 through R159 R160, and performs mixed amplifying with left and right channel of audio signal, the signals after being amplified through filtering, R_OUT L_OUT signal is divided into two ways: one way directly outputs to audio output terminal S5, the other way performs output sound source selection through U8 (LOOP_DECODER_C end is low level, R_OUT L_OUT signal outputs) to send to SCART terminal (SC1). After amplifying and filtering through U5, SUBWOOFER, CENTER signal outputs to audio output terminal S5 for output. After amplifying and filtering through U4, REAR_R, REAR_L signal outputs audio output terminal S5 for output. Audio amplifying circuit is mainly composed by operational amplifier, shown in the figure 3.2.2.2, take right channel signal amplifying as an instance, A_R_OUT signal arrives at reverse input end pin 6 of operational amplifier through R44, R45 for amplifying, and outputs from pin 7, in which C34, C35 are input and output filtering capacitors respectively, R43 is feedback resistor. R43 20K C32 151 A-12V 4 R45 4.7K + 7 5 R160 4558 U3B 8 1 + A_R_OUT C33 10u/16 - 6 R44 4.7K A+12V 15K C34 102 R50 R54 4.7K A_L_OUT R55 20K 4.7K 1 C36 151 A-12V 4 C38 102 C37 10u/16 + - 2 1 AV to OK_MIC C112 8 R159 15K + 3 0¦¸ Figure 3.2.2.2 Audio amplifying circuit - 40 - 4558 U3A A+12V 3. Digital audio signal output circuit Decode chip outputs digital audio signal (AO_IEC958) through R76 to decode board socket CN3, CN3 transmits this signal to AV board directly to input to optical terminal Op1 for output, at the same time, (AO_IEC958) also transmits through U5/R78/L5 to decode board socket CN3 and directly outputs the coaxial terminal S4 on AV board to output digital audio signal (coaxial signal). 4. Mute circuit Mute circuit is shown in the figure 3.2.2.3: R46 1K R47 47K R_OUT R_OUT 6,8 AMUTE 4,5 A-12V C35 102 Q3 3904 3906 5V_STB Q4 R49 10K C33 10u/16 + R53 R51 220 3.3k D3 1n4148 R52 + 3.3k R56 C39 1000u/16V 1K L_OUT R58 47K L_OUT 6,8 +3V3 5V_STB C40 102 Q5 3904 R60 2.7k Q6 3906 D4 1n4148 Q7 3906 + C37 10u/16 R62 MUTE 1 10K + R63 2.2K C47 1000u/10V Q8 3904 Figure 3.2.2.3 Mute circuit diagram Power-on mute: after power on, 5V_STB output is normal, Q4 base electrode is low level, 5V_STB arrives at mute pipe through Q4C E electrode to fulfill mute function, C39 charges, when the voltage drop of the two ends is more than 4.3V, Q4 cuts off, now panel begins working and machine enters standby state, panel MUTE pin outputs high level signal and transmits to R63 of AV board through decode to make Q8 Q5 saturated on, 5V_STB transmits to the mute pipe of each channel through C E electrode of Q5 to make audio output circuit in mute state to reach the purpose of power-on mute; when machine reads disc information or switches to other working mode, MUTE changes from high level to low level, mute circuit does not work, and audio output of the player is normal. Power-off mute: when machine enters standby state from power-on state, panel MUTE pin outputs high level signal and transmits to R63 of AV board through decode to make Q8 Q5 saturated on, 5V_STB transits to the mute pipe of each channel through C E electrode of Q5 to make audio output circuit in mute state to reach the purpose of mute. After power off, C47 discharges through Q7 to make mute pipe of each channel saturated on to realize the function of power-off mute. - 41 - 3.2.3 Video output circuit 1. Video signal output flow chart is shown in the figure 3.2.3.1: Low-pass filter Y L15 C237 C Pr/R U1 DMN-8602 C_O L16 C239 Y/G Pb/B Y_O Y/G_O L18 C245 Pr/R_O L17 C243 S_Y_OUT 2 S_C_OUT 4 G_Y_OUT 10 8 Cn5 R_V_OUT Pb/B_O L19 C248 12 B_U_OUT S_Y_OUT 2 S_C_OUT 4 G_Y_OUT 10 8 Cn2 R_V_OUT B_U_OUT 12 Q1, Q2 amplifying S-video 2 14 13 U7 74HC4053 15 4 5 13 R_V G_Y B_U R_Cr Q_13 Q_14 G_CR Q_15 amplifying B_Cr 3 1 SCART output terminal SC2_R SC2_G SC2_B SCART input terminal CVBS Video amplifying CVBS_O 6 V_OUT Component video terminal S4 V_OUT Video terminal S3 6 Figure 3.2.3.1 Video signal output flow chart 2. Filtering and amplifying circuit When the machine is playing again, decode chip U1 DMN-8602 reverts the disc information conveyed from loader into digital video signal, through D/A converter inside U1 DMN-8602, reverts digital video signal to analog video signal to output, analog signals are divided into 6 channels: chroma signal (C), brightness signal (Y), composite video signal (CVBS) and RGB signal. Shown in the figure 3.2.3.2, composite video signals, through video filtering circuit and amplifying circuit, perform filtering and amplifying to video signals and then output to AV board. VCC_VOUT_A R185 6.8K C249 *22PF CVBS R188 C251 180 *331 L20 1.8uH C250 220u/10 Q2 3904 + 2 C252 101 CVBS_O R189 6.8K 12 R184 470 Figure 3.2.3.2 Filtering and amplifying circuit 3. Video output circuit 5-channel video signals, after being filtered through filtering circuit, directly output to AV board for amplifying output. Video signal is sent to socket CN2 of AV board through Cn5, in which S_C_OUT S_Y_OUT signal, after being amplified by the amplifying circuit composed of Q1 Q2, directly transmits to S-video (S3) to output. One way of V_OUT signal is sent to composite video terminal S3 through R29 to output directly, the other way performs output selection (when LOOP_DECODER_C end is low level, V_ - 42 - Signal outputs) through U8 to output to SCART terminal (SC1). The 3-way component video signals of R_V_OUT, G_Y_OUT and B_U_OUT are sent to U7 for output selection (when LOOP_DECODER_C end is low level, R_V_OUT G_Y_OUT B_U_OUT signal outputs, when LOOP_DECODER_C end is high level, the component video signal inputted by the other SCART (input terminal) outputs). R_V G_Y B_ signals outputted through selection, after being amplified by the amplified circuit composed by Q13 Q14 Q15, output to component video terminal (S4) and SCART output terminal. 3.2.4 Audio input circuit The audio signals inputted by AV input terminal and tuner, through input switch circuit selection, audio signals performs A/D conversion through U17 Cs5340 and outputs serial audio data stream which transmits to U1 DMN-8602 digital audio input port, DMN-8602 performs coding to externally-inputted audio signal to transmit the signal after being coded to loader and controls loader and feed circuit through DMN-8602 to fulfill the record working of disc. 1. Audio input flow chart is shown in the figure 3.2.4.1: SC1_L_IN SC1_R_IN SCART terminal SC2_L_IN SC2_R_IN Tuner TV_IF 11 37 Front audio input CN3 38 40 U6 MSP3415 1 2 F_OUD10_IN_R 15 F_AUD10_IN_L BTSC_AINL 31 U11 4052 2 14 BTSC_AINR 41 2 NICAM processing 5 30 13 audio input switch 24 CN2 3 EXT_AUD10_IN_L A_L_IN A_R_IN 26 12 Rear audio EXT_AUD10_IN_R input S1 1 AV board part A_L_IN 24 A_L_IN 10 U17 CS5340 CN5 A_R_IN 7 AI_MCLKO AI_SCLK AI_FSYNC A_R_IN 26 2 Audio 8 A/D AI_DO conversion4 U1 DMN-8602 12 Figure 3.2.4.1 Audio input flow chart 2. Audio input working principle: take TV signal as an instance, other signals are the same on the whole. When the machine is set in TV signal input, TUN1 receives high frequency signal and then outputs audio signal after being processed. Tuner pin function introduction is shown in the following table: - 43 - PIN Name Function descr iption w orking voltage (v ) PIN Name Function descr iption w orking voltage (v ) 1 Vcc1 pow er supply pin 1 5 8 9 NC blank pin 0 2 BT channel selection pin (unus ed) 9.4 10 AGC AGC control pin (unused) 4.36/1.91 3 VCC2 pow er supply pin 2 5 11 2ND SIF audio signal output 0 4 SCL 3.63 12 VIDEO OUT video output 2.14/1.38 5 SDA data signal pin of IIC bus 3.63 13 VCC3 pow er supply pin 3 5 6 AS unused (gr ounding) 0 14 AUDIO OUT MONO audio signal output 2.44 7 AFC clock signal pin of IIC bus AFC control pin (unused) 1.42/0.9 3. NICAM processing circuit Audio signals output from pin 11 of TUN1, and also may output mono channel audio signal from pin 14. Now we do not use pin 14 to output mono channel audio signals. Audio signal TV_IF, after being coupled by C80 C81, arrives at NICAM decode IC U6 (MSP3415) for NICAM decode, at the same time, the audio input of SCART1 SCART2 also inputs to U6 for audio switch, and the audio signals after being switched are outputted by pin 30/31 of U6. The switch of this output sound source is decided by software; when the machine is set in TV signal input, BTSC_AINL and BTSC_AINR output the audio signal of TV set; the TV audio signals after being NICAM decoded output to UI for selection through pin 30, 31 of U6. 4. Audio input switch circuit Shown in the figure 3.2.4.2, U1 has 4 kinds of sound source input: front audio input (F_AUDIO), back audio input (R_AUDIO), audio signal (BTSC_AINR BTSC_AINL) inputted by NICAM decode IC and sound source or FM sound source used by LOOP function. Audio signals input from pin 1, 2, 4, 5, 12, 14, 15, 11 of U1, and then output from pin 3, 13 to audio A/D conversion circuit after switch. The sound source selection truth value table is shown as follows: C1 105 C2 105 C3 105 C5 105 +5V 7 BTSC_AINR 7 BTSC_AINL C4 104 16 EXT_AUDIO_IN_L BTSC_AINL F_AUDIO_IN_L EXT_AUDIO_IN_R BTSC_AINR 12 14 15 11 1 5 2 4 6 10 9 X0 X1 X2 X3 Y0 Y1 Y2 Y3 INH A B 8 VDD X Y 13 A_L_IN 3 A_R_IN U1 4052 -12V 7 -6.2V VSS VEE +5V +5V R8 4.7k C10 104 R5 1k R6 1k R7 4.7k ADC_SEL1 ADC_SEL0 Figure 3.2.4.2 Audio input switch circuit diagram - 44 - Sound source selection truth value table: B A ADC_SEL1 ADC_SEL0 SOURCE 1 1 1 1 R AUDIO 1 0 1 0 TUNER&SCART 0 1 0 1 F AUDIO 0 0 0 0 FM OR LOOP 5. Audio A/D conversion circuit Shown in the figure 3.2.4.3, the audio signals after being selected (A_L_IN A_R_IN) are outputted from pin 13, 3 of U1 to CN2 and then transmitted to decode board Cn5. The inputted audio signals directly input to audio A/D converter CS5340 (U17) for A/D conversion. Analog audio signals input from pin 16, 12, the digital audio signals AI_D0 after A/D conversion directly input to DMN8602 for coding and recording, and DMN8602 outputs this audio signal at the same time. Audio output circuit (output together with the played audio signal) outputs audio signal, which facilitates use to select something to record. In Audio V33_AIN_A A_L_IN A_R_IN R212 0 12 V33_AIN_A DV33 R186 6.8K *0 ADC_DIF R211 *0 ADC_DIV R122 U17 R124 6.8K 10 12 R213 0 C281 102 GND_AIN R210 12 DV33 /RST_A UDIO 5,12 R216 R217 9 1 16 10K 10K + C287 10u/16 L10 C282 R125 R123 B601 102 6.8K 6.8K 6 3 13 C289 104 V33_AIN_A AINL AINR RST M0 M1 10K MCLK SCLK LRCK SDOUT FILT+ VQ VD VL VA AIN_D R214 R215 22 *10K AI_MCLKO AI_SCLK AI_FSYNC AI_D0 GND_AIN 2 2 2 2 15 11 C285 + 104 REF_GND GND C288 104 2 7 8 4 14 5 C283 1u/50 C286 104 + C284 1u/50 CS5340 C193 + GND_AIN GND_AIN 10u/16 GND_AIN Figure 3.2.4.3 Audio A/D conversion circuit diagram 3.2.5 Video input circuit The video signals inputted by AV input terminal, S-Video terminal and tuner, through being selected by input switch circuit, video signals select through U14 U1 TVP5150 and perform A/D conversion, the video data stream is outputted to U1 DMN-8602 digital video input port. DMN-8602 performs code to externally-inputted video signal and transmits the signal after being coded to loader, DMN-8602 controls loader and circuit to complete the record working of disc. - 45 - 1. Video input flow chart is shown in the figure 3.2.5.1: R_Y_IN R_Y_IN 16 Rear S-video input R_C_IN R_C_IN 14 F_CVBS_IN F_CVBS_IN Front video input 18 CN2 Tuner Video amplifying TV_CVBS_IN 22 Rear video U10 4052 TV_CVBS_IN R_SC2_ SC1_CVBS_IN R_SC2_SC1_CVBS_IN 20 SC1 SC2 video input R_Y_IN 16 R_C_IN 14 Decode board part 12 11 U18 4052 F_CVBS_IN 11 18 V1_D0 1 13 U14 TVP5150 V1_D1 12 13 CN5 22 TV_CVBS_IN Video 2 input 3 mode selection Video D/A converter VI_D3 14 15 16 V1_D4 U1 DMN-8602 VI_D5 VI_D6 R_SC2_ SC1_CVBS_IN 20 V1_D2 17 18 4 VI_D7 Figure 3.2.5.1 Video input flow chart As for video signal input, take tuner input as an instance, when the machine is switching to TV signal input, tuner is controlled by IIC bus to perform audio channel selection or other function operation through firmware. Video signals output from pin 12 , through the amplified circuit composed of Q31/Q33, and amplify the video signals of TV set to input to decode board for selection. The definition of each video input signal on CN2 of Av board has TV_V1_IN (video signal transmitted from tuner), V3_IN (front composite video signal), R_Y_IN R_C_IN is chroma and brightness signal inputted by rear S-video, V2_IN is rear composite video signal input, this channel signal selects with SCART terminal and inputs to decode board through R_SC1_SC2_CVBS_IN pin (for the switch relationship with SCART, we will introduce in SCART terminal switch). 2. Video input switch circuit Shown in the figure 3.2.5.2, video input signals have: front video, rear video (includes SCART terminal input), TV signal input and rear SD-video (front terminal is not used in this player). This switch - 46 - Circuit is controlled by E5_GPIO32 E5_GPIO33 of U1 DMN8602 to realize different input selection, and the truth value table is shown as follows: R164 C205 474 39 12 R_Y_IN R160 C204 474 39 12V 12 F_Y_IN R156 C202 474 39 D11 6 1./ 2V W* C207 104 12 F_CVBS_IN R157 39 16 R161 39 39 12 14 15 11 R170 39 C208 474 C201 474 1 5 2 4 6 10 9 12 R_C_IN 39 R154 12 F_C_IN 39 12 TV_CVBS_IN C206 474 R168 X0 X1 X2 X3 VDD R165 13 X 3 Y Y0 Y1 Y2 Y3 INH A B 8 VSS VEE U18 4052 7 39 R_ 1 2 SC2_SC1_CVBS_IN R151 R169 R252 C209 474 R171 R172 39 39 39 39 12V SPDATA(B) SPLRCK(A) SOURCE 0 0 REAR_Y & C_IN 0 1 FRONT_Y & C_IN 1 0 R CVBS_IN & TV CVBS_IN 1 1 F_CVBS IN & R_SC2_SC1_CVBS_IN R246 10K R247 2 Q3 3904 E5_GPIOx32 3.3K R249 10K R250 Q4 3904 2 E5_GPIOx33 3.3K Figure 3.2.5.2 Video input switch circuit diagram 3. Video A/D conversion circuit Shown in the figure 3.2.5.3, video signals, after being selected by U18, directly input to pin 1, 2 of video coder U14 (TVP5150), under the control of system, U14 switches analog video signals to digital video signals, and adopts 8-bit parallel data means to input to UI DMN8602 for coding and recoding. SDA 13 1 SCL 18 U14 U18 TVP5150 3 17 VI_D1 16 VI_D2 15 VI_D3 14 VI_D4 13 VI_D5 12 VI_D6 11 2 VI_D0 24 VI_D7 VI_VSYNC Figure 3.2.5.3 Video A/D conversion circuit diagram - 47 - U1 DMN8602 3.2.6 Reset circuit 1. Reset circuit block diagram is shown in the figure 3.2.6.1: U8 FLASH 12 U6 EM6353A E5_GDIO3 10 U15 Cs4360 37 U10 TSB41AB 8 U14 TVP5150 SYS_RST E5_GDIO1 U1 DMN-8602 E5_GDIO7 Loader RST_AUDIO U5A 74AHC T14 C144 R71 9 U17 Cs5340 22 U10 MSP3415 RST_AUDIO RST_BTSC Main panel Q1C11 RESET 4 UPD16316 Figure 3.2.6.1 Reset circuit block diagram 2. System reset circuit Shown in the figure 3.2.6.2, when machine enters working mode from standby, V33 voltage increases, pin 1 of U6 outputs a level signal that maintains 25MS to reset system and FLASH; after system reset finishes, U1 outputs multi-channel reset signal to other subsidiary circuit for reset (loader, CS4360, TSB41AB, TVP5150). V33 VCC R155 0 R163 10K 1 2 /SYS_RST U6 Em6353AX1SP3B-3.1 3 R162 *10K Figure 3.2.6.2 System reset circuit diagram - 48 - 3. Audio reset circuit Shown in the figure 3.2.6.3, after machine enters working mode from standby, the voltage on two ends of C144 cannot change suddenly, pin 1 of U5 inputs high level during the course when C144 is charging, so pin 2 of U5 outputs low level; after C144 is fully charged, voltage of pin 1 of U5 changes to low level, and pin 2 of U5 keeps outputting high level. The reset time of this circuit is decided by C144 and RC of R71. VCC C144 10u/16 + U5A 74AHCT14 1 2 R71 10K R72 0 /RS T_AUDI O Figure 3.2.6.3 Audio reset circuit diagram 3.2.7 IIC bus control circuit IIC bus is a kind of simple, dual-direction and synchronous serial bus developed by PHILIPS company, only two lines (serial clock line and serial data line) are required to transmit information among the elements that connect bus. This bus is high-performance serial bus, with the judge and high/low speed device synchronous function required by multi-system and application is very wide. SDA SCL bus control connecting diagram is shown in the figure 3.2.7.1: U1 DMN-8602 decode chip U15 Cs4360 audio D/A U9 24C16 EEPROM AV board U6 MSP3415 NICAM processing U9 24C16 EEPROM AV board U2 8563 clock IC Figure 3.2.7.1 SDA SCL connecting diagram - 49 - Tuner 2. Data transmission regulation of IIC bus Once data transmission of IIC bus from main player is called a frame, which is composed of start initiating signal, address code, some data byte, response bit and stop signal. When communication starts up, it sends out an initiating signal (when SCL line is high level, SDA line produces a descend edge), address code of subordinate machine (8-digit) and read-write signal; when communication stops, main machine sends out a stop signal (when SCL line is high level, SDA line produces a ascend edge). During the course of data transmission, when SCL line is high level, data of SDA line must be assured stable; transmission of one byte’s data, receiver must send out a response signal. Transmission speed of bus is 100kbps (standard) 400kbps (high speed). When adopting +5V power to supply power, input level is ruled as: VILmax=1.5V, VIHmin=3V; when adopting wide power voltage, level is ruled as VILmax=1.5VDD, VIHmin=3VDD. 3. This player adopts the IIC bus defined by DMN8602 to control each function circuit. For the sake of understanding, we suppose DMN8602 is the main unit, other chips are subordinate unit, the main unit sends control information and receives the status report information sent back by subordinate unit, and sends new information according to report information to the function circuit that needs control. The subordinate unit may perform the control information sent from main unit and report the status information of this unit to main unit to realize the control function of I2C bus through the dual-direction information exchange course. In which, 24C16 is status memorizer used to store the user-set information required to save to facilitate the usage next time when power on, the main functions of this player may be controlled by IIC bus (such as, video A/D conversion, audio D/A conversion, tuner channel selection, clock, user information, and NICAM decode). 3.2.8 Voltage regulating circuit 1. 1.8V voltage regulating circuit, shown in the figure 3.2.8.1, is mainly provided for the usage of the logic circuit inside decode chip, 2.5V power inputs from pin 1 of U11, after being voltage regulated by 2_5V V18 + C184 220u/16 ADJ R145 *1K 4 GND 5 2 VC U11 PQ018EZ02/PQ070XZ02 1 3 VIN VOUT C185 104 R146 *2.2K Figure 3.2.8.1 1.8V voltage regulating circuit - 50 - + C182 330u/16 C183 104 Voltage regulating IC Po018, outputted by pin 3, the output voltage of this voltage regulating circuit may be adjusted through R145 R146. 2. 3.3V voltage regulating circuit, shown in the figure 3.2.8.2, mainly supplies power for decode chip, FLASH and SDRAM. 5V power inputs from pin 3 of U12, through being voltage regulated by voltage regulating IC Lt1117, is outputted by pin 2, output voltage of this voltage regulating circuit can be adjusted through R147. DV33 VCC L9 *FB V33 U12 LT1117- 3. 3 VIN VOUT 2 ADJ 3 C190 + 104 1 C189 104 R147 *1K C191 103 C192 104 C188 47u/16 R148 0 Figure 3.2.8.2 3.3V voltage regulating circuit diagram 3. 2.5V voltage regulating circuit, shown in the figure 3.2.8.3, mainly supplies power for decode chip, 3.3V power inputs from pin 1 of U13, through being voltage regulated by voltage regulating IC Pq025, is outputted by pin 3, output voltage of this voltage regulating circuit can be adjusted through R149 R150. V33 U13 PQ025EZ01 C196 220u/16 C197 104 ADJ 3 R149 *1K 4 5 2 C143 *104 + VOUT GND VIN VC 1 V25 R150 *1K Figure 3.2.8.3 2.5V voltage regulating circuit diagram - 51 - + C194 330u/16 C195 104 3.2.9 USB jack circuit 1. DMN-8602 integrates USB module circuit inside, shown in the figure 3.2.9.1, and it can directly read external USB device. After the integrated USB module circuit inside DMN-8602 detects external equipment connection, it applies for intermission continuously to the control module of DMN-8602 to wait for the response of DMN-8602 control module; after control module gives response, USB module circuit achieves internal bus to read data of external equipment in directly. C167 104 USB VCC J4 2 USB_D0- 2 USB_D0+ R134 R139 R143 R144 15K 15K 22 22 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 USB_BDM0 R137 R140 USB_BDP0 FB34 FB35 0 0 B601 B601 *7P2.0 mode) the in used reserve(no 2 USB_OC0 2 USB_PO0 mode) the in used reserve(no Figure 3.2.9.1 USB circuit diagram 2. Introduction to pin of USB is shown in the following table: Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal 1 +5V 1 +5V 3 Data+ 3 Data- 2 Data- 2 Data+ 4 Grounding 4 Grounding 3.2.10 DV jack circuit In DV player and DVCAM player, you will see a flat 4P or 6P port, which is usually called DV digital jack and named as i.LINK by SONY company. It accords with IEEE 1394 standard and has the following features: Directly transmit digital data, so there is no picture and audio distortion. Only one cable is needed to make video, audio and control signals perform data multi-channel transmission. Hot plugging and unplugging function may perform data transmission among multiple data TSB41AB1: it has DV monitoring circuit inside, which can automatically detect DV input. System selects DV mode, DMN-8602 communicates with TSB41AB1, when DV jack has signal input, signals inputted by DV input to pin 28-31 of TSB41AB1, after being processed by TSB41AB1, then they are sent to DMN-8602 for coding and decoding. - 52 - 3.2.11 Loader jack circuit A complete “loader components” is used in this machine, which includes servo circuit, laser head and mechanical part. Working principle is the same with that of other players, so we will not repeat here. The following is loader pin introduction shown in the following table: Pin Name 1 /RESET 2 GND 3 DD7 4 Description Pin Name Reset reset s ignal 21 n/c Ground ground 22 GND Data 7 23 /IOW DD8 Data 8 24 GND Ground ground 5 DD6 Data 6 25 /IOR Read Strobe read gating 6 DD9 Data 9 26 GND Ground ground 7 DD5 Data 5 27 IO_CH_RDY I/O ready 8 DD10 Data 10 28 ALE Addres s Latch Enable 9 DD4 Data 4 29 n/c 10 DD11 Data 11 30 GND 11 DD3 Data 3 31 IRQR Interrupt Request 12 DD12 Data 12 32 /IOCS16 IO ChipSelect 16 13 DD2 Data 2 33 DA1 Addres s 1 14 DD13 Data 13 34 n/c 15 DD1 Data 1 35 DA0 Addres s 0 16 DD14 Data 14 36 DA2 Addres s 2 17 DD0 Data 0 37 /IDE_CS0 (1F0-1F7) 18 DD15 Data 15 38 /IDE_CS1 (3F6-3F7) 19 GND 39 /ACTIVE Led driver indicator light drive 20 KEY 40 GND Ground ground Key Description Not connected blank Ground ground Write Strobe w rite gating Not connected blank Ground ground Not connected blank Ground ground 3.2.12 Control panel 1. Control panel block diagram is shown in the figure 3.2.12.1: VFD VFD_DIO Working indication circuit 5MHZ clock circuit Y1 32.776MHZ clock circuit Y2 VFD_CLK U1 UPD16316 VFD_STB To decode board CN4 D_HOST P_CTL_PSW Reset circuit Remote control receiver Panel button Figure 3.2.12.1 Control panel circuit block diagram - 53 - 2. Reset circuit Shown in the figure 3.2.12.2, it is a low level effective reset circuit, after power on, VDD power charges C11 through R24, the voltage on two ends of capacitor cannot change suddenly, so Q1 base electrode is high level, Q1 is saturated on, RESET end outputs low level; the charge course of capacitor makes the electric potential of Q1 base electrode decreases quickly, Q1 cuts off, RESET end outputs high level and reset finishes. VDD 1 C11 4.7u/16 R14 10K 2 + R24 10K RESET R22 4.7K Q1 8050D C17 102 D5 1N4148 Figure 3..2.12.2 Reset circuit 3. Remote control circuit The power supply of remote control circuit uses 5V_STB power to ensure the remote control receiver can receive the instruction transmitted from remote controller in standby status. The remote control instruction received by remote control receiver directly transmits to panel IC for remote control decode. In standby status, panel IC only receives the wake code transmitted from remote controller. 4. Standby working status After power on, P_CTL_PSW control end is low level, Q2 is saturated on to make the standby light of subsidiary board on and perform standby instruction, now power board main power +12V, +5V, +3.3V have no voltage output, 5V_STB and other supplementary winding power outputs normally to provide reset circuit to reset U1 (pin 4 of U1) at the same time of power on, panel IC standby module enters working status, in which Y2 and the clock circuit inside IC produce clock signal to realize the time display and timing function in standby status, Y1 is externally connected clock of D16316. In standby status, panel control IC and display screen have working power, so the display screen of machine can normally display the time in standby status. 5. Working status after power on When users are pressing POWER button on the panel or remote controller, UPD16312 enters normal working status, P_CTL_PSW ens inputs high level, panel standby indicator light turns out, the - 54 - Blue light of panel receives power and is on, main power output of power board is normal, each circuit of the player begins working, machine displays power-on picture and enters working status. After power on, audio circuit will produce noise in the course of power on, to avoid noise being amplified outputted, panel IC (46PIN) outputs MUTE signal to mute circuit (working principle will be introduced in mute circuit), after decode system works, it communicates with panel IC to fulfill functions of panel display and remote control function operation. 3.2.13 AV circuit AV circuit is mainly in charge of audio/video signal input and output, audio/video amplifying circuit, audio input switch circuit, NICAM processing circuit, clock circuit, SCART terminal input and output control circuit. 1. AV circuit block diagram is shown in the figure 3.2.13.1: OPTICAL Optical terminal SPDIF_OUT B_U B_Cr R_V R_Cr G_Y G_Cr V_out Video amplifying B_Cr S-video Cn1 Output V_OUT S_Y_OUT input/ output and control circuit R_Y_IN Rear video terminal input R_C_IN V2_IN SC1_CVBS_IN U10 4052 SC2_CVBS_IN R_SC2_SC1 _CVBS_IN CN2 F_CVBS_IN Front F_AUDIO_IN_L input F_AUDIO_IN_R Input CN3 AV REAR_R REAR_L CENTER U4 SUBWOOFER U5 S5 R_OUT A_L_IN AUDIO_IN_L Audio output terminal A_R_OUT A_L_OUT S2 G_Cr SCART V_OUT TV_CVBS_IN TV_IF Component R_Cr video terminal S_C_OUT Video amplifying Tuner U3 S1 L_OUT rear audio input AUDIO_IN_R U5 MSP 3415 Mute circuit MIC signal CN6 BTSC_AINR U1 4052 R_L_IN BTSC_AINL TV_IF Figure 3.2.13.1 AV circuit block diagram 2. Clock circuit: shown in the figure 3.2.13.2, clock circuit mainly provides a clock signal for system, which can record year, month and date. Power supply means of External battery or standby power is adopted, U2 is clock IC with working voltage between 2.0 and 5.5V, after machine power off, battery Bt1 supplies power for U2 through D2, after the player power on or enters standby status, 5V_STB supplies power for U2 through D1. D1 D2 makes a separation function in the circuit. - 55 - 5V_STB D1 1N4148 1 2 3 4 D2 LL60P X1 32.768KHZ/20PF BT1 3V C30 20PF C31 20PF(open) U2 M41T80(OPEN)/PCF8563 8 X1 VCC 7 X2 SQW 6 INT SCL 5 GND SDA IIC_SDA 1,7 IIC_SCL 1,7 C28 104 Figure 3.2.13.2 Clock circuit diagram 3. SCART output mode control circuit (1) CVBS/RGB output control circuit: when the machine is in power-on status, SCART terminal is required to output RGB signal, we switch the output mode if machine in RGB state, shown in the figure 3.2.13.3, decode chip E5_GPIOX4 outputs high level to make Q28, Q26 saturated on, SC1_CVBS_RGB_SEL end outputs high level; when output mode of the machine is composite video, decode chip E5_GPIOX4 outputs low level to make Q28, Q26 cutoff, SC1_CVBS_RGB_SEL end outputs low level; when machine enters standby status (machine enters LOOP working mode), +5V power is 0V, Q29 cuts off, Q27 is controlled by VI_FSS end level of SCART input terminal, so SC1_CVBS_RGB_SEL end is controlled by VI_FSS end, now output mode is decided by external input source. Q23 5V_STB S8050 R146 470 R149 510 Q26 3906 R150 3.3K VI_FSS R155 75 R152 10 SC1_CVBS_RGB_SEL R156 1K R151 1K +5V Q27 3904 R157 3.3K Q28 3904 Q29 3904 Figure 3.2.13.3 CVBS/RGB output control circuit diagram - 56 - E5_GPIOx4 1 (2) Screen display ratio control circuit When the machine is playing discs with different ratio pictures, if SCART terminal output is needed, we set “screen ratio setup” item in machine setup page according to requirements, shown in the figure 3.2.13.4, E5_GPIOX2 end of decode chip outputs level to make Q17, Q20 on, AV_CONTROL end outputs the voltage required by screen ratio switch to TV set. When machine enters standby status (machine enters LOOP working mode), AV_CONTROL ens is controlled by pin 8 of SCART input terminal. Q17 s8050 AV_CONTROL Function select (AV CONTROL) Pin8 E5_GPIOx2 AV mode L Levele of PIN8 (AV_COMTROL) +12V R192 47k R114 High(9.5-12V) 12mA 1k 4mA 5V_STB Wide-screen 16:9 H Mid(5-8V) C94 220u/16 R118 1.5k + R128 15k 0.12mA LOOP_DECODER_C R130 15k Figure 3.2.13.4 Screen display ratio control circuit - 57 - R193 4.7k Q19 3904 D6 1N4148 R120 *4.7k Q20 3904 AV_MODE_SEL1 7 E5_GPIOx2 1 SC1_L_OUT SC2_L_IN X SC2_CVBS_IN SC2_R_IN SC1_R_OUT Z L_OUT X0 Y1 V_OUT Y0 Z1 Z0 R_OUT Audio output terminal TV_MOMO VI_IN Video output terminal Tuner video Audio output terminal TV_MOMO 4. SCART circuit block diagram is shown in the figure 3.2.13.5: SC1_CVBS_IN Y1 Y0 SC1_R_IN Z0 U9 74HC4053 X Video amplifying Q21 U6 MSP3415G Y SC2_R_OUT Z TV_IF SC1_CVBS_IN SC2_CVBS_IN SCART2 IN PUT SC1_L_IN X1 Z1 SC2_L_OUT SC2_CVBS_OUT X0 V2_IN Rear video U10 74HC4052 Video amplifying Q34 Q35 R_SC1_SC2_CVBS_IN Decode board U18 SC2_R R_V R_Cr SC2_G SC2_B U7 74HC4053 R_V_OUT G_V_OUT B_V_OUT Decode board component video output G_Y AV_CONTROL Decode board control signal B_Cr B_U RGB output terminal VIFSS Decode board control signal G_Cr R G B amplifying circuit Q13 Q14 Q15 E5_GPIOX4 E5_GPIOX1 E5_GPIOX2 CVBS RGB output switch circuit SC1_CVBS_RGB_SEL AV_CONTROL Picture display ratio control circuit, LOOP_DECODER_ LOOP_DECODER_C U8 U9 U7 SC2_L_IN SC2_R_IN SCART1 OUT PUT - 58 - U8 74HC4053 Figure 3.2.13.5 SCART circuit block diagram X1 SC1_CVBS_OUT Video amplifying Q22 Y (1) Audio, video signals output flow chart and working principle When the player is in DVD playback status or external input status, LOOP_DECODER_C end is low level, CVBS/RGB switch circuit and screen display ratio control circuit are both controlled by the control signals outputted by decode. Audio/video signals input to U8 and output from pin 14, 15, 4 of U8, audio signals are directly sent to SCART output terminal for output, video signals are amplified through the amplified circuit composed of Q22 and then sent to SCART output terminal for output. There is one group of input port in output terminals. Suppose output terminal is connected with TV set, audio/video signals sent from TV set input from input port to NICAM decode IC for selection, and input to main board for record usage. Video signals select through U10, Q34/Q35 amplifies and inputs to main board for record usage. Audio/video signals sent from tuner output through U9 to the output port of SCART input terminal to connect decoder or other re record devices. Component video switches through U7 and we have introduced in video output part. Remark: this player does not use DECODER function; to be easy to understand, we define SCART (SC2) is input terminal, and SCART (SC1) is output terminal. (2) LOOP working mode signal flow chart and working principle When the player is in standby status, the machine enters LOOP working mode (only when SCART input and output are inserted at the same time, there is LOOP working mode function), LOOP_DECODER_C end is high level; pin 14, 15 of U8 output the audio/video signals inputted by SCART input terminal to make signals of input terminal connect to SCART output terminal through U8 for output. There is one group of input port in output terminal. When output ens is connected with TV set, audio/video signals sent from TV set input from the input port, after selection through U9, output to the output port of “SCART input terminal” for output. The component video signals inputted by SCART input terminal output to the amplified circuit composed of Q13 Q14 Q15 through U7 for output. When LOOP is working, CVBS/RGB output control circuit and screen display ratio control circuit do not work and are totally controlled by input source. Remark: LOOP function is a switch function, in this period, the machine has no contact with external signal, but is only used as a switch port. To be easy to understand, we define Sc1 as output terminal, and Sc2 as input terminal (different from principle diagram, only for reference). 5 SCART terminal function selection is shown as the following table: PIN Definition Description Signal direction PIN Definition Description 1 SC1_R_OUT right channel audio output OUT 12 NC unused 2 SC1_R_IN right channel audio input IN 13 GND R_Cr signal ground 3 SC1_L_OUT left c hannel audio output OUT 14 NC unused 4 GND audio ground w ire 15 R_Cr component video R_Cr signal output - 59 - Signal direction OUT 16 SC1_CVBS_RGB_SEL CVBS/RGB control output IN 17 GND ground w ire component video B_Cr signal output OUT 18 GND CVBS ground w ire AV_CONTROL scr een ratio control output OUT 19 SC1_CVBS_OUT video output OUT 9 GND G_Cr signal ground 20 SCI_CVBS_IN video input IN 10 NC unused 21 GND ground w ire 11 G_Cr component video G_Cr signal output 5 GND B_Cr signal ground 6 SC1_L_IN left c hannel audio input 7 B_Cr 8 OUT OUT 6. SCART input terminal pin function introduction is shown in the following table: PIN Definition Description Signal direction PIN Definition Description 1 SC2_R_OUT right channel audio output OUT 12 NC unused 2 SC2_R_IN right channel audio input IN 13 GND R signal ground 3 SC2_L_OUT left c hannel audio output OUT 14 NC unused 4 GND audio ground w ire 15 SC2_R R signal input IN 5 GND B_Cr signal ground 16 VI_FSS scr een ratio control input IN 6 SC2_L_IN left c hannel audio input IN 17 GND ground w ire 7 SC2_B B signal input IN 18 GND video ground 8 AV_CONTROL scr een ratio control 19 SC2_CVBS_OUT video output OUT 9 GND G signal ground 20 SC2_CVBS_IN video input IN 10 NC unused 21 GND ground w ire 11 SC2_G G signal input IN 3.2.14 MIC circuit 1. MIC circuit block diagram is shown in the figure 3.2.14.1: MICI IN VR1 U1A Amplifying MIC2 IN Potentiometer U1B MIC_OUT Amplifying AV board MIC_DET MIC mute circuit Figure 3.2.14.1 MIC circuit block diagram - 60 - Signal direction 2. MIC mute circuit Shown in the figure 3.2.14.2, microphone detect is fulfilled through judging the level change of microphone socket MIC_DET pin; when microphone is inserted, MIC_DET +12V voltage suddenly decreases to 0V, C13 C14 in the circuit discharge through Q3 to make Q3 continue on, MIC_DET end keeps outputting high level to MIC signal in mute. For the electric charge of C13 C14 discharges quickly, after a period, MIC_DET end outputs negative voltage and MIC signal may output normally. The delayed time may be changed through changing the RC constant of C14 C13 R17 R19. D2 1N4148 R17 101 C14 273 J1 3 2 4 1 1K MIC_DE T R24 562 D1 1N4148 R19 101 R18 5.6K I NIC1 M R22 39406 Q AV_BOARD R25 47K 39304 Q 2N3906/TO C13 273 +12V 2N3904/TO -12V J2 3 2 4 1 L3 FB C4 1U U1 I NIC2 M L4 R5 FB 1K Figure 3.2.14.2 MIC mute circuit diagram 3. Amplifying circuit Shown in the figure 3.2.14.3, the MIC signals inputted by MIC1, MIC2, through filtering circuit, input to pin 3 of U1 and then output from pin 1 after being amplified by U1A, input to potentiometer for volume adjustment, input to pin 5 of U1 for the second time amplification, R11 is feedback resistor and VR1 is potentiometer. R11 6.2K C11 100P -9VA 5 1 10U CE5 1 2 R14 1K MIC_ OUT 2R9 4.7K 8 + 7 + 21 4558 + 6 50K(C) CE4 - 3 4 VR1 R10 15K R12 391 U1B 10U +9VA C12 R13 47K Figure 3.2.14.3 Amplifying circuit diagram - 61 - 102 3.2.15 Power circuit 1. Power circuit block diagram is shown in the figure 3.2.15.1: Rectification, filtering -12V Rectification Power grid filtering Transformer Absorption loop Protector tube Switch IC Rectification, B+12V filtering 12V voltage regulating Rectification, filtering 3.3V voltage regulating Rectification, filtering 5V voltage regulating +12V +3.3V 5VSTB +5V +2.5V -25V FL+ FL- Rectification, filtering Photoelectric coupler D16 B+12V V-CRL Power socket TLV 431 Sampling circuit Standby control circuit P-CTL Figure 3.2.15.1 Power circuit block diagram 2. Working principle: after city power is inputted, through protection circuit and power grid filtering circuit, it directly enters the rectification circuit composed of D9 D12, in which protection circuit has over-voltage, over-current and temperature protection circuit. After being rectified, city power changes to DC current (the effective value is 1.4 times of city power, that is 300V) and is rectified by CE5. 300V power is divided into two ways: one way, through R6 voltage drop, is supplied to the start pin of switch module (IC1_6/IC6_4), the other way, through the 24 winding of transformer, arrives at the power pin of switch module (IC1_1/IC6_2) to make transformer perform the storage and discharge of energy through the internal switch pipe. When discharging energy, reverse peak voltage will produce, to prevent damaging the MOS pipe in switch module, the absorption loop protects MOS pipe. 6-7 winding is sampling winding, when the primary winding of transformer is discharging energy, the induction current forms between secondary winding and sampling winding, and induction voltage forms on the two ends of each secondary winding, after being rectified through secondary rectification diode, provides the required DC power for each circuit of the player. For power wave is large, to provide stable DC output, one winding of output end, after rectification and filtering (+5V or +3.3V generally), performs sampling, which is fulfilled by IC3 and the sampling circuit composed of the peripheral); when output voltage is on high side, IC3A K is on to make the light emission diode inside IC2 emit light to control the photo triode inside IC2, CE is on to change the space occupation ratio of switch pipe control end to make the output voltage become low, or else output voltage is on high side. - 62 - 3. Working principle for standby switching to power on Power-on standby: 5V_STB is supplied to panel IC13616 to make panel circuit begin working, display screen displays time, P_CTL pin of panel IC outputs low level to V_CRL end output low level, power of +3.3V +12V +5V cannot output (other power is normally supplied during this period), and machine enters standby status. After panel or remote controller inputs power-on instruction, P_CTL pin of UPD16316 outputs high level to make B+12V arrive at the switch control circuit of +3.3V, +12V, +5V through C-E electrode of Q9. Q2/Q7/Q11 is on, +3.3V +12V +5V output is normal, and the player enters working status. 4. Working principle On/off control: when the player is in standby mode, P_CTL is low level, shown in the figure 3.2.15.2, Q6 cuts off to make Q9 cutoff, V_CRL end is low level, Q10 and Q11 cutoff, +12V has no power output, and the machine enters standby status. When power on, P_CTL is high level, Q6 is on, and Q9 is on at the same time, V_CRL end is high level, Q10 and Q11 are both on, +12V has power output and machine enters working status. Voltage regulating principle: when output voltage is on high side, shown in the figure 3.2.15.2, the control pin voltage of IC4 (in normal conditions, control voltage, after R13/R12 partial voltage, is 2.5V) is on high side (more than 2.5V), cathode and anode of IC4 is on to make Q10, Q11 cutoff, now load power is supplied by CE16 discharge, after discharging, power is on low side, IC4 control pin voltage is on low side, anode and cathode disconnect, Q10 and Q11 resumes on status to supply power for load, this the repeat on/off course reaches the purpose of voltage regulating. V_CRL end also controls the switch control circuit of +5V +3.3V at the same time, and its on/off course and voltage regulating principle are the same with +12V. +5V is controlled by Ic3 and no voltage regulating circuit is added. Figure 3.2.15.2 Switch control, voltage regulating circuit diagram - 63 - Section Three Servicing Cases 3.3.1 Servicing cases [ Example 1 ] Symptom: power not on Description: after inserting power plug, power indicator light is not on, picture of the player has no output, panel has no screen display , panel buttons have no function. Analysis and troubleshooting: according to trouble description, we can judge that trouble lies in power or decode part, use DC level of multimeter to test voltage of two ends of CE5, normal voltage is about 300V and test result is normal, then test pin 4 of IC6 and it is 0V, which is about 16V in normal conditions, after power off, use multimeter to test resistence to ground of pin 4 of IC6 and it is 0 ohm, after changing IC1 KA5L0380, trouble is removed. [ Example 2 ] Symptom: player not switch on Description: after inserting power plug, power indicator light is on, press POWER button, power indicator light is off but the player has no power-on picture output Analysis and troubleshooting: firstly test power supply and find that +3.3, +5V, +12V have no voltage output, so we preliminarily judge that trouble lies in standby control circuit. Shown in the figure 3.3.1.1, test V_Crl end and find that voltage is 0V, test P_CTL end and it is high level (normal), test Q9E electrode voltage and it is 13V, so we doubt that Q9 has trouble, after changing it, trouble is removed. B+12V V_Crl Q9 3906 R27 1/k6W R16 P_CTL 1.2k Q6 3904/9014 Figure 3.3.1.1 Standby circuit diagram - 64 - R26 1.2K [ Example 3 ] Symptom: machine down after power on Description: after inserting power plug, power indicator light is on, picture of the player has output, but after pressing POWER switch, HELLO always displays and panel buttons have no function. Analysis and troubleshooting: troubleshooting of this type of trouble is difficult; when loader, decode board, AV board, I2C bus and each voltage is abnormal, HELLO will display and the player will get down. It is easy to use substitution method to repair this type of machine. Firstly judge that which board has caused the trouble, then repair that board, which will be easier. Firstly use multimeter to test loader power supply 5V, 12V. When testing 12V, this voltage displays 0. This voltage is supplied by power board to AV board audio amplifying and loader. When checking this type of trouble, firstly use disconnection method, if rear stage is disconnected, load voltage restores to be normal, it means that trouble is caused by rear stage load; if load voltage is still 0, check power board; if voltage restores to be normal after disconnecting loader, it means that the short circuit of loader causes that there is 12V power supply, loader cannot start up, so machine will be down after power on; after changing loader, trouble is removed. [ Example 4 ]Symptom: no sound Description: when playing DVD, switching external signal and receiving TV signal, there is no sound. Analysis and troubleshooting: the reason to cause this trouble is that the common channel of sound is blocked. Use oscillograph to test AV board C33, C37 and there is audio signal output, but output terminal has no sound output. Because other channels also have no sound output, we preliminarily judge that trouble lies in mute circuit, use multimeter to test mute circuit and MUET is high level, which should be negative voltage when in normal playback, which means that mute circuit has started up. This mute circuit is divided into power-on mute and power-off mute circuit, if any one of the two has trouble, incorrect mute phenomenon will appear. After testing, we find that MUTE_1 end is high level (low level when playing normally, high level when power on), this signal is controlled by pin 47 of panel U1 (UPD16316), after changing IC (UPD16316), trouble us removed. [ Example 5 ] Symptom: no sound output when receiving TV signal Description: when playing DVD disc normally or using external signal input, sound and picture output is normal. When switching TV signal input, image output is normal. Analysis and troubleshooting: TV signal sound is outputted by pin 14 of AV board high frequency tuner to AV board U6 for NICAM processing, then outputted by pin 30, 31 of U6 and sent to U1 for switch input to decode board for audio processing. Use oscillograph to test pin 14 of AV board tuner and output is normal, pin 30, 31 of U6 has no waveform output, which means that this IC does not work normally, firstly test power supply of U6 and it is normal, test clock of U6 (two ends of X2 crystal oscillator have no oscillation waveform), after changing X2 (18.432MHZ crystal oscillator), trouble is removed. - 65 - [ Example 6 ] Symptom: machine down Description: after inserting power plug, power indicator light is on, picture of the player has no output, panel has no screen display, panel buttons have no function. Analysis and troubleshooting: firstly test power supply conditions, and each group of power supply voltage is normal, then use substitution method: firstly judge which board has caused the trouble, then repair the trouble board. We use substitution method to judge that the trouble in main panel causes the machine down, which has the following aspects: clock is not correct, reset circuit cannot work normally, main panel U1 (UPD16316) cannot work normally, shown in the figure 3.3.1.2, use multimeter to check U1 (UPD16316) and voltage of each pin is normal, use oscillograph to test 5MHZ crystal oscillator and there is no oscillation frequency, after change the crystal oscillator with the same specification, trouble is removed. UPD16312 Y1 5MHZ/20pF C6 30PF/0603 C7 30PF/0603 Figure 3.3.1.2 Clock circuit diagram [ Example 7 ] Symptom: clock not saved Description: after power off each time, screen of panel does not display the local time Analysis and troubleshooting: this player is with RTC function, only when local time is well set, power on after power off each time, the local time will be kept. For this type of machine, we start from AV board RTC circuit troubleshooting, use oscillograph to test X1 32.768KHZ crystal oscillator, and there should be oscillation waveform when in normal conditions, but there is no waveform at this time, after changing crystal oscillator with the same specification, trouble is removed. [ Example 8 ] Symptom: picture of the player has mosaic when switching in external input Description: when player is switching from normal playback to external signal input, TV picture appears disturbance, no external input image, but there is sound output. Analysis and troubleshooting: according to trouble description, we can judge that trouble appears in externally-inputted video processing circuit, firstly test each power supply voltage of decode board U14 (TVP5150) and it is normal, use oscillograph to test clock signal of P5, P6, and pin 6 has no waveform output, but it should have 14.31818MHZ waveform output in normal working condition, after changing crystal oscillator with the same specification, trouble is removed. - 66 - [ Example 9 ] Symptom: machine down when searching TV signal Description: machine down each time when searching TV signal, that is, panel button and remote controller have no function Analysis and troubleshooting: shown in the figure 3.3.1.3, machine will be down when receiving TV signal, and this trouble is in AV board high frequency tuner and its peripheral circuit, use multimeter to test voltage of power supply pin (pin 1) and I2C bus pin (pin 5, 6) of high frequency tuner and the real test value is that IIC bus pin voltage is 3.3V and tuner power supply pin (pin 1) voltage is 0V (power supply pin voltage is 5V and IIC bus pin voltage is 3.3V in normal conditions). According to circuit principle, power supply of frequency tuner is provided by power board, +5V is supplied to the power supply pin of high frequency tuner through (FB1), observe carefully and find that FB1 inductor has been broken to make high frequency tuner have no working voltage to make it cannot work, so machine down when searching channels, after changing elements with the same specification, trouble is removed. BT VCC2 SCL SDA AS AFC NC NC AGC 2 S2ND n IF d SIF Oiudteo OUT V VIDEO VCC3 Ouudtio A 1 2 VCC_TUNE R C11 103 R14 *0 C14 104 R15 0 IIC_SCL 5 IIC_SDA 6 B 1 1 0 0 7 8 +5V + 3 4 L1 FB C13 2200uF A 1 0 1 0 ADC_SEL1 1 1 0 0 ADC_SEL0 1 0 1 0 SOURCE R_AUDIO TUNER&SCART F_AUDIO LOOP OR FM A+12V 9 R181 330K 10 11 12 TV_IF C29 Q31 3904 13 V1_IN 14 TUN1 JS-6B2F/L121-D5 7 104 R20 0R/*4.7K R21 *10K C20 *102 Q33 3904 8 + VCC1 C12 103 TV_MONO C19 *4.7u/ 50 R182 150K R190 R183 4.7k 4.7k TV_MONO 7,8 Figure 3.3.1.3 High frequency tuner circuit diagram [ Example 10 ] Symptom: no external sound Description: when playing DVD, sound and picture are normal, when switching external, there is picture but no sound - 67 - Analysis and troubleshooting: this kind of trouble mainly lies in external input audio signal processing circuit. Check from rear stage circuit of AV board U1, switch the machine in rear audio input state, use oscillograph to test pin 3, 13 of AV board U1 and there is audio signal output, then test pin 10, 12 of decode board U17 (Cs5340) and there is also audio signal input, but pin 4 of U17 has no digital signal output. Test each pin voltage of U17 (Cs5340) and it is normal, so we doubt that U17 has trouble, after changing U17, trouble is removed. [ Example 11 ]Symptom: not read disc Description: when reading DVD, VCD, CD, "NO DISC" displays Analysis and troubleshooting: it is easy to adopt substitution method to check this type of trouble. Firstly use a good loader and computer flat cable to substitute the original loader and computer flat cable. After using loader component with the same specification to substitute, disc reading, playback and recording are all normal. (Loader component are all in one, change directly after damaging loader) [ Example 12 ] Symptom: DV cannot input Description: other external inputs are normal, DV signal cannot input Analysis and troubleshooting: firstly judge the location of PCB board in which trouble lies, test DV jack board flat cable position and check whether there is signal input, if there is signal input, the trouble lies in decode board. After testing, we find that trouble lies in DV board, so we doubt trouble lies in DV socket part, after changing DV socket, trouble is removed. [ Example 13 ]Symptom: no sound Description: no sound when in external input and playing DVD player Analysis and troubleshooting: we judge that trouble lies in audio processing circuit, test pin 2 of U15 and there is signal input, clock and power supply of U15 are both normal, test U15 audio output pin and find that there is no analog audio signal output, so we doubt that U15 has trouble, firstly weld U15 again, trouble disappears, so the rosin joint of IC leads to it after confirmation. Conclusion: before changing IC, weld IC again firstly to avoid incorrect judgment. [ Example Symptom: player not switch on Description: after power on, standby indicator light is on, press POWER button, indicator light cannot turn out, and the player cannot enter power-on state. Analysis and troubleshooting: according to trouble symptom, we can judge that trouble lies in panel, test P_CTL_PSW pin and there is no high level output, test STB_5V voltage and it is normal, so we doubt that power button has trouble, after changing it, trouble is removed. - 68 - [ Example 15 ] Symptom: component video output picture has distortion Description: the output picture has no red Analysis and troubleshooting: it is judged that trouble is in red fundamental olor output circuit, shown in the figure 3.3.1.5, test C65 and there is signal output, test R89 and there is no signal output, so we doubt that amplifying circuit has trouble, after changing Q13, trouble is removed. 5V_STB C64 105 R_V R88 330k C65 474 Q13 MMTBA1 4 R89 R90 220k R92 4.7k Figure 3.3.1.5 Component video output circuit - 69 - B601 3.3.2 Troubleshooting flow chart 1. Troubleshooting process for “DV has no output” is shown in the figure 3.3.2.1: DV has no output Whether TSB41 power supply is normal N Check power supply circuit Y Check whether Y2 works normally N Change 24.576MHZ crystal oscillator and check whether it is normal N Check C160, C161 Y Check whether pin 37 reset is normal N Check whether reset line is normal N Troubleshooting Y Y Main chip has trouble and change decode board Check whether pin 1 output clock is normal N Change U10 Y Check whether Cn1 has signal input N Check whether DV terminal contact is good N Change DV terminal Y Y Check whether data to main chip is normal Y Main chip has trouble or rosin joint, change main board Figure 3.3.2.1 Check DV board flat cable and line N Check whether U10 has rosin joint N Change U10 Y Check DV board flat cable and line Troubleshooting flow chart for “DV has no output” - 70 - 2. Troubleshooting process for “Not read USB device” is shown in the figure 3.3.2.2: Not read USB device Change USB socket board and check whether it is normal N Check USB socket and flat cable Y Check whether +5V power supply is normal N Check power supply loop Y Whether elements of USB line is normal N Troubleshooting Y Upgrade firmware of the player and check whether it is normal N Main chip has trouble and change main board Y OK Figure 3.3.2.2 Troubleshooting flow chart for “Not read USB device” - 71 - 3. Troubleshooting process for “Power not on” is shown in the figure 3.3.2.3; Power not on (standby light is not on after power on) Test whether two ends of CE5 has 300V voltage N Y Whether two ends of Lf1 has 220V input N Check whether protector tube has open circuit Y Check whether D9~D12 is normal Check power cord Y N Change Check whether rear stage is short circuited N Change protector tube Y Y Check whether CE5 is normal N N Change Check whether D9~D12 is short circuited N Change diode Y Y Change 5L0380 Check whether CE5 is normal N Change Y Check whether pin 4 of IC6 has 16V voltage N Check whether R6 is normal N Change R6 Check whether IC6 and transformer are shortcircuited Y Y Change 5L0380 Check whether 5L0380 is normal N Change 5L0380 Y Check whether transformer is normal N Change transformer Y Check peripheral elements of 5L0380 Figure 3.3.2.3 Troubleshooting flow chart for “Power not on” - 72 - N Change 4. Troubleshooting process for “Cannot enter power-on from standby” is shown in the figure 3.3.2.4: Cannot enter power-on from standby Whether P_CTL outputted by panel is normal, whether standby red light is off N Check panel Y Whether B+12V is normal N Y Check whether D2, CE3 is normal N Change Y Check whether B+12 is short-circuited to ground N Change transformer Y Remove rear stage short circuit elements Whether V_CrL is high level N Check whether Q6, Q9 is normal Y Check whether +3.3V, +5V, +12V output is normal N Check on/off control circuit of each group Y Check main board if it has trouble Figure 3.3.2.4 Troubleshooting flow chart for “cannot enter power-on from standby” - 73 - 5. Troubleshooting process for “No display” is shown in the figure 3.3.2.5: No display VFD has no display when in standby Y N Check whether filament is on Check F-, F+ power supply loop Y Whether 5MHZ clock is normal N Change crystal oscillator or C6, C7 Y Whether VDD power supply is normal N Check VDD power supply loop Y N Whether reset is normal Check reset circuit Y Whether UPD16316 is normal N Change UPD16316 Y Change VFD Figure 3.3.2.5 Troubleshooting flow chart for “No display” - 74 - 6. Troubleshooting process for “+12V has no voltage output” is shown in the figure 3.3.2.6: +12V has no voltage output Check whether Q11E electrode voltage is 13V N Check whether D2, L2, CE3 is normal N Change Y Test whether V_CrL is high level N Check Q6, Q9 Y Whether Q10 B electrode is 2.7V voltage N N Whether IC4 is normal Change IC4 Y Y Change Q10 Whether Q10 E electrode is 2.7V voltage N Check whether Q10 is normal N Change Q10 Y Y Check D30, D22, D23 N Whether Q11 is normal Change Q11 Y N Whether CE16 is normal Change CE16 Y OK Figure 3.3.2.6 Troubleshooting flow chart for “+12V has no voltage output” - 75 - 7. Troubleshooting process for “External input has no sound output” is shown in the figure 3.3.2.7: External input has no sound output Whether AV board U1 CD4052 3PIN , 13PIN has sound output N Y Whether AV board U1 C D4052 7PIN, 16PIN power supply is normal N Check AV board U1 CD4052 power supply circuit Y Whether AV board U1 Cd4052 9PIN , 10PIN control voltage is normal N Y N N Change Q1, Q2 triode Y Change decode board main chip U1 DMN8602 Change AV board U1 CD4052 Whether decode board 10PIN , 12PIN has sound output Whether AV board SEL1, SEL2 voltage is normal Check the circuit between AV board and decode board Y Whether decode board U17 CS5340 4IN has digital audio signal Y N Check whether each pin voltage, clock and reset of decode board U17 CS5340 is normal N Check decode board U17 CS5340 peripheral circuit Y Change main chip MDN8602 Change decode board U17 CS5340 Figure 3.3.2.7 Troubleshooting flow chart for “External input has no sound output” - 76 - 8. Troubleshooting process for “TV signal has no sound output” is shown in the figure 3.3.2.8: TV signal has no sound output Whether AV board tuner 1PIN has sound N Change AV tuner Y Whether AV board U6_30 PIN 31PIN has sound output N Y Whether U6 43PIN has sound N Change R22, C15 Y Change U6 Whether AV board U1 3PIN 13PIN has sound output Y OK N Whether power supply of each pin of U1 is normal N Check each power supply circuit Y Change U1 Figure 3.3.2.8 Troubleshooting flow chart for “TV signal has no sound output” - 77 - 9. Troubleshooting process for “TV signal input has no image” is shown in the figure 3.3.2.9: TV signal input has no image Other external inputs have no image output N Y Whether AV board tuner 12PIN has video output N Change AV board tuner Y Whether decode board U18 2PIN has video signal N Check the circuit from AV board to decode board video jack Y Whether decode board U18 3PIN, 13PIN has video N Whether decode board U18 peripheral circuit is normal N Check decode board U18 peripheral circuit Y Y Change decode board U18 Whether decode board U14 TVP5150 24PIN has digital video signal output Y Change U1DMN8602 N Check whether decode board U14 peripheral circuit is normal N Check U14 peripheral circuit Y Change decode board U14 Figure 3.3.2.9 Troubleshooting flow chart for “TV signal input has no image” - 78 - 10. Troubleshooting process for “Cannot receive TV signal” is shown in the figure 3.3.2.10: Cannot receive TV signal Whether AV board tuner 5V power supply is normal N Check 5V power supply circuit Y Whether tuner SCL, SDA is normal N Check SCL, SDA electricity Y Whether AV board X2 crystal oscillator starts up N Check X2 oscillation circuit Y Change tuner Figure 3.3.2.10 troubleshooting flow chart for “Cannot receive TV signal” - 79 - 11. Troubleshooting process for “No sound when playing disc” is shown in the figure 3.3.2.11: No sound when playing disc Whether decode board U45 has digital audio signal N Change decode board U14 Y Whether decode board U15 19PIN, 20PIN has audio signal output N Y Whether voltage of each pin of decode board U15 is normal N Change decode board U14 Y Change decode board U15 Whether AV board U3 1PIN, 7PIN has audio output N Y Whether AV board U3 peripheral circuit is normal N Check AV board U3 peripheral circuit Y Change AV board U3 Check whether pin 5 of CN4 is low level N Change main panel U1 D16316 Y Check whether Q4_C electrode is negative voltage Y Change terminal N Check whether Q5 Q8 is normal N Change triode Y Check Q7 Figure 3.3.2.11 Troubleshooting flow chart for “No sound when playing disc” - 80 - 12. Troubleshooting process for “External input picture has mosaic” is shown in the figure 3.3.2.12: External input picture has mosaic Disconnect 24P flat cable from AV board to decode board and check whether picture has mosaic N Change AV board U6 or X2 crystal oscillator Y Whether voltage of each pin of decode board U14 is normal Y Change decode board U1 MDN8602 N Check whether peripheral circuit of decode board U14 is normal N Check U14 peripheral circuit Y Change decode board U14 Figure 3.3.2.12 Troubleshooting flow chart for “External input picture has mosaic” - 81 - 13. Troubleshooting process for “Machine down after power on” (there is power-on picture but no button function) is shown in the figure 3.3.2.13: Machine down after power on Whether power board voltage is normal N Check each power supply circuit of power board Y Whether decode board each power supply is normal N Y Check whether decode board 3.3Vpower supply is normal N Check U12 and peripheral line N Check U13 and peripheral line Y Check whether decode board 2.5Vpower supply is normal Y Check whether decode board 1.8V power supply is normal Change decode board and check whether it is ok N Y Whether loader components are normal N Check U11 and peripheral line N Change loader components Y Check power supply of AV board and whether the IC that has communication with IIC bus is normal Whether decode board U8 works normally N Y Check whether decode board U8 is normal N Change U8 Y Check decode board U7 peripheral and line Whether decode board U14 works normally N Y Check whether decode board U14 is normal N Y Check decode board U14 peripheral and line Change U3/U4 and check whether it is normal N Change U1 DMN8602 Figure 3.3.2.13 Troubleshooting floe chart for “Machine down after power on” - 82 - Change U14 14. Troubleshooting process for “The player has no output” (no power-on picture and no button function) is shown in the figure 3.3.2.14: The player has no output Whether power board voltage is normal N Check each power supply circuit of power board Y Whether decode board each power supply is normal N Check whether decode board 3.3Vpower supply is normal N Check U12 and peripheral line N Check U13 and peripheral line Y Y Check whether decode board 2.5V power supply is normal Y Check whether decode board 1.8V power supply is normal Whether decode board reset signal is normal N Y Check whether pin 1 of U6 has reset signal output N Check U11 and peripheral line N Change U6 Y Check whether the line from reset signal to FLASH and U1 is normal Whether decode board 13.5 clock works normally N Change Y1 and check whether it is normal N Change C1 C2 Y Whether decode board U8 works (FLASH) N Check whether decode board U8 is normal N Y Y Check decode board U7 peripheral and line Change N U3/U4 45pin clock signal and check whether it is normal Change SDRAM and check whether it is normal Change U1 DMN8602 N Change U1 DMN8602 Figure 3.3.2.14 Troubleshooting flow chart for "The player has no output" - 83 - Change U8 Section Four Servicing Parameters 3.4.1 Signal waveform diagram This section collects signal waveform diagram of audio, video and each unit circuit with the purpose to help servicing personnel to judge where trouble lies in accurately and quickly to improve servicing skills. For the difference of oscillograph's type, model and tuner, a certain difference may exist, so the servicing personnel are expected to pay more attention to check in daily operation. 1. Panel main clock (5MHZ) test point U1_51 peak value 3.64V 2.Externally connected crystal oscillator of panel clock signal (32.766KHZ) test point U1_2 peak value 3.16V - 84 - 3. VFD_CLK decode board clock signal waveform, test point, panel flat cable position 4. SDRAM clock signal waveform diagram test point U3_45 U4_45 peak value 736MV frequency 150MHZ SPDIF_OUT signal waveform diagram test point U5_12 peak value 6.56V - 85 - 6. System reset signal waveform diagram test point 3.3V power and U5_4 Video coder clock waveform diagram test point U14_5 peak value 1.46V frequency 14.3MHZ 8. Main clock signal waveform (13.5MHZ) test point Y1 peak value voltage 1.44V - 86 - Waveform of digital audio signal (AO_D1) outputted by decode chip, when in 5.1CH output, AO_DI/AO_D3 and AO_D1 are the same, test point U15_4 peak value 4.04V test point U15_4 10. AO_SCLK bit clock signal peak value 4.12V voltage 1.64V test point U15_5 11. AO_FSYNC left/right clock signal peak value 3.52V voltage 1.63V test point U15_6 - 87 - 12. AO_ MCLKO main clock signal peak value 4.16V voltage 1.66V test point U15_7 Waveform diagram of analog audio signal outputted by CS4360 (1K 0DB signal) left channel, test point R194 (except bass signals, other analog audio output pin waveform is the same) 14. Waveform diagram of the analog audio signal outputted by CS4360 (200HZ 0DB signal) test point R191 - 88 - Left channel signal after being filtered, test point CN3_14 16. Subwoofer signal after being filtered, test point CN3_4 17. Waveform of left channel signal outputted by terminal test point: audio output terminal - 89 - 18. Bass signal waveform outputted by terminal test point audio output terminal Y_OUT (S-Y_OUT) signal waveform diagram, test point CN5_2 20. C_OUT(S-C_OUT) signal waveform diagram, test point CN5_4 - 90 - CVBS_OUT(V_OUT) signal waveform diagram, test point CN5_6 PR_OUT(R_V_OUT) signal waveform diagram, test point CN5_8 Y_OUT(G_Y_OUT) signal waveform diagram, test point CN5_10 - 91 - 24. PB_OUT(B_U_OUT) signal waveform diagram, test point CN5_12 25. External audio input analog audio waveform diagram, test point U17_10 U17_12 26.I_MCLKO A/D converter main clock signal waveform diagram test point U17_2, peak value 3.56V voltage 1.24V - 92 - 27. Waveform diagram of digital signal outputted after being converted by AI_DO A/D converter test point U17_4 peak value 4.04Vvoltage 1.24V I_SCLK A/D converter bit clock signal waveform diagram test point U17_7 29. I_FSYNC A/D converter function clock signal waveform diagram test point U17_8 - 93 - 30. Analog input video signal waveform diagram test point U18_3 or U18_13 pin 31. Waveform diagram of that switched to digital signal test point RP33 pin voltage 1.03V 32. Video signal inputted by tuner test point AV board CN2_22 - 94 - 33. Audio reset signal waveform diagram test point 3.3V power supply end and U17_9 34. NICAM processing IC clock signal X2 test point U6_5 pin voltage 2.76 frequency 18.432MHZ 35. standby panel VFD_DIO signal waveform diagram - 95 - 36. AV board clock circuit waveform diagram, test point U2_1 37. Power board D2 anode waveform diagram - 96 - 3.4.2 Key point voltage 1. Power board Key point Working voltage (V) Standby voltage (V ) Key point Working voltage (V) Standby voltage (V ) CE5 anode 326 326 Q11_B 12.5 12.3 D4 cathode 450 425 Q10_B 2.6 0 D4 anode 340 340 Q10_E 2 2 D7 cathode 15 12 IC4_K 2.5 0 D1 anode -12.5 -11 CE17 anode 3.3 0 D2 cathode 13 12.8 D16 cathode 2.5 0 D18 cathode 3.9 4.7 IC5_K 2.5 0 D21 cathode 5.1 5.2 IC5_A 5.8 0 D13 anode -27 -22 L3 3.8 4.7 F- -21.9 -17 IC3_K 2.5 2.5 F+ -18.9 -14 IC3_A 3.8 3.8 B+12V 13V 12.8 IC2_1 5 5.2 Q9_B 12.1 12.4 Q2_E 5 5.2 V_Crl 10.2 0 Q2_C 5 5.1 P_CTL 4.1 0 Q2_B 5.8 0 Q11_C 12 0 Key point Playback s tatus (V ) TV external input status ( V) Key point Playback s tatus (V ) TV external input status ( V) U2_4 1.25 1.25 U15_13 3.3 3.3 U3_10 2.5 2.5 CN3_1 1.66V 1.66V U3_49 1.25 1.25 CN3_7 4.3V 4.3V U3_45 1.25 1.25 CN3_15 0.03 0.03 U6_1 0--3.3 0--3.3 CN3_16 3.31 3.31 U5_2 3.3 3.3 CN3_17 0 0 U9_5 3.2 3.2 CN3_18 3.24 3.24 U9_6 3.2 3.2 CN3_19 3.24 3.24 U10_1 1.6 1.6 CN3_20 0 0 U10_42 1.52 1.52 CN3_21 3.62 3.62 U10_43 1.52 1.52 CN3_22 3.64 3.64 V33_PHY_A 3.3 3.3 CN3_23 0 0 U14_5 0.8 0.8 CN3_24 5.17 5.17 2. Decode board - 97 - U14_6 0.6 0.6 CN5_1 2.99 2.99 U14_9 1.6 1.6 CN5_2 0.57 0.57 U14_11 0 1.03 CN5_4 0.78 0.78 U14_2 0 0.1 CN5_6 0.64 1.45 U15_10 0--3.3 0--3.3 CN5_8 0.6 0.6 U17_9 0--4.3 0--4.3 CN5_10 0.58 0.58 U15_1 3.3 3.3 Key point Working voltage (V) Standby voltage (V ) Key point Working voltage (V) Standby voltage (V ) U1_50 2.6 2.6 Q1_C 4.4 0---4.4 U1_51 2 2 MUTE 0 4.3 U1_2 1.6 1.6 P_CTL_PSW 4.3 0 U1_3 2.6 2.6 RST_HOST_LED 4.3 0 U1_12 4.4 4.4 VFD_DIO 4.3 0-4.3 U2_3 5 5 Key point Playback s tatus (V ) TV input status ( V) Key point Playback s tatus (V ) TV input status ( V) TUN1_1 5 5 Q1_C 5 5 TUN1_2 9.4 9.4 Q1_E 1.7 1.7 TUN1_3 5 5 Q2_B 2.5 2.5 TUN1_4 3.63 3.63 Q2_C 5 5 TUN1_5 3.63 3.63 Q2_E 1.7 1.7 TUN1_6 0 0 U2_1 0 0 TUN1_7 1.42 0.9 U2_2 0.4 0.4 TUN1_8 0 0 U2_5 3.5 3.5 TUN1_9 0 0 U2_6 3.5 3.5 TUN1_10 4.36 1.91 Q4_C -8 -8 TUN1_11 0 0 U6_1 5 5 TUN1_12 2.14 1.38 U6_2 1.5 1.5 TUN1_13 5 5 U6_5 2.4 2.4 TUN1_14 2.44 2.44 U6_6 2.38 2.38 U1_7 6.2 U6_30 3.75 3.75 U1_9 0 0 U6_31 3.75 3.75 U1_10 3.25 3.25 U6_22 4.19 4.19 Q1_B 2.5 2.5 3. Panel 4. AV board - 98 - Section Five Function Introduction to IC 3.5.1 function introduction to MT 8602 1. Description The DMN-8602 accepts video from broadcast TV and other analog video sources, and compresses and formats the video for storage on DVD in industry-standard recordable formats (DVD-RAM, DVD-RW/R, DVD+RW/R). The DMN-8602 allows half-duplex operation (record or play back) or full-duplex operation (simultaneous record and playback – time shifting) with only a change of memory configuration. The device permits control of DV camcorders connected via FireWire using the AV/C protocol, and transcodes DV-25 video for storage on DVD. The DMN-8602 also supports leading-edge DVD playback features. The DMN-8602 supports video compression and decompression in compliance with the MPEG-1, MPEG-2, and DV -25 specifications. It also transcodes between DV-25 and MPEG-2. The product supports corresponding audio compression and decompression in compliance with the Dolby Digital CE and MPEG-1 layer 2 specifications. The DMN-8602 supports the playback of DVD-Video disks with Dolby Digital 5.1 and DTS audio encoding, DVD Audio disks (MLP), VCD, and SVCD disks. DMN-8602 also supports the play back of audio encoded in MP3 and WMA formats, and the display of pictures encoded in JPEG format. The DMN-8602 integrates a RISC processor dedicated to video processing that, coupled with a dedicated video digital signal processor and motion estimation engine, enables the handling of multiple advanced-image processing tasks. The DMN-8602 also integrates a RISC processor dedicated to system-level processing and all audio processing tasks. The DMN-8602 supports industry standard audio encoding and decoding formats, as well as audio post-processing tasks such as 3D audio effects and bass management functions. This combination allows the DMN-8602 to simultaneously handle multiple A/V processing functions while managing all system control tasks, eliminating the need for an external host CPU. The DMN-8602 has an on-chip ATAPI controller that supports DVD-RAM, DVD-RW/R, and DVD+RW/R recordable DVD drives. The DMN-8602 integrates an analog video encoder, and provides built-in support for simultaneous progressive and interlaced video output. A 1394 link layer function is integrated, requiring only a simple external physical layer device. One USB port is provided, as well as support for PCMCIA 2.1 cards with minimal logic. The DMN-8602 integrates a RISC processor dedicated to video processing that, coupled with a dedicated video digital signal processor and motion estimation engine, enables the handling of multiple - 99 - advanced-image processing tasks. The DMN-8602 also integrates a RISC processor dedicated to system-level processing and all audio processing tasks. The DMN-8602 supports industry standard audio encoding and decoding formats, as well as audio post-processing tasks such as 3D audio effects and bass management functions. This combination allows the DMN-8602 to simultaneously handle multiple A/V processing functions while managing all system control tasks, eliminating the need for an external host CPU. 2. Features A/V Encode/Decode Transcoding/rating Multiformat audio and video encode/decode Multiformat transcoding, multirate transrating Horizontal: 720, 704, 640, 544, 480, 352 Resolutions Digital video Vertical: NTSC (480i, 480p) and PAL (576i) Formats NTSC, PAL, ITU- R BT.656/601, SMPTE 260M 8- or 10-bit digital video from ITU-R BT.656 (parallel D1) sources; A single 8-bit digital Input video stream (SMPTE 260M) at 27 MHz Output Single 8-bit ITU-R BT.656 interlaced video output. Baseband composite (M) NTSC or (B,D,G,H,I) PAL analog video. Output Separate analog Y/C outputs to support S-video. Separate analog component video RGB or SMPTE YpbPr outputs. Single stream input, supporting common audio formats, Input including I2S, with four input channels Single stream output, supporting common audio formats, Audio Output including I2S with eight output channels Resolutions 16 to 32 bits/sample Analog Audio Sampling 32, 44.1, 48, and 96 kHz output Frequency Digital Audio Sampling 8- to 192 kHz over IEC-958 Frequency Serial I/O Parallel IEEE1394, IDC, SPI, IR receive, IR blaster, dual UARTs ATAPI Host low speed and full speed interface. A single port USB1.1 is available for down stream hub or device connection. Host System Graphics Encryption/decryption Memory Memory 16/32-bit generic host interface or internal host 2D, 24-bit RGB, 8-bit alpha channel, OSD, flicker filter and video scaler CPRM, CPPM, CSS, 5C (via 1394), Watermark detection 8-256 Mbytes of SDRAM, SDR or DDR - 100 - Controller On-chip, 32-bit-wide SDRAM interface, 148.5 MHz Peak Bandwidth 1.2 Gbytes/s 3.3 V I/O; 1.8 V Core; 2.5 / 3.3 V SDRAM; 3.3 V Isolated Input Voltages Analog Physical JTAG System Clock 13.5 or 27 MHz Operating Power < 2.7 W @ Vdd = 1.8 V typical Package 308-Pin Ball Grid Array (BGA) Compliance IEEE 1149.1 compliance for boundary scan testing and board assembly testing 3. Signal Descriptions I This input provides the timing reference for CLKI internally generated DMN-8602 clocks. I Connected to the second pin of the 13.5 MHz CLKX crystal. O The output of the internal 13.5 MHz crystal oscillator or output a train of digital pulses System CLKO_DAC controlled by the TC Sigma-Delta DAC Control Services Register (TCdacCtl). I Bypasses the PLL used to generate the internal BYPASS_PLL processing clock #RSEO O Reset Out. #EPD O External Power Down. USB_48MHz I 1394_PHY_DATA[7:0] I/O Data 0 through data 7 of the phy -link data-bus. 1394/ 1394_PHY_CTL[1:0] I/O Control 0 and 1 of the phy-link control bus. Firewire 1394_LREQ O Link Request. (Bitstream 1394_LPS O Link Power Status. I/O) 1394_LINK_ON I Occurrence of a link-on event. 1394_PHY_CLK I PHY_CLK is the 49.152MHz clock supplied by the PHY device. SDRAM SDRAM_CLK[1:0] O Clock. These outputs are buffered versions of the internal DMN-8602 clock. Interface #SDRAM_CLK[1:0] O Clock. Differential clock. SDRAM_CKE O Clock Enable. #SDRAM_CAS O Column Address Strobe. #SDRAM_RAS O Row Address Strobe (Activate). SDRAM_DQM[3:0] O Data Mask (Byte Enables). - 101 - SDRAM_A[17:0] O Address, Bank Select, Chip Select. SDRAM_DQ[31:0] I/O Read / Write Data. #SDRAM_WE O Write Enable. SDRAM_DQS[3:0] I/O SDRAM Data Strobe. #SDRAM_VREF I Reference voltage for SSTL. VI_CLK I Video Input Clock. VI_D[9:2] I Video Input Data. Video I/O VO_D[7:0] O Video Output Data. Interface VI_VSYNC I Video Input Vertical Sync. VO_CLK I/O DAC_OUT[6:1] I IDC SIO_SDA I/O IDC clock (open drain). Serial I/O) SIO_SCL I/O IDC data (open drain). #TRST I Test Reset Boundary TDO O Test Data Out Scan TDI I Test Data In (JTAG) TMS I Test Mode Select TCK I Test Clock Dplus I/O Dminus] I/O I Video Output Clock. Analog Video DAC output. This is the USB transceiver port differential D+ and D– signals. This is the USB transceiver port 0 power enable for the external USB power Host_OC USB management chips. O Host_PO This is the USB transceiver port 0 over-current status signal from the external USB power management chips. SIO_UART[2:1]_TX I UART clear to send. SIO_UART[2:1]_RX O UART receive. SIO_UART[1]_RTS I UART request to send. SIO_UART[1]_CTS O UART transmit. IR SIO_IRTX1 I IR transmit 1. (Serial SIO_IRTX2 O IR transmit 2 I/O) SIO_IRRX O IR receive input. SPI SIO_SPI_CLK O SPI clock. (Serial SIO_SPI_MOSI O SPI master out slave in. I/O) SIO_SPI_MISO I SPI master in slave out. UART[2:1] (Serial I/O) - 102 - SIO_SPI_CS[2:0] O SPI chip selects. ATAPI_RESET O DMN-8602 reset of connected ATAPI devices. ATAPI_DATA[15:8] I ATAPI_DATA is the bidirectional data bus. ATAPI_ADDR[4:0] I Device register address. ATAPI 1 #ATAPI_DIOW I ATAPI I/O write request. (Bitstream #ATAPI_DIOR O ATAPI I/O read request. I/O) ATAPI_INTRQ O ATAPI device interrupt request. ATAPI_IORDY I ATAPI device IO ready. ATAPI_DMARQ I/O ATAPI device DMA request. #ATAPI_DMAACK O ATAPI DMA acknowledgement. HMST_GPIO[6:0] I/O General purpose dedicated I/O [6:0]. #HMST_RST I Master Reset signal. #HMST_ CS[10:0] O Master chip select [10:0] outputs. M_Addr[26:22] O Most significant five host address bits [26:22]. M_Addr[21:6]/M_Data[15:0] I/O Host address bus bits [21:6]./ Host data bus. M_Addr[5:1] O Least significant five host address bits [5:1] #HMST_UWE, HMST_UDS O Master upper data strobe (68K-mode). Host #HMST_RD/WR, O Master data transfer direction (68K-mode). Interface HMST_LWE #HMST_OE, HMST_LDS O Master lower data strobe (68K-mode). #HMST_ALE O Master address latch enable. #HMST_WAIT I Master wait signal from peripheral. #HMST_DTACK I Master data transfer acknowledge. HMST_CS0_8BIT I Set host CS[0] to 8-bit mode in master mode. #PCMCIA_IOR I PCMCIA I/O read. #PCMCIA_IOW I PCMCIA I/O write. Audio I/O AI_SCLK I/O Serial audio bit clock for the audio input stream. Interface AO_SCLK O Serial audio bit clock for the audio output stream. O Audio Master Input Clock output for the internally AI_MCLKO generated master input clock. I Audio Master Input Clock input for an externally AI_MCLKI generated master input clock. O Audio Master Output Clock output for the internally generated master output AO_MCLKO clock. - 103 - I Audio Master Output Clock input for an externally AO_MCLKI generated master output clock. AI_D[1:0] I Audio Input Data. AO_D[3:0] O Audio Stream Output Data. I/O AI_FSync determines the start or end of the next AI_FSYNC stream input sample AO_FSYNC O AO_FSync determines the start or end of the next stream output sample AO_IEC958 O IEC-958 Interface Output. 3.5.2 Function introduction to CD4053 CD4053 is a 4-group 2-channel data selection device, and is mainly used in the input, output selection of SCART and the realization of LOGO function in DVD recorder. Each pin function is shown as follows: Pin Name Function Remark 1、2 Y1、Y0 Y signal input I 13、12 X1、X0 X signal input I 3、5 Z1、Z0 Z signal output I 6 EN Enable end: low level effective I 7 VEE -6.2V power 8 GND ground 16 VCC +5V power 9、10、11 C、B、A Gating signal control input I 14 X X signal output O 15 Y Y signal output O 4 Z Z signal output O A, B signal strobe condition: A、B、C 0 X、Y、Z X0、Y0、Z0 Remark When A, B, C end is low level, output end X, Y, Z outputs the signals inputted by X0, Y0, Z0. 1 X1、Y1、Z1 When A, B, C end is high level, output end X, Y, Z outputs the signals inputted by X1, Y1, Z1. Note: in the circuit, part of input pins are not used, A、B、C control end is controlled by LOOP control circuit. When in standby status, LOOP_DECODER_C is high level, when power on, LOOP_DECODER_C is low level. - 104 - 3.5.3 function introduction to TSB41AB1 1. description The TSB41AB1 provides the digital and analog transceiver functions needed to implement a one-port node in a cable-based IEEE 1394 network. The cable port incorporates one differential line transceiver. The transceiver includes circuitry to monitor the line conditions as needed for determining connection status, for initialization and arbitration, and for packet reception and transmission. The TSB41AB1 is designed to interface with a link layer controller (LLC). The TSB41AB1 requires only an external 24.576-MHz crystal as a reference. An external clock may be provided instead of a crystal. An internal oscillator drives an internal phase-locked loop (PLL), This reference signal is internally divided to provide the clock signals used to control transmission of the outbound encoded strobe and data information. The power-down (PD) function, when enabled by asserting the PD terminal high, stops operation of the PLL. The TSB41AB1 supports an optional isolation barrier between itself and its LLC. When the ISO input terminal is tied high, the LLC interface outputs behave normally. When the ISO terminal is tied low, internal differentiating logic is enabled, and the outputs are driven such that they can be coupled through a capacitive or transformer galvanic isolation barrier as described in Annex J of IEEE Std 1394-1995 and in IEEE 1394a-2000 (section 5.9.4) (hereinafter referred to as Annex J type isolation). To operate with TI bus holder isolation the ISO terminal on the PHY must be high. Data bits to be transmitted through the cable port are received from the LLC on two, four or eight parallel paths (depending on the requested transmission speed) and are latched internally in the TSB41AB1 in synchronization with the 49.152-MHz system clock. These bits are combined serially, encoded, and transmitted at 98.304, 196.608, or 393.216 Mbits/s (referred to as S100, S200, and S400 speeds, respectively) as the outbound data-strobe information stream. During transmission, the encoded data information is transmitted differentially on the TPB cable pair, and the encoded strobe information is transmitted differentially on the TPA cable pair. During packet reception the TPA and TPB transmitters of the receiving cable port are disabled, and the receivers for that port are enabled. The encoded data information is received on the TPA cable pair, and the encoded strobe information is received on the TPB cable pair. The received data-strobe information is decoded to recover the receive clock signal and the serial data bits. The serial data bits are split into two-, four-, or eight-bit parallel streams (depending upon the indicated receive speed), resynchronized to the local 49.152-MHz system clock and sent to the associated LLC. Both the TPA and TPB cable interfaces incorporate differential comparators to monitor the line states during initialization and arbitration. The outputs of these comparators are used by the internal logic to determine the arbitration status. The TPA channel monitors the incoming cable common-mode voltage. The value of this common-mode voltage is used during arbitration to set the speed of the next packet transmission. In addition, the TPB channel monitors the incoming cable common-mode voltage on the TPB pair for the presence of the remotely supplied twisted-pair bias voltage. - 105 - The TSB41AB1 provides a 1.86-V nominal bias voltage at the TPBIAS terminal for port termination. This bias voltage, when seen through a cable by a remote receiver, indicates the presence of an active connection. This bias voltage source must be stabilized by an external filter capacitor of 1 μF. TPBIAS is typically VDD¨C0.2 V when the port is not connected to another node. The line drivers in the TSB41AB1 operate in a high-impedance current mode, and are designed to work with external 112- ? line-termination resistor networks in order to match the 110- ? cable impedance. One network is provided at each end of a twisted-pair cable. Each network is composed of a pair of series-connected 56- ? resistors. The midpoint of the pair of resistors that is directly connected to the twisted-pair-A terminals is connected to its corresponding TPBIAS voltage terminal. The midpoint of the pair of resistors that is directly connected to the twisted-pair-B terminals is coupled to ground through a parallel R-C network with recommended values of 5 k? and 220 pF. The values of the external line termination resistors are designed to meet IEEE Std 1394-1995 when connected in parallel with the internal receiver circuits. An external resistor connected between the R0 and R1 terminals sets the driver output current, along with other internal operating currents. This current-setting resistor has a value of 6.34 k? ±1.0%. When the power supply of the TSB41AB1 is off while the twisted-pair cables are connected, the TSB41AB1 transmitter and receiver circuitry presents a high impedance to the cable and does not load the TPBIAS voltage at the other end of the cable. Fail-safe circuitry blocks any leakage path from the port back to the device powerplane. The TESTM, SE, and SM terminals are used to set up various manufacturing test conditions. For normal operation, the TESTM terminal should be connected to VDD through a 1-k ? resistor, SE should be tied to ground through a 1-k ? resistor, and SM should be connected directly to ground. Four package terminals are used as inputs to set the default value for four configuration status bits in the self-ID packet, and are tied high through a 1-k ? resistor or hardwired low as a function of the equipment design. The PC0¨CPC2 terminals are used to indicate the default power-class status for the node (the need for power from the cable or the ability to supply power to the cable). See Table 9 for power-class encoding. The C/LKON terminal is used as an input to indicate that the node is a contender for either isochronous resource manager (IRM) or for bus manager (BM). The TSB41AB1 supports suspend/resume as defined in the IEEE 1394a-2000 specification. The suspend mechanism allows pairs of directly connected ports to be placed into a low-power state (suspended state) while maintaining a port-t o-port connection between bus segments. While in the suspended state, a port is unable to transmit or receive data transaction packets. However, a port in the suspended state is capable of detecting connection status changes and detecting incoming TPBIAS. When the port of the TSB41AB1 is suspended, all circuits except the band gap reference generator and bias detection circuit is powered down, resulting in significant power savings. For additional details of suspend/resume operation see IEEE 1394a-2000. The use of suspend/resume is recommended for new designs. The port transmitter and receiver circuitry is disabled during power down (when the PD input terminal is asserted high), during reset (when the RESET input terminal is asserted low), when no active cable is - 106 - connected to the port, or when controlled by the internal arbitration logic. The TPBIAS output is disabled during power down, during reset, or when the port is disabled as commanded by the LLC. The cable-not-active (CNA) output terminal (64-terminal PAP package only) is asserted high when there are no twisted-pair cable ports receiving incoming bias (that is, they are either disconnected or suspended), and can be used along with LPS to determine when to power down the TSB41AB1. The CNA output is not debounced. When the PD terminal is asserted high, the CNA detection circuitry is enabled (regardless of the previous state of the ports) and a pulldown is activated on the RESET terminal so as to force a reset of the TSB41AB1 internal logic. The LPS (link power status) terminal works with the C/LKON terminal to manage the power usage in the node. The LPS signal from the LLC is used in conjunction with the LCtrl bit (see Table 1 and Table 2 in the Application Information section) to indicate the active/power status of the LLC. The LPS signal is also used to reset, disable, and initialize the PHY-LLC interface (the state of the PHY-LLC interface is controlled solely by the LPS input, regardless of the state of the LCtrl bit). The LPS input is considered inactive if it remains low for more than 2.6 μs and is considered active otherwise. When the TSB41AB1 detects that LPS is inactive, it places the PHY-LLC interface into a low-power reset state in which the CTL and D outputs are held in the logic zero state and the LREQ input is ignored; however, the SYSCLK output remains active. If the LPS input remains low for more than 26 μs, the PHY-LLC interface is put into a low-power disabled state in which the SYSCLK output is also held inactive. The PHY-LLC interface is also held in the disabled state during hardware reset. The TSB41AB1 continues the necessary repeater functions required for normal network operation regardless of the state of the PHY-LLC interface. When the interface is in the reset or disabled state and LPS is again observed active, the PHY initializes the interface and returns it to normal operation. When the PHY -LLC interface is in the low-power disabled state, the TSB41AB1 automatically enters a low-power mode if the port is inactive (disconnected, disabled, or suspended). In this low-power mode, the TSB41AB1 disables its internal clock generators and also disables various voltage and current reference circuits depending on the state of the port (some reference circuitry must remain active in order to detect new cable connections, disconnections, or incoming TPBIAS, for example). The lowest power consumption (the ultralow-power sleep mode) is attained when the port is either disconnected, or disabled with the port interrupt enable bit cleared. The TSB41AB1 exits the low-power mode when the LPS input is asserted high or when a port event occurs which requires that the TSB41AB1 become active in order to respond to the event or to notify the LLC of the event (for example, incoming bias is detected on a suspended port, a disconnection is detected on a suspended port, a new connection is detected on a nondisabled port, etc.). The SYSCLK output becomes active (and the PHY-LLC interface is initialized and becomes operative) within 7.3 ms after LPS is asserted high when the TSB41AB1 is in the low-power mode. The PHY uses the C/LKON terminal to notify the LLC to power up and become active. When activated, the C/LKON signal is a square wave of approximately 163-ns period. The PHY activates the C/LKON output when the LLC is inactive and a wake-up event occurs. The LLC is considered inactive when either the LPS - 107 - input is inactive, as described above, or the LCtrl bit is cleared to 0. A wake-up event occurs when a link-on PHY packet addressed to this node is received, or when a PHY interrupt occurs. The PHY deasserts the C/LKON output when the LLC becomes active (both LPS active and the LCtrl bit set to 1). The PHY also deasserts the C/LKON output when a bus reset occurs unless a PHY interrupt condition exists which would otherwise cause C/LKON to be active. 2. FEATURE ◆ Fully Supports Provisions of IEEE 1394-1995 Standard for High Performance Serial Bus. and IEEE 1394a-2000 ◆ Fully Interoperable With FireWire and i.LINK Implementation of IEEE Std 1394 ◆ Fully Compliant With OpenHCI Requirements ◆ Provides One IEEE 1394a-2000 Fully Compliant Cable Port at 100/200/400 Megabits Per Second (Mbits/s) ◆ Full IEEE 1394a-2000 Support Includes: Connection Debounce, Arbitrated Short Reset, Multispeed Concatenation, Arbitration Acceleration, Fly-By Concatenation, Port Disable/Suspend/Resume ◆ Register Bits Give Software Control of Contender Bit, Power Class Bits, Link Active Control Bit, and IEEE 1394a-2000 Features ◆ IEEE 1394a-2000 Compliant Common Mode Noise Filter on Incoming TPBIAS ◆ Extended Resume Signaling for Compatibility With Legacy DV Devices, and Terminal- and Register-Compatibility With TSB41LV01, Allow Direct Isochronous Transmit to Legacy DV Devices With Any Link Layer Even When Root ◆ Power-Down Features to Conserve Energy in Battery Powered Applications Include: Automatic Device Power Down During Suspend, Device Power-Down Terminal, Link Interface Disable via LPS, and Inactive Ports Powered Down ◆ Failsafe Circuitry Senses Sudden Loss of Power to the Device and Disables the Port to Ensure That the Device Does Not Load TPBIAS of the Connected Device and Blocks Any Leakage Path From the Port Back to the Device Power Plane ◆ Software Device Reset (SWR) ◆ Industry Leading Low Power Consumption ◆ Ultralow-Power Sleep Mode ◆ Cable Power Presence Monitoring ◆ Cable Ports Monitor Line Conditions for Active Connection to Remote Node ◆ Data Interface to Link-Layer Controller Through 2/4/8 Parallel Lines at 49.152 MHz ◆ Interface to Link Layer Controller Supports Low Cost TI Bus-Holder Isolation and Optional Annex J Electrical Isolation ◆ Interoperable With Link-Layer Controllers Using 3.3 V ◆ Single 3.3-V Supply Operation - 108 - ◆ Low-Cost 24.576-MHz Crystal Provides Transmit, Receive Data at 100/200/400 Mbits/s, and Link-Layer Controller Clock at 49.152 MHz ◆ Low-Cost High-Performance 48/64-Pin TQFP (PHP/PAP) Thermally Enhanced Packages Increase Thermal Performance by up to 210% ◆ Meets Intel Mobile Power Guideline 2000 3. PIN DESCRIPTION PIN Symbol I/O Description 1 SYSCLK O System clock output. 2 CTL0 I/O Control I/Os. 3 CTL1 4 D0 5 D1 6 D2 7 D3 Data I/Os. I/O 8 D4 9 D5 10 D6 11 D7 12 PD I Power-down input. 13 LPS I Link power status input. 14 DGND I Digital ground 15 C/LKON I Bus manager contender programming input and link-on output. 16 PC0 I 17 PC1 I 18 PC2 I 19 #ISO I Link interface isolation control input. 20 CPS I Cable power status input. 21 DVDD I Digital power 22 TESTM I Test control input. 23 SE I Test control input. 24 SM I Test control input. 25 AVDD I Analog power 26 AGND I Analog ground Power class programming inputs. - 109 - 27 TPB+ I/O 28 TPB- I/O 29 TPA - I/O 30 TPA+ I/O 31 TPBIAS O Twisted-pair bias output. 32 AGND I Analog ground 33 R0 34 R1 35 AVDD I Analog power 36 AGND I Analog ground 37 #RESET 38 FILTER0 39 FILTER1 40 PLLVDD I PLL power 41 PLLGND I PLL ground 42 XI I Crystal oscillator inputs. 43 XO 44 DVDD I 45 DVDD I 46 DGND I 47 DGND I 48 LREQ I Twisted-pair cable B differential signal terminals. Twisted-pair cable A differential signal terminals. Current setting resistor terminals. Reset input I/O PLL filter terminals. Digital power Digital ground LLC request input. 3.5.4 function introduction to M13S128168A 1. DESCRIPTION 2M x 16 Bit x 4 Banks Double Data Rate SDRAM 2. FATUER ◆ JEDEC Standard ◆ Internal pipelined double-data-rate architecture, two data access per clock cycle ◆ Bi-directional data strobe (DQS) ◆ On-chip DLL - 110 - ◆ Differential clock inputs (CLK and CLK ) ◆ DLL aligns DQ and DQS transition with CLK transition ◆ Quad bank operation ◆ CAS Latency : 3 ◆ Burst Type : Sequential and Interleave ◆ Burst Length : 2, 4, 8 ◆ All inputs except data & DM are sampled at the rising edge of the system clock(CLK) ◆ Data I/O transitions on both edges of data strobe (DQS) ◆ DQS is edge-aligned with data for reads; center-aligned with data for WRITE ◆ Data mask (DM) for write masking only ◆ VDD = 2.375V ~ 2.75V, VDDQ = 2.375V ~ 2.75V ◆ Auto & Self refresh ◆ 7.8us refresh interval ◆ SSTL -2 I/O interface ◆ 66pin TSOPII package 3. PIN DESCRIPTION PIN Symbol Description 1 VDD Supply Voltage 2 DQ0 Data-in/Data-out 3 VDDQ 4 DQ1 Data-in/Data-out 5 DQ2 Data-in/Data-out 6 VSSQ 7 DQ3 Data-in/Data-out 8 DQ4 Data-in/Data-out 9 VDDQ 10 DQ5 Data-in/Data-out 11 DQ6 Data-in/Data-out 12 VSSQ 13 DQ7 Data-in/Data-out 14 NC No connection 15 VDDQ Supply Voltage for DQ 16 LDQS LDQS corresponds to the data on DQ0~DQ7; 17 NC Supply Voltage for DQ Ground for DQ Ground for DQ Ground for DQ No connection - 111 - 18 VDD Power supply 19 NC No connection 20 LDM LDM corresponds to the data on DQ0~DQ7; 21 #WE Write enable 22 #CAS Column address strobe 23 #RAS Row address strobe 24 #CS Selection input 25 NC No connection 26 BA Bank selects 27 BA Bank selects 28 A10/AP Address inputs 29 A0 Address inputs 30 A1 Address inputs 31 A2 Address inputs 32 A3 Address inputs 33 VDD Supply Voltage 34 VSS Ground 35 A4 Address inputs 36 A5 Address inputs 37 A6 Address inputs 38 A7 Address inputs 39 A8 Address inputs 40 A9 Address inputs 41 A11 Address inputs 42 NC No connection 43 NC No connection 44 CKE Clock enable 45 CLK Clock input 46 #CLK Clock input 47 UDM UDM correspond to the data on DQ8~DQ15. 48 VSS Ground 49 VREF Reference Voltage for SSTL-2 50 NC No connection - 112 - 51 UDQS Ground 52 VSSQ Ground for DQ 53 NC No connection 54 DQ8 Data-in/Data-out 55 VDDQ 56 DQ9 Data-in/Data-out 57 DQ10 Data-in/Data-out 58 VSSQ Ground for DQ 59 DSQ11 Data-in/Data-out 60 DQ12 Data-in/Data-out 61 VDDQ Supply Voltage for DQ 62 DQ13 Data-in/Data-out 63 DQ14 Data-in/Data-out 64 VSSQ Ground for DQ 65 DQ15 Data-in/Data-out 66 VSS Ground Supply Voltage for DQ 3.5.5 Function introduction to CD4052 CD4052 is a 2-group 4-channel data selection device and mainly used in the input selection of audio and video signals in DVD recorder. Each pin function is shown as follows: Pin Name Function I/O 1、2、4、5 Y0-Y3 Y signal input I 11、12、14、15 X0-X3 X signal input I 3、13 Y Y signal output O 6 INH Two groups have no output when two ends are high level I 7 VEE -12V power (grounding) 8 VSS ground 16 VDD +5V power 9、10 B、A Strobe signal I 13 X X signal output O A、 signal strobe condition: A(10) B(9) X(13) Y(3) - 113 - Remark 0 0 X0 Y0 X/Y outputs signals inputted by XO/YO 0 1 X1 Y1 X/Y outputs signals inputted by X1/Y1 1 0 X2 Y2 X/Y outputs signals inputted by X2/Y2 1 1 X3 Y3 X/Y outputs signals inputted by X3/Y3 Note: in the circuit, part of input pins are not used, A, B control end is controlled by main chip. When main chip is switching input signal source, it will control signals to make 4052 perform input source selection. 3.5.6 function introduction to TVP5150A 1. DESCRIPTION The TVP5150A device is an ultralow power NTSC/PAL/SECAM video decoder. Available in a space saving 32-pin TQFP package, the TVP5150A decoder converts NTSC, PAL, and SECAM video signals to 8-bit ITU -R BT.656 format. Discrete syncs are also available. The optimized architecture of the TVP5150A decoder allows for ultralow-power consumption. The decoder consumes 115 mW of power in typical operation and consumes less than 1 mW in power-down mode, considerably increasing battery life in portable applications. The decoder uses just one crystal for all supported standards. The TVP5150A decoder can be programmed using an I2C serial interface. The decoder uses a 1.8-V supply for its analog and digital supplies, and a 3.3-V supply for its I/O. The TVP5150A decoder converts baseband analog video into digital YCbCr 4:2:2 component video. Composite and S-video inputs are supported. The TVP5150A decoder includes one 9-bit analog-t o-digital converter (ADC) with 2x sampling. Sampling is ITU-R BT.601 (27.0 MHz, generated from the 14.31818-MHz crystal or oscillator input) and is line-locked. The output formats can be 8-bit 4:2:2 or 8-bit ITU-R BT.656 with embedded synchronization. The TVP5150A decoder utilizes Texas Instruments patented technology for locking to weak, noisy, or unstable signals. A Genlock/real-time control (RTC) output is generated for synchronizing downstream video encoders. Complementary 4-line adaptive comb filtering is available for both the luma and chroma data paths to reduce both cross-luma and cross-chroma artifacts; a chroma trap filter is also available. Video characteristics including hue, contrast, brightness, saturation, and sharpness may be programmed using the industry standard I2C serial interface. The TVP5150A decoder generates synchronization, blanking, lock, and clock signals in addition to digital video outputs. The TVP5150A decoder includes methods for advanced vertical blanking interval (VBI) data retrieval. The VBI data processor slices, parses, and performs error checking on teletext, closed caption, and other data in several formats. The TVP5150A decoder detects copy-protected input signals according to the Macrovision. standard and detects Type 1, 2, 3, and colorstripe pulses. - 114 - The main blocks of the TVP5150A decoder include: ◆ Robust sync detector ◆ ADC with analog processor ◆ Y/C separation using 4-line adaptive comb filter ◆ Chrominance processor ◆ Luminance processor ◆ Video clock/timing processor and power-down control ◆ Output formatter ◆ I2C interface ◆ VBI data processor ◆ Macrovision. detection for composite and S-video 2. Features ◆ Accepts NTSC (M, 4.43), PAL (B, D, G, H, I, M, N), and SECAM (B, D, G, K, K1, L) video data ◆ Supports ITU-R BT.601 standard sampling ◆ High-speed 9-bit ADC ◆ Two composite inputs or one S-video input ◆ Fully differential CMOS analog preprocessing channels with clamping and automatic gain control (AGC)for best signal-to-noise (S/N) performance ◆ Ultralow power consumption: 115 mW typical ◆ 32-pin TQFP package ◆ Power-down mode: <1 mW ◆ Brightness, contrast, saturation, hue, and sharpness control through I2C ◆ Complementary 4-line (3-H delay) adaptive comb filters for both cross-luminance and cross-chrominance noise reduction ◆ Patented architecture for locking to weak, noisy, or unstable signals ◆ Single 14.31818-MHz crystal for all standards ◆ Internal phase-locked loop (PLL) for line-locked clock and sampling ◆ Subcarrier Genlock output for synchronizing color subcarrier of external encoder ◆ Standard programmable video output format: ◆ ITU -R BT.656, 8-bit 4:2:2 with embedded syncs ◆ 8-bit 4:2:2 with discrete syncs ◆ Macrovision? copy protection detection ? ◆ Advanced programmable video output formats: - 2x oversampled raw VBI data during active video - Sliced VBI data during horizontal blanking or active video ◆ VBI modes supported - 115 - - Teletext (NABTS, WST) - Closed-caption decode with FIFO, and extended data services (EDS) - Wide screen signaling, video program system, CGMS, vertical interval tme code - Gemstar 1x/2x electronic program guide compatible mode - Custom configuration mode that allows the user to program the slice engine for unique VBI data signals ◆ Power-on reset 3. PIN DESCRIPTION PIN Symbol I/O Description 1 AIP1A I 2 AIP1B I 3 PLL_AGND I PLL ground. 4 PLL_AVDD I PLL power supply 5 XTAL1/OSC I External clock reference. 6 XTAL2 O External clock reference. 7 AGND I Substrate. Connect to analog ground. 8 RESETB I Active-low reset. 9 PCLK/SCLK O System clock at either 1x or 2x the frequency of the pixel clock. 10 IO_DVDD I Digital supply. 11 YOUT7/I2CSEL I/O Analog input. Connect to the video analog input via 0.1-? F capac itor. MSB of output decoded ITU-R BT.656 output/YCbCr 4:2:2 output. Determines address for I2C 12 YOUT6 13 YOUT5 14 YOUT4 15 YOUT3 16 YOUT2 17 YOUT1 18 YOUT0 19 DGND I Digital ground 20 DVDD I Digital supply 21 SCL I/O I2C serial clock 22 SDA I/O I2C serial data 23 FID/GLCO O Odd/even field indicator or vertical lock indicator. I/O Output decoded ITU-R BT.656 output/YCbCr 4:2:2 output with discrete sync. - 116 - General-purpose control logic. 24 Vertical synchronization signal VSYNC/PAL1 O PAL line indicator or horizontal lock indicator 25 HSYNC O Horizontal synchronization signal 26 AVID O Active video indicator. 27 INTREQ I/O INTREQ: Interrupt request output. GPCL: General-purpose control logic. 28 PDN I Power-down terminal 29 REFP I A/D reference ground. 30 REFM I A/D reference ground. 31 CH_AGND O Analog ground 32 CH_AVDD O Analog supply 3.5.7 function introduction to 16316-52 1. DESCRIPTION FRONT PANEL CONTROLLER WITH POWER CONTROL FUNCTION The 16316-52 is a FIP (Fluorescent Indicator Panel, or Vacuum Fluorescent Display) controller/driver that is driven on a 1/4 to 1/16 duty factor. It consists of 25 FIP, a display memory, a control circuit, a key scan circuit and a remote control decoder. Serial data is input to the 16316-52 through a 5-line serial interface which is fully hand-shake with the HOST. This FIP controller is ideal as a peripheral device for front panel control for DVD/VCD. 2. FEATURES ◆ FIP controller/driver : 25 display output (1-segment and 24 digits to 24 segment and 1 digit) ◆ Key scanning (3 X 16) ◆ Stand-by control ◆ Remote control code decoding with programmable custom code, support remote formats : N EC, RC5, Kaisakyo, Sony 12 bit, Sony 15 bit ◆ User configurable wake-up code (8 key-code, 8 remote code) ◆ Dimming control ◆ High-voltage output ◆ User data storage (32 bytes) ◆ LED ports (4 chs., 20 mA max) ◆ Serial interface ◆ Fully compatible with C-CUBE ZIVA Font Panel (MIS) protocol. - 117 - 3. PIN DESCRIPTION Description PIN Symbol I/O 1 Vdd Logic Power 2 XT1 Oscillator Circuit input (Sub-clock) 3 XT2 Oscillator Circuit output(Sub-clock) 4 RESET 5 RDY_FM Front Panel Microcontroller Ready 6 ATN_FM Attention by Front Micom 7 #HOST_RST O The reset output to main processor 8 SCK I Clock input 9 D_FM O Data Output 10 D_HOST I The Host transmits 8-bit serial data with LSB first. 11 SCK1 I Clock input 12 POWER_FAIL I Power control pin to control the main power 13 IR I Connect to IR receiver module 14 FIP0 15 FIP1 16 FIP2 17 FIP3 18 FIP4 19 FIP5 20 FIP6 21 FIP7 22 FIP8 23 FIP9 24 FIP10 25 FIP11 26 FIP12 27 Vdd I Logic Power 28 VLoad I Pull-Down level 29 FIP13 O FIP Driving Pins 30 FIP14 31 FIP15 Reset FIP Driving Pins O - 118 - 32 FIP16 33 FIP17 34 FIP18 35 FIP19 36 FIP20 37 FIP21 38 FIP22 39 FIP23 40 FIP24 41 KEY_R1 42 KEY_R2 43 KEY_R3 44 POWER_CTL 45 LED1 46 LED2 47 LED3 48 LED4 49 IC 50 I Input signal for keyboard scan Power control pin to control the main power O LED Output X1 I Oscillator Circuit input (main clock) 51 X2 O Oscillator Circuit output (main clock) 52 VSS I Ground 3.5.8 function introduction to SN74LVC16373 1. Description This 16-bit transparent D-type latch is designed for 2.7-V to 3.6-V VCC operation. The SN74LVC16373 is particularly suitable for implementing buffer registers, I/O ports, bidirectional bus drivers, and working registers. It can be used as two 8-bit latches or one 16-bit latch. When the latch-enable (LE) input is high, the Q outputs follow the data (D) inputs. When LE is taken low, the Q outputs are latched at the levels set up at the D inputs. A buffered output-enable (OE) input can be used to place the eight outputs in either a normal logic state (high or low logic levels) or a high-impedance state. In the high-impedance state, the outputs neither load nor drive the bus lines significantly. The high-impedance state and the increased drive provide the capability to drive bus lines without need for interface or pullup components. OE does not affect internal operations of the latch. Old data can be retained or new data can be entered while the outputs are in the - 119 - high-impedance state. To ensure the high-impedance state during power up or power down, OE should be tied to VCC through a pullup resistor; the minimum value of the resistor is determined by the current-sinking capability of the driver. Active bus-hold circuitry is provided to hold unused or floating data inputs at a valid logic level. 2. Feature ◆ Member of the Texas Instruments Widebus? ? Family ◆ EPIC? ? (Enhanced-Performance Implanted CMOS) Submicron Process ◆ Typical VOLP (Output Ground Bounce) < 0.8 V at VCC = 3.3 V, TA = 25? C ◆ Typical VOHV (Output VOH Undershoot) > 2 V at VCC = 3.3 V, TA = 25? C ◆ Latch-Up Performance Exceeds 250 mA Per JEDEC Standard JESD-17 ◆ Bus Hold on Data Inputs Eliminates the Need for External Pullup/Pulldown Resistors ◆ Package Options Include Plastic 300-mil Shrink Small-Outline (DL) and Thin Shrink Small-Outline (DGG) Packages DGG OR DL PACKAGE 3. PIN DESCRIPTION PIN Symbol I/O Description 1 #1OE I Lacth1 enable input 2 1Q1 O Latch1 output 3 1Q2 O Latch1 output 4 GND I Ground 5 1Q3 O Latch1 output 6 1Q4 O Latch1 output 7 VCC I Power supply 8 1Q5 O Latch1 output 9 1Q6 O Latch1 output 10 GND I Ground 11 1Q7 O Latch1 output 12 1Q8 O Latch1 output 13 2Q1 O Latch2 output 14 2Q2 O Latch2 output 15 GND I Ground 16 2Q3 O Latch2 output 17 2Q4 O Latch2 output 18 VCC I Power supply 19 2Q5 O Latch2 output - 120 - 20 2Q6 O Latch2 output 21 GND I Ground 22 2Q7 O Latch2 output 23 2Q8 O Latch2 output 24 #2OE I Lacth2 enable input 25 2LE I Clock input 2 26 2D8 I Latch2 input 27 2D7 I Latch2 input 28 GND I Ground 29 2D6 I Latch2 input 30 2D5 I Latch2 input 31 VCC I Power supply 32 2D4 I Latch2 input 33 2D3 I Latch2 input 34 GND I Ground 35 2D2 I Latch2 input 36 2D1 I Latch2 input 37 1D8 I Latch1 input 38 1D7 I Latch1 input 39 GND I Ground 40 1D6 I Latch1 input 41 1D5 I Latch1 input 42 VCC I Power supply 43 1D4 I Latch1 input 44 1D3 I Latch1 input 45 GND I Ground 46 1D2 I Latch1 input 47 1D1 I Latch1 input 48 1LE I Clock input 1 3.5.9 function introduction to MSP 34x5G 1. Description The MSP 34x5G family of single-chip Multistandard Sound Processors covers the sound processing of - 121 - all analog TV standards worldwide, as well as the NICAM digital sound standards. The full TV sound processing, starting with analog sound IF signal-in, down to processed analog AF-out, is performed in a single chip. Figure 1–1 shows a simplified functional block diagram of the MSP 34x5G. This new generation of TV sound processing ICs now includes versions for processing the multichannel television sound (MTS) signal conforming to the standard recommended by the Broadcast Television Systems Committee (BTSC). The DBX noise reduction is performed alignment-free. Other processed standards are the Japanese FM-FM multiplex standard (EIA-J) and the FM-Stereo-Radio standard. Current ICs have to perform adjustment procedures in order to achieve good stereo separation for BTSC and EIA-J. The MSP 34x5G has optimum stereo performanceb without any adjustments. All MSP 34xxG versions are pin compatible to the MSP 34xxD. Only minor modifications are necessary to adapt a MSP 34xxD controlling software to the MSP 34xxG. The MSP 34x5G further simplifies controlling software. Standard selection requires a single I2C transmission only. 2. PIN DESCRIPTION PIN Symbol I/O Description 1 AVSUP I Analog power supply +5 V 2 ANA_IN1+ I IF input 1 3 ANA_IN- I IF common 4 TESTEN I Test pin 5 XTAL_IN I Crystal oscillator 6 XTAL_OUT O Crystal oscillator 7 TP I Test pin 8 D_CTR_I/O_1 I/O D_CTR_I/O_1 9 D_CTR_I/O_0 I/O D_CTR_I/O_0 10 ADR_SEL I I2C Bus address select 11 STANDBYQ I Standby 12 I2C_SCL I/O I2C clock 13 I2C_SDA I/O I2C data 14 I2C_CL I I2C clock 15 I2C_WS I I2C word strobe 16 I2C_DA_OUT O I2C data output 17 I2C_DA_IN1 I I2C data input 18 TP_CO I ADR clock 19 DVSUP I Digital power supply +5 V - 122 - 20 DVSS I Digital ground 21 I2C_DA_IN2 I I2S2-data input 22 RESETQ I Power-on-reset 23 NC Not connected 24 NC Not connected 25 VREF2 I Reference ground 2 high-voltage part 26 DACM_R O Loudspeaker out R 27 DACM_L O Loudspeaker out L 28 NC 29 VREF1 I Reference ground 1 high-voltage part 30 SC1_OUT_R O SCART 1 output R 31 SC1_OUT_L O SCART 1 output L 32 NC 33 AHVSUP I Analog power supply 8.0 V 34 CAPL_M I Volume capacitor MAIN 35 AHVSS I Analog ground 36 AGNDC I Analog reference voltage high-voltage part 37 SC2_IN_L I SCART 1 input 2 38 SC2_IN_R I SCART 1 input 2 39 ASG1 I Analog shield ground 40 SC1_IN_L I SCART 1 input 1 41 SC1_IN_R I SCART 1 input 1 42 VREFTOP I Reference voltage IF A/D converter 43 MONO_IN I Mono input 44 AVSS I Analog ground Not connected Not connected 3.5.10 function introduction to TPS2041A 1. Description The TPS2041A through TPS2044A and TPS2051A through TPS2054A power-distribution switches are intended for applications where heavy capacitive loads and short circuits are likely to be encountered. These devices incorporate 80-mW N-channel MOSFET high-side power switches for power-distribution systems that require multiple power switches in a single package. Each switch is controlled by an independent logic enable input. Gate drive is provided by an internal charge pump designed to control the power-switch rise times and - 123 - fall times to minimize current surges during switching. The charge pump requires no external components and allows operation from supplies as low as 2.7 V. When the output load exceeds the current-limit threshold or a short is present, these devices limit the output current to a safe level by switching into a constant-current mode, pulling the overcurrent (OCx) logic output low. When continuous heavy overloads and short circuits increase the power dissipation in the switch, causing the junction temperature to rise, a thermal protection circuit shuts off the switch to prevent damage. Recovery from a thermal shutdown is automatic once the device has cooled sufficiently. Internal circuitry ensures the switch remains off until valid input voltage is present. These power-distribution switches are designed to current limit at 0.9 A. 2. FEATURE ◆ 80-mW High-Side MOSFET Switch ◆ 500 mA Continuous Current Per Channel ◆ Independent Thermal and Short-Circuit Protection With Overcurrent Logic Output ◆ Operating Range . . . 2.7 V to 5.5 V ◆ CMOS- and TTL-Compatible Enable Inputs ◆ 2.5-ms Typical Rise Time ◆ Undervoltage Lockout ◆ 10 mA Maximum Standby Supply Current for Single and Dual (20 mA for Triple and Quad) ◆ Bidirectional Switch ◆ Ambient Temperature Range, 0°C to 85°C ◆ ESD Protection ◆ UL Listed ¨C File No. E169910 3. PIN DESCRIPTION PIN Symbol I/O Description 1 GND I Ground 2 IN I Input voltage 3 IN I Input voltage 4 #EN I Enable input 5 #OC O Over current 6 OUT I 7 OUT I 8 OUT I Power-switch - 124 - 3.5.11 function introduction to LP2995 1. Description The LP2995 linear regulator is designed to meet the JEDEC STL-2 and SSTL-3 specifications for termination of DDRSDRAM. The device contains a high-speed operational amplifier to provide excellent response to load transients. The output stage prevents shoot through while delivering 1.5A continuous current and transient peaks up to 3A in the application as required for DDR-SDRAM termination. The LP2995 also incorporates a VSENSE pin to provide superior load regulation and a VREF output as a reference for the chipset and DDR DIMMS. 2. Features ◆ Low output voltage offset ◆ Works with +5v, +3.3v and 2.5v rails ◆ Source and sink current ◆ Low external component count ◆ No external resistors required ◆ Linear topology ◆ Available in SO-8, PSOP-8 or LLP-16 packages ◆ Low cost and easy to use 3. PIN DESCRIPTION PIN Symbol Description 1 NC 2 GND 3 VSENSE 4 VREF Buffered internal reference voltage of VDDQ/2. 5 VDD Input for internal reference equal to VDDQ/2. 6 AVIN Analog input pin. 7 PVIN Power input pin. 8 VTT Output voltage for connection to termination resistors. No internal connection. Ground Feedback pin for regulating VTT . 3.5.12 function introduction to FSDM0565R 1. Description The FSDM0565R is specially designed for an off-line Switched mode power supply (SMPS). This device is a current mode PWM controller combined with a high voltage power SenseFET in a single package using BCDMOS technology. The PWM controller includes integrated fixed frequency oscillator, under voltage - 125 - lockout, leading edge blanking (LEB), optimized gate driver, internal soft start, temperature compensated precise current sources for a loop compensation and self protection circuitry. Compared with discrete MOSFET and PWM controller solution, it can reduce total cost, component count, size and weight simultaneously increasing efficiency, productivity, and system reliability. This device is well suited for cost effective design of LCD monitor adapter. 2. Features ◆ Precise fixed operating frequency (70kHz) ◆ Low power consumption (under 1W) at 265VAC with 0.5W load with a burst-mode operation ◆ Pulse by pulse current limit ◆ Abnormal over current protection (auto restart mode) ◆ Over voltage protection (auto restart mode) ◆ Over load protection (auto restart mode) ◆ Thermal shutdown (auto restart mode) ◆ Under voltage lockout ◆ Fully avalanche rated and 100% tested senseFET ◆ Internal soft start 3. PIN DESCRIPTION PIN Symbol 1 Drain 2 Ground 3 Vcc 4 Feedback 5 Nc 6 Vstr Description This pin is the high voltage power SenseFET drain. This pin is the control ground and the SenseFET source. This pin is the positive supply voltage input. This pin is internally connected to the inverting input of the PWM comparator. This pin is connected directly to the high voltage DC link. 3.5.13 Function introduction to M41T80 1. DESCRIPTION M41T80 is the latest serial real-time clock chip, and used in batter power supply. M41T80 includes I2C jack and warning function of 400KHz, special 32KHz output, when in low power mode or clock generator reference input, the micro controller of 32Khz is very useful. The warning function of M41T80 includes repeat mode, from once in a year to once in a second. The programmable wave function may perform program from 1Hz to 32KHz, power classification of 2, when voltage power supply is normal, 32KHz output is continuous and may be screen-shielded by software. 126 - 2. Features ◆ 2.0 TO 5.5V CLOCK OPERATING VOLTAGE ◆ COUNTERS FOR TENTHS/HUNDREDTHS OF SECONDS, SECONDS, MINUTES, HOURS, DAY, DATE, MONTH, YEAR, and CENTURY ◆ SERIAL INTERFACE SUPPORTS I2C BUS (400KHz) ◆ PROGRAMMABLE ALARM and INTERRUPT FUNCTION ◆ LOW OPERATING CURRENT OF 200¦ÌA ◆ OPERATING TEMPERATURE OF -40 TO 85 °C 3. PIN DESCRIPTION PIN Symbol I/O Description 1 XI I Crystal oscillator input 2 XO O Crystal oscillator output 3 F32K O 32KHz square wave output 4 VSS I Ground 5 SDA I/O Serial data input/output 6 SCL I Serial clock input 7 IRQ O Interrupt / Output Driver / Square Wave (Open Drain) 8 VCC I Supply voltage 3.5.14 function introduction to EM6353 1. Description The EM6353 is an ultra-low current reset circuit available in a large variety of configurations and very small packages for maximum flexibility in all end-applications up to 125°C and using power supplies between 1.5V and 5.5V. This circuit monitors the supply voltage of any electronic system, and generates the appropriate reset signal after a fixed reset timeout period. The threshold defines the minimum allowed voltage which guarantees the good functionality of the system. When VDD rises above VTH, the output remains active for an additional delay time. This allows the system to stabilize before getting fully active. The EM6353 features three output types: active-low pushpull, active-low open-drain and active-high push-pull. Small SC70-5L and SOT23-3L packages as well as ultra-low supply current of 2.9µA make the EM6353 an ideal choice for portable and battery-operated devices. 2. Features ◆ 200ms reset timeout period (25ms on request) ◆ Ultra-low supply current of 2.9µA (VDD=3.3V) - 127 - ◆ Operating temperature range: -40°C to +125°C ◆±1.5% reset threshold accuracy ◆ 11 reset threshold voltages VTH: 4.63V, 4.4V, 3.08V, 2.93V, 2.63V, 2.2V, 1.8V, 1.66V, 1.57V, 1.38V, 1.31V ◆ 3 reset output options: Active -low RESET push-pull Active -low RESET open-drain Active -high RESET push-pull ◆ No external components ◆ Immune to short negative VDD transients ◆ Guaranteed Reset valid down to 0.8V ◆ Threshold hysteresis: 2.1% of VTH ◆ Very small SOT23-3L and SC70-5L packages 3. PIN DESCRIPTION PIN Symbol I/O Description 1 NC 2 VDD I Power supply 3 NC 4 GND I Ground 5 RESET O Active-low RESET output. 3.5.15 function introduction to KA5H0380R 1. Description The Fairchild Power Switch(FPS) product family is specially designed for an off-line SMPS with minimal external components. The Fairchild Power Switch(FPS) consist of high voltage power SenseFET and current mode PWM IC. Included PWM controller features integrated fixed frequency oscillator, under voltage lock-out, leading edge blanking, optimized gate turn-on/turn-off driver, thermal shutdown protection, over voltage protection, and temperature compensated precision current sources for loopcompensation and fault protection circuitry. Compared to discrete MOSFET and PWM controller or RCC solution, a Fairchild Power Switch(FPS) can reduce total component count, design size, weight and at the same time increase efficiency, productivity, and system reliability. It has a basic platform well suited for cost effective design 2.Features ◆ Precision fixed operating frequency (100/67/50kHz) ◆ Low start -up current(typ. 100uA) - 128 - ◆ Pulse by pulse current limiting ◆ Over current protection ◆ Over voltage protecton (Min. 25V) ◆ Internal thermal shutdown function ◆ Under voltage lockout ◆ Internal high voltage sense FET ◆ Auto-restart mode 3. PIN DESCRIPTION PIN Symbol I/O Description 1 GND I Ground 2 DRAIN O Drain 3 VCC I Power supply 4 FB I Feedback 3.5.16 function introduction to 74HC/HCT14 1. Description The 74HC/HCT14 are high-speed Si-gate CMOS devices and are pin compatible with low power Schottky TTL (LSTTL). They are specified in compliance with JEDEC standard no. 7A. The 74HC/HCT14 provide six inverting buffers with Schmitt-trigger action. They are capable of transforming slowly changing input signals into sharply defined, jitter-free output signals. 2. FEATURES ◆ Output capability: standard ◆ ICC category: SSI 3. PIN DESCRIPTION PIN Symbol I/O Description 1、3、5、9、11、13 1A to 6A I Data inputs 2、4、6、8、10、12 1Y to 6Y O Data outputs 7 GND I Ground (0 V) 14 VCC I Positive supply voltage - 129 - Chapter Four Disassembly and Assembly Process DVD players manufactured in BBK are largely identical but with minor differences and are mainly composed of loader components, control panel components, decode and servo board components, power board components, power amplifier board components, MIC board components and AV board components. In order to speed up the compilation of “Service Manual”, we shall not give repeat explanation to model with minor differences in chapter four “Disassembly and Assembly Process” for the later compiled service manuals. For disassembly and assembly process in this chapter, please refer to chapter 4 of “DK1005S Service Manual” or “DK1020S Service” . The pictures of this model are shown as follows: - 130 - Chapter Cinque PCB board & Circuit diagram Section One PCB board 5.1.1 Surface layer of AV OUT Board - 131 - 5.1.2 Bottom layer of AV OUT Board - 132 - 5.1.3 Surface layer of DECODE&SERVO Board - 133 - 5.1.4 Bottom layer of DECODE&SERVO Board - 134 - 5.1.5 Surface layer of KEY SCAN Board - 135 - 5.1.6 Bottom layer of KEY SCAN Board - 136 - 5.1.7 MIC Board - 137 - 5.1.8 POWER Board - 138 - A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 A9 A10/AP A11 A12 BA0 BA1 SDRAM_CS0 SDRAM_CLKE SDRAM_RAS# SDRAM_CAS# SDRAM_WE# SDRAM_DQM0 SDRAM_DQM1 SDRAM_DQS0 SDRAM_DQS1 24 44 23 22 21 20 47 16 51 CS# CKE RAS# CAS# WE# LDM UDM LDQS UDQS 3 SDRAM_CLK0 3 SDRAM_CLK#0 45 46 CLK CLK# 49 1 18 33 3 9 15 55 61 VREF VCC VCC VCC VCCQ VCCQ VCCQ VCCQ VCCQ SDRAM_A0 SDRAM_A1 SDRAM_A2 SDRAM_A3 SDRAM_A4 SDRAM_A5 SDRAM_A6 SDRAM_A7 SDRAM_A8 SDRAM_A9 SDRAM_A10 SDRAM_A11 SDRAM_A12 SDRAM_A14 SDRAM_A15 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 2,3 VREF DDR_VDD D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10 D11 D12 D13 D14 D15 2 4 5 7 8 10 11 13 54 56 57 59 60 62 63 65 NC NC NC NC 14 17 19 25 NC NC NC 43 50 53 GND GND GND GNDQ GNDQ GNDQ GNDQ GNDQ 34 48 66 6 12 52 58 64 SDRAM_DQ0 SDRAM_DQ1 SDRAM_DQ2 SDRAM_DQ3 SDRAM_DQ4 SDRAM_DQ5 SDRAM_DQ6 SDRAM_DQ7 SDRAM_DQ8 SDRAM_DQ9 SDRAM_DQ10 SDRAM_DQ11 SDRAM_DQ12 SDRAM_DQ13 SDRAM_DQ14 SDRAM_DQ15 PLACEMENT M2 U25 E5 SDRAM_CLK1 M1 SSTL2_VDD U22 DDR_VDD FB2 B601 SDRAM_CLK0 V33 Option for DDR with 3.3V VDD FB3 B601 C108 C109 C110 C111 C112 C113 104 104 104 102 102 102 + C114 10UF/1206 GND SSTL2_VDD 8MX16 DDR + GND C124 10UF/1206 C115 C116 C117 C118 C119 C120 C121 C122 C123 104 104 104 104 104 102 102 102 102 C125 C126 C127 C128 C129 C130 104 104 104 102 102 102 C132 C133 C134 C135 C136 C137 C138 C139 C140 104 104 104 104 104 102 102 102 102 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 SDRAM_A0 SDRAM_A1 SDRAM_A2 SDRAM_A3 SDRAM_A4 SDRAM_A5 SDRAM_A6 SDRAM_A7 SDRAM_A8 SDRAM_A9 SDRAM_A10 SDRAM_A11 SDRAM_A12 SDRAM_A14 SDRAM_A15 SDRAM_A0 SDRAM_A1 SDRAM_A2 SDRAM_A3 SDRAM_A4 SDRAM_A5 SDRAM_A6 SDRAM_A7 SDRAM_A8 SDRAM_A9 SDRAM_A10 SDRAM_A11 SDRAM_A12 SDRAM_A14 SDRAM_A15 29 30 31 32 35 36 37 38 39 40 28 41 42 26 27 A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 A9 A10/AP A11 A12 BA0 BA1 CS# CKE RAS# CAS# WE# LDM UDM LDQS UDQS 3 SDRAM_CS0 3 3 3 3 SDRAM_DQM2 SDRAM_DQM3 SDRAM_DQS2 SDRAM_DQS3 24 44 23 22 21 20 47 16 51 3 SDRAM_CLK1 3 SDRAM_CLK#1 45 46 CLK CLK# 49 1 18 33 3 9 15 55 61 VREF VCC VCC VCC VCCQ VCCQ VCCQ VCCQ VCCQ DDR_VDD D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 R109 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10 D11 D12 D13 D14 D15 2 4 5 7 8 10 111 13 54 56 57 59 60 62 63 65 NC NC NC NC 14 17 19 25 NC NC NC 43 50 53 GND GND GND GNDQ GNDQ GNDQ GNDQ GNDQ 34 48 66 6 12 52 58 64 SDRAM_DQ16 SDRAM_DQ17 SDRAM_DQ18 SDRAM_DQ19 SDRAM_DQ20 SDRAM_DQ21 R109 SDRAM_DQ22 1 SDRAM_DQ23 SDRAM_DQ24 SDRAM_DQ25 SDRAM_DQ26 SDRAM_DQ27 SDRAM_DQ28 SDRAM_DQ29 SDRAM_DQ30 SDRAM_DQ31 + C131 T47u/16 GND 8MX16 DDR 10UF/1206 GND_SSTL2 GND GND SSTL2_VDD C141 DDR_VDD SSTL2_VDD + - 139 - GND U4 GND Section Two circuit diagram U3 SDRAM_A0 SDRAM_A1 SDRAM_A2 SDRAM_A3 SDRAM_A4 SDRAM_A5 SDRAM_A6 SDRAM_A7 SDRAM_A8 SDRAM_A9 SDRAM_A10 SDRAM_A11 SDRAM_A12 SDRAM_A14 SDRAM_A15 29 30 31 32 35 36 37 38 39 40 28 41 42 26 27 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 SDRAM_CS0 5.2.1 MPEG&SERVO Board LAYOUT NOTE: 3 SDRAM_DQ[31..0] 3 E5_SDRAM_A0 3 E5_SDRAM_A1 3 E5_SDRAM_A2 3 E5_SDRAM_A3 3 E5_SDRAM_A4 3 E5_SDRAM_A5 3 E5_SDRAM_A6 3 E5_SDRAM_A7 3 E5_SDRAM_A8 3 E5_SDRAM_A9 3 E5_SDRAM_A10 3 E5_SDRAM_A11 3 E5_SDRAM_A12 3 E5_SDRAM_A14 3 E5_SDRAM_A15 3 E5_SDRAM_CS0 3 E5_SDRAM_CAS# 3 E5_SDRAM_RAS# 3 E5_SDRAM_CLKE 3 E5_SDRAM_WE# 3 E5_SDRAM_CLK0 3 E5_SDRAM_CLK#0 3 E5_SDRAM_CLK1 3 E5_SDRAM_CLK#1 3,4 VREF 5,9 E5_GPIOx35 E5_GPIO6 R33 R34 E5_GPIOx32 R35 E5_GPIO6 22 22 22 AISCLK A12 A IFSYNC D13 C13 AIMCLKO A16 CLKI CLKX (Reset_Audio) E5_GPIOx35 E1 F1 H1 G1 AI_D0 AI_D1 GPIO[6] GPIO[7] AI_SCLK AI_FSYNC AI_MCLKI AI_MCLKO CLKI 3.3v only CLKX GPIOx[35] CLKO BYPASS_PLL DACO G ND G ND 9 9 9 B7 A7 C6 B6 D6 B10 C10 B11 C11 D11 D10 B12 C12 D12 A11 VI_D0 VI_D1 VI_D2 VI_D3 VI_D4 VI_D5 VI_D6 VI_D7 VI_D[7..0] VI_VSYNC VI_CLK0 VI_VSYNC VI_CLK0 A10 A9 TCK TDI TDO TMS TRST_L PEC VI_VSYNC0 VI_CLK0 10K E5_GPIOx5 R40 10K E5_GPIOx6 R41 10K E5_GPIOx7 R42 10K (SCART_GPIO) (SCART_GPIO) (SCART_GPIO) (BIO_PHY_PD)7 12 - 140 - 12 (VI_AVID) 9 (MIC_DET) 12 12 (INT_VI) 9 (/RST_VI) 9 E5_GPIOx0 E5_GPIOx1 E5_GPIOx2 E5_GPIOx3 E5_GPIOx4 E5_GPIOx5 E5_GPIOx6 E5_GPIOx7 E5_GPIOx0 E5_GPIOx1 E5_GPIOx2 E5_GPIOx3 E5_GPIOx4 E5_GPIOx5 E5_GPIOx6 E5_GPIOx7 D7 C7 D8 C8 B8 D9 C9 B9 20-bit vin VI_D10 VI_D11 VI_D12 VI_D13 VI_D14 VI_D15 VI_D16 VI_D17 VI_D18 VI_D19 VO_D16 VO_D17 VO_D18 VO_D19 VO_D20 VO_D21 VO_D22 VO_D23 GPIOx[0] GPIOx[1] GPIOx[2] GPIOx[3] GPIOx[4] GPIOx[5] GPIOx[6] GPIOx[7] GPIOx[8] GPIOx[9] GPIOx[10] GPIOx[11] GPIOx[12] GPIOx[13] GPIOx[14] GPIOx[15] VO_D0 VO_D1 VO_D2 VO_D3 VO_D4 VO_D5 VO_D6 VO_D7 GPIOx[30] A8 2nd vout VO_D0 VO_D1 VO_D2 VO_D3 VO_D4 VO_D5 VO_D6 VO_D7 E5_GPIOx41 E5_GPIOx42 Y17 Y18 U14 V15 IRTX1 IRRX V18 U16 CS7CS6- IDC_DAT IDC_CLK UART2_TX UART2_RX Y15 W19 U15 U17 Y19 UART1_RTS UART1_CTS UART1_TX UART1_RX SPI_CS2 SPI_CS1 SPI_CS0 SPI_MISO SPI_MOSI Y16 V16 W16 W18 W17 E5_GPIOx25 E5_GPIOx24 E5_SDRAM_DQM0 E5_SDRAM_DQS0 E5_SDRAM_DQ7 E5_SDRAM_DQ6 E5_SDRAM_DQ5 E5_SDRAM_DQ4 E5_SDRAM_DQ3 E5_SDRAM_DQ2 E5_SDRAM_DQ1 E5_SDRAM_DQ03 3 K19 M20 K18 L17 L18 L19 M17 N20 M19 M18 E5_SDRAM_DQM1 E5_SDRAM_DQS1 E5_SDRAM_DQ15 E5_SDRAM_DQ14 E5_SDRAM_DQ13 E5_SDRAM_DQ12 E5_SDRAM_DQ11 E5_SDRAM_DQ10 E5_SDRAM_DQ9 E5_SDRAM_DQ83 3 H20 J20 G20 H17 H18 J18 J17 H19 J19 K17 E5_SDRAM_DQM2 E5_SDRAM_DQS2 E5_SDRAM_DQ23 E5_SDRAM_DQ22 E5_SDRAM_DQ21 E5_SDRAM_DQ20 E5_SDRAM_DQ19 E5_SDRAM_DQ18 E5_SDRAM_DQ17 3 E5_SDRAM_DQ16 3 F20 F19 E17 E18 E19 F17 F18 G17 G18 G19 E5_SDRAM_DQM3 E5_SDRAM_DQS3 E5_SDRAM_DQ31 E5_SDRAM_DQ30 E5_SDRAM_DQ29 E5_SDRAM_DQ28 E5_SDRAM_DQ27 E5_SDRAM_DQ26 E5_SDRAM_DQ25 3 E5_SDRAM_DQ24 3 D18 C18 C20 B19 C19 B20 A20 A19 B18 A18 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 GPIOx[23] GPIOx[22] GPIOx[21] GPIOx[20] GPIOx[19] GPIOx[18] GPIOx[17] GPIOx[16] SBP_FRAME SBP_ACK SBP_RD SBP_REQ SBP_CLK SBP_D[7] SBP_D[6] SBP_D[5] SBP_D[4] SBP_D[3] SBP_D[2] SBP_D[1] SBP_D[0] CD_C2PO CD_BCK CD_LRCK CD_DATA SD_D[7] SD_D[6] SD_D[5] SD_D[4] SD_D[3] SD_D[2] SD_D[1] SD_D[0] SD_SECSTART SD_ERROR SD_CLK SD_ACK SD_RDREQ SD_WRREQ V10 W11 Y10 V9 V11 Y12 W10 W12 Y13 U11 V13 W13 Y14 U12 U13 W14 R32 DIGITAL 104 VO_GND C11 10UF/1206 101 G ND VO_GND E5_V5BIAS G ND E5_VCORE GND G ND C15 C16 C17 C18 C19 C20 C21 C22 102 102 104 104 104 104 104 104 C23 + C25 + T47u/16 C24 10UF/1206 C33 C34 C35 C36 C37 102 102 102 103 103 + C26 + 10UF/1206 E5_VDDREF C51 103 E5_AVDD C52 C53 104 103 GND C54 103 GND 104 102 G ND C46 C47 C48 C49 C50 102 102 102 103 104 C39 + 10UF/1206 10UF/1206 E5_GPIO2 R15 10K E5_GPIO3 R16 *10K E5_GPIO4 R18 10K E5_GPIO5 R22 10K /WAIT R25 10K GPIO1 R153 10K 10K E5_GPIOx32 R158 10K E5_GPIOx33 R159 10K E5_UART2_TX 1 TX1 E5_UART2_RX 1 RX1 V18_E5_DAC_DVDD FB1 601 CA1 C3 + T47u/16 104 G ND 5,6 HD[15..0] 2.5V V25 SSTL2_VDD 3.3V -12V L1 601 L2 601 L3 601 L4 601 V33_E5_USB E5_VDDX E5_AVDD E5_VDDREF V33_E5_DAC_AVDD C4 + T47u/16 G ND 5V C27 C28 C29 C30 C31 C32 104 104 104 104 104 104 10UF/1206 C38 + 10K R14 104 E5_VCORE C56 10K R13 E5_VPAD E5_VDDX C55 R12 E5_GPIO1 C5 G ND G ND /E5_CS2 E5_GPIO0 V33 V33 E5_VPAD C14 102 10K E5_VCORE ATAPI_DATA7 6 ATAPI_DATA6 6 ATAPI_DATA5 6 ATAPI_DATA4 6 ATAPI_DATA3 6 ATAPI_DATA2 6 ATAPI_DATA1 6 ATAPI_DATA0 6 ATAPI_RESET 6 ATAPI_DMAACK_L 6 ATAPI_DMARQ 6 ATAPI_IORDY 6 ATAPI_INTRQ 6 ATAPI_DIOR_L 6 ATAPI_DIOW_L 6 Caps with smaller capacitance values to be closer to respective power pins compared to those of larger values. All should be as close as possible. E5_VDDX R9 V18 M3 M4 N3 N4 P2 P4 R3 T1 Y1 T2 W1 T3 V2 U3 R2 General decoupling cap placement: SSTL2_VDD 10K MUTE 1.8V ATAPI_DATA7 ATAPI_DATA6 ATAPI_DATA5 ATAPI_DATA4 ATAPI_DATA3 ATAPI_DATA2 ATAPI_DATA1 ATAPI_DATA0 ATAPI_RESET_L ATAPI_DMAACK_L ATAPI_DMARQ ATAPI_IORDY ATAPI_INTRQ ATAPI_DIOR_L ATAPI_DIOW_L GND GND E5_AVDD 10K R8 6 5,6 5,6 5,6 5,6 5,6 AtapiAddr0 6 AtapiAddr1 6 AtapiAddr2 6 AtapiAddr3 6 AtapiAddr4 6 ATAPI_DATA15 6 ATAPI_DATA14 6 ATAPI_DATA13 6 ATAPI_DATA12 6 ATAPI_DATA11 6 ATAPI_DATA10 6 ATAPI_DATA9 6 ATAPI_DATA8 6 R43 104 C13 C302 G ND SSTL2_VDD 5 6 V3 T4 V1 U2 U4 W2 U1 R4 R1 P3 P1 N2 M2 A21 FS0 C12 + /E5_CS1 /E5_CS0 AtapiAddr0 AtapiAddr1 AtapiAddr2 AtapiAddr3 AtapiAddr4 ATAPI_DATA15 ATAPI_DATA14 ATAPI_DATA13 ATAPI_DATA12 ATAPI_DATA11 ATAPI_DATA10 ATAPI_DATA9 ATAPI_DATA8 7 7 7 7 E5_VPAD IN4148 /WAIT 5,6 5 (FP D_HOST) 12(/RST_PHY) 7 (/ETHER_IRQ) 5 (RST_CS4360) 11 (AUDIO_SEL0) 12 (AUDIO_SEL1) 12 5,6 5 5 HD15 HD14 HD13 HD12 HD11 HD10 H D9 H D8 H D7 H D6 H D5 H D4 H D3 H D2 H D1 H D0 1.18K 1% 103 7 7 7 7 7 104 BIO_PHY_DATA1 BIO_PHY_DATA0 BIO_PHY_CTL1 BIO_PHY_CTL0 BIO_LREQ BIO_LPS BIO_LINK_ON BIO_PHY_CLK 7 77 104 D3 USB_D0+ USB_D0USB_PO0 USB_OC0 C10 22 /E5_OE /E5_UDS E5_GPIO0 E5_GPIO1 E5_GPIO2 E5_GPIO3 E5_GPIO4 E5_GPIO5 /E5_WEL /WAIT E5_/DTACK E5_MA22 E5_MA5 E5_MA4 E5_MA3 E5_MA2 E5_MA1 V33_E5_USB 12 C9 5,6 5,6 10K R7 VCC 1 IN4148 C8 E5_ALE /SYS_RST /E5_CS2 E5_VDDREF 2 + D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 /DTACK D2 V33_E5_DAC_AVDD CA2 T47u/16 R27 22 R28 22 E5_GPIO0 E5_GPIO1 E5_GPIO2 E5_GPIO3 E5_GPIO4 E5_GPIO5 R31 22 DATA PLL 11,12 G ND VSS_REF R_REF VDD_REF 3.3V 22 MCONFIG B1 C1 C2 5V VSS_PC2_CTR1 VSS_PC2_CTR2 VSS_PC2_CTR3 VSS_PC2_CTR4 VSS_PC2_CTR5 VSS_PC2_CTR6 VSS_PC2_CTR7 VSS_PC2_CTR8 VSS_PC2_CTR9 VSS_PC2_CTR10 VSS_PC2_CTR11 VSS_PC2_CTR12 VSS_PC2_CTR13 VSS_PC2_CTR14 VSS_PC2_CTR15 VSS_PC2_CTR16 VSS_PC2_CTR17 VSS_PC2_CTR18 VSS_PC2_CTR19 VSS_PC2_CTR20 VSS_PC2_CTR21 VSS_PC2_CTR22 VSS_PC2_CTR23 VSS_PC2_CTR24 VSS_PC2_CTR25 VSS_PC2_CTR26 VSS_PC2_CTR27 VSS_PC2_CTR28 VSS_PC2_CTR29 VSS_PC2_CTR30 VSS_PC2_CTR31 VSS_PC2_CTR32 VSS_PC2_CTR33 VSS_PC2_CTR34 VSS_PC2_CTR35 VSS_PC2_CTR36 VSS_PC2_CTR37 VSS_PC2_CTR38 PLL 2.5V VREF C15 C17 H8 H9 H10 H11 H12 H13 J8 J9 J10 J11 J12 J13 K8 K9 K10 K11 K12 K13 L8 L9 L10 L11 L12 L13 M8 M9 M10 M11 M12 M13 N8 N9 N10 N11 N12 N13 3.3V DDR AGND1 AGND2 AGND0 AGND3 GNDX USB_Avdd0(3.3v) USB_VSS0 F4 F3 G ND 1.8V C3 D4 E3 D1 F2 DAC_Vdd0(3.3v) DAC_Vdd1(3.3v) DAC_Dvss DAC1bar DAC0bar C7 103 3.3V SDR AVDD1 AVDD2 AVDD0 AVDD3 VDDX C CPST DAC_Dvdd (1.8v) B2 B3 C5 B4 B5 C6 104 SDRAM CORE C4 E4 D3 D2 E2 DAC6 R/Pr D5 10 V18_E5_DAC_DVDD PADS BIAS Pr/R A6 POWER - 5V_BIAS0 C CPST 3.3V GND D15 Y DAC5 B/Pb VDD_25V1 VDD_25V2 VDD_25V3 VDD_25V4 VDD_25V5 VDD_25V6 DAC4 G/Y A5 C16 D17 J16 K16 L16 M16 DAC3 A4 VDD_CORE1 VDD_CORE2 VDD_CORE3 VDD_CORE4 VDD_CORE5 VDD_CORE6 VDD_CORE7 VDD_CORE8 VDD_CORE9 A3 Y/G Pb/B 10 GND L5 M5 T9 T10 E9 E10 D19 T17 V17 - C 10 10 POWER 1394 VDD_PAD1 VDD_PAD2 VDD_PAD3 VDD_PAD4 VDD_PAD5 VDD_PAD6 VDD_PAD7 C CPST USB H4 J5 K5 E11 E12 T12 T11 - BIO_PHY_DATA7 BIO_PHY_DATA6 BIO_PHY_DATA5 BIO_PHY_DATA4 BIO_PHY_DATA3 BIO_PHY_DATA2 BIO_PHY_DATA1 BIO_PHY_DATA0 BIO_PHY_CTL1 BIO_PHY_CTL0 BIO_LREQ BIO_LPS BIO_LINK_ON BIO_PHY_CLK Y CPST K2 K3 K4 J1 L3 L4 L2 J2 K1 J3 N1 M1 J4 L1 2 - DAC2 GPIOx[43] GPIOx[44] GPIOx[36] 1 Y DAC1 CPST A2 Dplus_0 Dminus_0 Host_PO_0 Host_OC_0 0 A1 Y G3 G4 H2 H3 SEL CVBS OEUWEGPIO0 GPIO1 GPIO2 GPIO3 GPIO4 GPIO5 LWEWAITDTACKCS5CS4CS3CS2CS1CS0MA[26] MS[25] MA[24] MA[23] MA[22] MA[5] MA[4] MA[3] MA[2] MA[1] Y9 V14 V6 V12 W9 V8 W8 U10 Y7 U8 U9 W3 Y2 Y6 Y4 Y5 Y3 V4 V5 W4 U5 W5 U6 W7 W6 U7 V7 MA[21] MA[20] MA[19] MA[18] MA[17] MA[16] MA[15] MA[14] MA[13] MA[12] MA[11] MA[10] MA[9] MA[8] MA[7] MA[6] VDENC 10 R20 PCMCIA_IOWPCMCIA_IORWR- RD WAITDTACKD31 D30 D29 D28 D27 D26 D25 D24 D23 D22 D21 D20 D19 D18 D17 D16 VO_CLK 10 ALE RSTMCONFIG CS0_8BIT Y8 W15 G2 Y11 LDSUDS- D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 A B C D E F G H J K L M N P R T U V W Y TOP VIEW IR_FMUTE CONTROL 10K E5_GPIOx4 R39 24-bit vout IR SD/CD E5_GPIOx3 R38 2nd vin VI_D0 VI_D1 VI_D2 VI_D3 VI_D4 VI_D5 VI_D6 VI_D7 VI_D8 VI_D9 VIO 10K UART2 IDC VOUT E5_GPIOx1 R37 V33 3.3V ONLY 10K UART1 SIO A B C D E F G H J K L M N P R T U V W Y GPIOx[45] GPIOx[29] E5_GPIOx2 R36 SPI 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 JTAG VI_D0 VI_D1 VI_D2 VI_D3 VI_D4 VI_D5 VI_D6 VI_D7 VI_D8 VI_D9 I/F E5.1-BGA-308-A U1 VIN TCK TDI TDO TMS TRST_L DATA SDRAM CS[8]- GPIOx[32] 13.5MHZ C2 27P ADDR MUTE R5 MCONFIG /E5_CS0 /DTACK ADDR AI_SCLK AI_FSYNC E5_GPIOx32 AI_MCLKO CONTROL CS[9]- GPIOx[33] GND GPIO1 12 ATAPI2 I/F AI_D0 RDS_DATA 11 11 9 11 AO_IEC958 AO_MCLKI AO_MCLKO 1 2 3 4 5 MASTER RDDMAREQ HINTA0 A1 A2 I/F 11 7 C14 D14 DI DO CL CE *0 RSTMCONFIG CS- GPIOx[40] GPIOx[39] B13 A13 AOMCLKOA15 GPIOx[38] GPIOx[37] AOIEC SLAVE 22 22 22 22 5 5 6,7,9,11,12 6,7,9,11,12 R10 HOST Y1 22 CN8 5P1.0 R237 R238 R239 R240 D1 *1N6263 2 1 SBP C1 27P 22 (Input Only) R6 *10K ATAPI I/F G ND R29 E5_GPIOx33 R30 E5_GPIOx33 AO_MCLKO SPI_MOSI SPI_MISO SPI_SCK SPI_CS2 (RDY_FM) (ATN_FM) (FP SCLK) (FP D_FM) 12 12 12 12 E5_UART2_TX E5_UART2_RX SDA SCL E5_VDDX GPIOx[41] GPIOx[42] 9 11 GPIOx[31] GPIOx[34] SPI_CLK AO_IEC958 AO_D0 AO_D1 AO_D2 AO_D3 AO_SCLK AO_FSYNC GPIOx[25] CS11GPIOx[24] CS10- 5 A17 AO_1 B15 AO_2 B16 AO_3 B17 AOSCLK B14 AOFS YNCA14 SDRAM_DQM0 SDRAM_DQS0 SDRAM_DQ7 SDRAM_DQ6 SDRAM_DQ5 SDRAM_DQ4 SDRAM_DQ3 SDRAM_DQ2 SDRAM_DQ1 SDRAM_DQ0 AO_D1 AO_D2 AO_D3 AO_SCLK AO_FSYNC 22 22 22 22 22 SDRAM_DQM1 SDRAM_DQS1 SDRAM_DQ15 SDRAM_DQ14 SDRAM_DQ13 SDRAM_DQ12 SDRAM_DQ11 SDRAM_DQ10 SDRAM_DQ9 SDRAM_DQ8 11 11 11 11 11 R19 R21 R23 R24 R26 SDRAM_DQM2 SDRAM_DQS2 SDRAM_DQ23 SDRAM_DQ22 SDRAM_DQ21 SDRAM_DQ20 SDRAM_DQ19 SDRAM_DQ18 SDRAM_DQ17 SDRAM_DQ16 1 AO_D0 SDRAM_DQM3 SDRAM_DQS3 SDRAM_DQ31 SDRAM_DQ30 SDRAM_DQ29 SDRAM_DQ28 SDRAM_DQ27 SDRAM_DQ26 SDRAM_DQ25 SDRAM_DQ24 10K E5_SDRAM_A12 E5_SDRAM_A11 E5_SDRAM_A10 E5_SDRAM_A9 E5_SDRAM_A8 E5_SDRAM_A7 E5_SDRAM_A6 E5_SDRAM_A5 E5_SDRAM_A4 E5_SDRAM_A3 E5_SDRAM_A2 E5_SDRAM_A1 E5_SDRAM_A0 G ND R11 U20 V19 U18 W20 U19 V20 T20 T18 R18 R19 P17 T19 R17 TRST_L SDRAM__A17 SDRAM__A16 SDRAM__A15 SDRAM__A14 *SDRAM__A13 SDRAM__A12 SDRAM__A11 SDRAM__A10 SDRAM__A9 SDRAM__A8 SDRAM__A7 SDRAM__A6 SDRAM__A5 SDRAM__A4 SDRAM__A3 SDRAM__A2 SDRAM__A1 SDRAM__A0 TCK N19 N18 N17 P20 TDI TDO P19 P18 E5_SDRAM_CS1 R20 E5_SDRAM_A15 Y20 E5_SDRAM_A14 TMS E5_GPIOx25 E5_GPIOx24 E5_GPIOx41 E5_GPIOx42 E5_SDRAM_DQ[31..0] 3 SDRAM_WE_L SDRAM_CKE SDRAM_RAS_L SDRAM_CAS_L 10K D16 VREF 10K DI DO CL CE R233 R234 R235 R236 10K 10K 10K 10K D20 E20 K20 L20 R4 SDRAM_VREF 10K 10K R3 SDRAM_CLK_L1 SDRAM_CLK1 SDRAM_CLK_L0 SDRAM_CLK0 R2 AOUT R1 OPEN FOR DW9916 V CC SYSTEM AIN V33 C40 C41 C42 C43 C44 C45 104 104 104 104 104 104 G ND E5_V5BIAS E5_SDRAM_DQ[31..0] 2 4 SDRAM_DQ[31..0] SSTL2_VDD VTT RP1 E5_SDRAM_DQ0 E5_SDRAM_DQ1 E5_SDRAM_DQ2 E5_SDRAM_DQ3 8 7 6 5 E5_SDRAM_DQ4 E5_SDRAM_DQ5 E5_SDRAM_DQ6 E5_SDRAM_DQ7 1 2 3 4 SDRAM_DQ0 SDRAM_DQ1 SDRAM_DQ2 SDRAM_DQ3 51/RP 8 7 6 5 SDRAM_DQ4 SDRAM_DQ5 SDRAM_DQ6 SDRAM_DQ7 RP5 51/RP 1 2 3 4 SDRAM_DQ8 SDRAM_DQ9 SDRAM_DQ10 SDRAM_DQ11 RP7 51/RP 1 2 3 4 SDRAM_DQ12 SDRAM_DQ13 SDRAM_DQ14 SDRAM_DQ15 RP9 51/RP 1 2 3 4 SDRAM_DQ16 SDRAM_DQ17 SDRAM_DQ18 SDRAM_DQ19 RP3 E5_SDRAM_DQ8 E5_SDRAM_DQ9 E5_SDRAM_DQ10 E5_SDRAM_DQ11 4 SDRAM_DQ[31..0] 51/RP 1 2 3 4 8 7 6 5 E5_SDRAM_DQ16 E5_SDRAM_DQ17 E5_SDRAM_DQ18 E5_SDRAM_DQ19 8 7 6 5 E5_SDRAM_DQ20 E5_SDRAM_DQ21 E5_SDRAM_DQ22 E5_SDRAM_DQ23 RP11 51/RP 1 8 2 7 3 6 4 5 SDRAM_DQ20 SDRAM_DQ21 SDRAM_DQ22 SDRAM_DQ23 E5_SDRAM_DQ24 E5_SDRAM_DQ25 E5_SDRAM_DQ26 E5_SDRAM_DQ27 5 6 7 8 RP12 51/RP 4 3 2 1 SDRAM_DQ24 SDRAM_DQ25 SDRAM_DQ26 SDRAM_DQ27 E5_SDRAM_DQ31 E5_SDRAM_DQ28 E5_SDRAM_DQ30 E5_SDRAM_DQ29 1 2 3 4 RP14 51/RP 8 7 6 5 SDRAM_DQ31 SDRAM_DQ28 SDRAM_DQ30 SDRAM_DQ29 1 2 3 4 RP16 22/RP 8 7 6 5 E5_SDRAM_A1 2 E5_SDRAM_A6 2 E5_SDRAM_A3 2 E5_SDRAM_A15 2 8 7 6 5 RP18 22/RP 1 2 3 4 SDRAM_A1 SDRAM_A6 SDRAM_A3 SDRAM_A15 E5_SDRAM_A8 E5_SDRAM_A0 E5_SDRAM_A4 E5_SDRAM_A2 1 2 3 4 RP20 22/RP 8 7 6 5 SDRAM_A8 SDRAM_A0 SDRAM_A4 SDRAM_A2 E5_SDRAM_A7 2 E5_SDRAM_A14 2 E5_SDRAM_A9 2 E5_SDRAM_A12 2 8 7 6 5 RP22 22/RP 1 2 3 4 SDRAM_A7 SDRAM_A14 SDRAM_A9 SDRAM_A12 E5_SDRAM_A11 2 E5_SDRAM_A10 2 E5_SDRAM_A5 2 1 2 3 4 RP24 22/RP 8 7 6 5 SDRAM_A11 SDRAM_A10 SDRAM_A5 - 141 - 2 2 2 2 E5_SDRAM_DQS0 E5_SDRAM_DQS1 E5_SDRAM_DQS2 E5_SDRAM_DQS3 2 2 2 2 R44 R45 R47 R49 51 51 51 51 C59 C60 104 103 103 C61 C62 C63 104 104 103 VREF SDRAM_DQM0 SDRAM_DQM1 SDRAM_DQM2 SDRAM_DQM3 R52 R53 R55 R57 E5_SDRAM_RAS# 2 E5_SDRAM_CLKE 2 E5_SDRAM_CAS# 2 E5_SDRAM_WE# 2 E5_SDRAM_CS0 2 R65 RP26 1 2 3 4 22 22 22 22 22/RP 8 7 6 5 C64 C65 C66 C67 C68 C69 104 104 103 103 104 104 C70 C71 C72 C73 C74 C75 104 104 103 103 104 104 VTT 22 SDRAM_DQ4 SDRAM_DQ5 SDRAM_DQ6 SDRAM_DQ7 8 7 6 5 SDRAM_DQ8 SDRAM_DQ9 SDRAM_DQ10 SDRAM_DQ11 4 3 2 1 SDRAM_DQ12 SDRAM_DQ13 SDRAM_DQ14 SDRAM_DQ15 GND_SSTL2 SSTL2_VDD SSTL2_VDD C76 C77 C78 C79 C80 C81 C82 C83 C84 C85 104 104 103 103 104 104 102 102 102 104 VTT C86 C87 C88 104 102 102 VTT V REF C89 C90 C91 C92 C93 C94 C95 C96 C97 C98 C99 C100 C101 104 104 103 103 104 104 102 102 102 104 104 102 102 GND_SSTL2 51/RP 1 2 3 4 RP6 51/RP 5 6 7 8 RP8 4 3 2 1 51/RP 5 6 7 8 SDRAM_DQ16 SDRAM_DQ17 SDRAM_DQ18 SDRAM_DQ19 8 7 6 5 RP10 51/RP 1 2 3 4 SDRAM_DQ20 SDRAM_DQ21 SDRAM_DQ22 SDRAM_DQ23 8 7 6 5 RP13 51/RP 1 2 3 4 SDRAM_DQ24 SDRAM_DQ25 SDRAM_DQ26 SDRAM_DQ27 8 7 6 5 SDRAM_DQ28 SDRAM_DQ29 SDRAM_DQ30 SDRAM_DQ31 8 7 6 5 VREF GND_SSTL2 2,4 SDRAM_A0 SDRAM_A1 SDRAM_A2 SDRAM_A3 4 4 4 4 8 7 6 5 RP19 51/RP 1 2 3 4 SDRAM_A7 SDRAM_A6 SDRAM_A5 SDRAM_A4 4 4 4 4 1 2 3 4 RP21 51/RP 8 7 6 5 SDRAM_A12 SDRAM_A11 SDRAM_A9 SDRAM_A8 4 4 4 4 RP23 1 2 3 4 RP15 RP17 SDRAM_RAS# 4 SDRAM_A14 4 SDRAM_A15 4 SDRAM_A10 4 VTT 1 2 3 4 V REF NC GND VSENSE VREF VTT PVIN AVIN VDDQ 8 7 6 5 SDRAM_DQM0 SDRAM_DQM1 SDRAM_DQM2 SDRAM_DQM3 4 4 4 4 R54 R56 R58 R59 51 51 51 51 SDRAM_CLK#0 4 R60 SDRAM_CLK#1 4 R61 SDRAM_CLK0 4 R62 SDRAM_CLK1 4 R63 51 51 51 51 C106 SDRAM_CLKE 4 R64 51 104 SDRAM_WE# 4 R66 51 SDRAM_CAS# 4 R67 51 SDRAM_CS0 4 51 SSTL2_VDD + C107 104 GND_SSTL2 CA4 220u/16 RP25 51/RP 1 2 3 4 51 51 51 51 LP2995 SDRAM_CS0 51/RP 8 7 6 5 R46 R48 R50 R51 220u/16 VREF 51/RP 1 2 3 4 4 4 4 4 + U2 2,4 8 7 6 5 51/RP 1 2 3 4 SDRAM_DQS0 SDRAM_DQS1 SDRAM_DQS2 SDRAM_DQS3 CA3 SDRAM_CLK0 SDRAM_CLK1 SDRAM_CLK#0 SDRAM_CLK#1 1 2 3 4 RP4 VTT SDRAM_DQS0 SDRAM_DQS1 SDRAM_DQS2 SDRAM_DQS3 SDRAM_RAS# SDRAM_CLKE SDRAM_CAS# SDRAM_WE# 8 7 6 5 GND_SSTL2 + E5_SDRAM_CLK0 2 E5_SDRAM_CLK1 2 E5_SDRAM_CLK#0 2 E5_SDRAM_CLK#1 2 SDRAM_DQ0 SDRAM_DQ1 SDRAM_DQ2 SDRAM_DQ3 2,4 SSTL2_VDD 8 7 6 5 2 2 2 2 C58 104 V REF E5_SDRAM_DQ12 E5_SDRAM_DQ13 E5_SDRAM_DQ14 E5_SDRAM_DQ15 E5_SDRAM_DQM0 E5_SDRAM_DQM1 E5_SDRAM_DQM2 E5_SDRAM_DQM3 C57 RP2 51/RP C102 10u/16 C104 104 + C103 T47u/16 C105 104 R68 /RST_HOST 12 /RST_HOST 2 2 /RST_SW D5 IN4148 V33 VCC 1 R69 10K C144 10u/16 Q1 3906 2 + U5A 74AHCT14 1 3 1 1 D4 *IN4148 2 VCC 2 3 R70 0 4 R71 10K D6 IN4148 2,6 /SYS_RST C145 102 1 C146 104 U5B 74AHCT14 V33 VCC R72 0 V33 R155 0 R163 10K R73 10K 2 - 142 - 2 5 E5_GPIOx35 6 U5D 74AHCT14 9 8 R74 *0 /RST_AUDIO /RST_AUDIO 11,12 1 /SYS_RST U5C 74AHCT14 U6 R162 *10K Em6353AX1SP3B-3.1 3 V33 R76 33 2 2 1 2 3 4 E5_UART2_TX E5_UART2_RX OPTICAL J2 DIP4/P2.0 U5E 74AHCT14 2 AO_IEC958 11 10 13 U5F 74AHCT14 C147 R78 L5 104 330 0 12 SPDIF_OUT GND R79 120 GND 12 12 FLASH MEMORY(2 or 4 or 8 Mb) 2,5 HD[15..0] SKT-U2 BA[22..1] U7 HD0 HD1 HD2 HD3 HD4 HD5 HD6 HD7 HD8 HD9 HD10 HD11 HD12 HD13 HD14 HD15 E5_ALE V33 2,5 47 46 44 43 41 40 38 37 1 48 36 35 33 32 30 29 27 26 24 25 1A1 1A2 1A3 1A4 1A5 1A6 1A7 1A8 1OE 1LE 2A1 2A2 2A3 2A4 2A5 2A6 2A7 2A8 2OE 2LE V33 C154 C155 104 102 C152 + C153 104 7 18 31 42 10u/16 C157 104 VCC VCC VCC VCC 1B1 1B2 1B3 1B4 1B5 1B6 1B7 1B8 2 3 5 6 8 9 11 12 BA6 BA7 BA8 BA9 BA10 BA11 BA12 BA13 2B1 2B2 2B3 2B4 2B5 2B6 2B7 2B8 13 14 16 17 19 20 22 23 BA14 BA15 2,5 BA16 2,5 BA17 BA18 BA19 BA20 BA21 GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND 4 10 15 21 28 34 39 45 SKT-TSOP48 HD[15..0] BA16 BA15 BA14 BA13 BA12 BA11 BA10 BA9 A19/A19/A21 NC/A20/A20 V33 R82 R80 *4.7k 10K /E5_WEL /SYS_RST ACC WP# /ACC RY/BY/A 19 BA19 BA18 BA8 BA7 BA6 BA5 BA4 BA3 BA2 R83 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 A15 A14 A13 A12 A11 A10 A9 A8 A19/A19/A21 NC/A20/A20 WE RST ACC WP/ACC RY/BY/A19 A18 A17 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A16 BYTE/VIO VSS D15 D7 D14 D6 D13 D5 D12 D4 VCC D11 D3 D10 D2 D9 D1 D8 D0 OE VSS CE A0 BA17 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 HD15 HD7 HD14 HD6 HD13 HD5 HD12 HD4 HD11 HD3 HD10 HD2 HD9 HD1 HD8 HD0 BA1 C156 /E5_OE 2,5 /E5_CS0 2 MX29LV160 104 BA1 BA17 74LVC16373 V33 E5_MA1 E5_MA2 E5_MA3 E5_MA4 E5_MA5 E5_MA22 V33 VCC R81 BA1 BA2 BA3 BA4 BA5 BA22 2,5 2,5 2,5 2,5 2,5 2 CA5 U9 1 2 3 4 A0 VCC A1 WP A2 SCL GND SDA *104 8 7 6 5 R88 5.6K S CL SDA SCL SDA *4.7k /SYS_RST R84 0 WP# /ACC BA22 R85 DNS-0 A19/A19/A21 BA21 R86 DNS-0 NC/A20/A20 BA20 R87 DNS-0 RY/BY/A 19 R90 0 R89 5.6K 2,7,9,11,12 2,7,9,11,12 - 143 - *AT24C16 Size Stuff Not Stuff 1MB R85,R86,R87,R90 2MB(Default) R90 R85,R86,R87 4MB R86,R90 R85,R87 8MB R85,R86,R87 R90 DEDICATED ATAPI INTERFACE RP27 33/RP 4 3 2 1 HD_AT8 HD_AT7 HD_AT9 HD_AT6 R101 R102 R103 R104 0 82 82 82 RSTATA 2 ATAPI_INTRQ 2 ATAPI_IORDY 2 ATAPI_DMARQ 5 6 7 8 RP28 33/RP 4 3 2 1 HD_AT10 HD_AT5 HD_AT11 HD_AT4 2,5 ATAPI_DATA10 2 ATAPI_DATA5 2 ATAPI_DATA11 2 ATAPI_DATA4 2 R106 C159 680 22PF 4.7K ATAPI_DATA12 2 ATAPI_DATA3 2 ATAPI_DATA13 2 ATAPI_DATA2 2 5 6 7 8 RP29 33/RP 4 3 2 1 HD_AT12 HD_AT3 HD_AT13 HD_AT2 ATAPI_DATA14 2 ATAPI_DATA1 2 ATAPI_DATA15 2 ATAPI_DATA0 2 5 6 7 8 RP30 33/RP 4 3 2 1 HD_AT14 HD_AT1 HD_AT15 HD_AT0 ATAPI_DIOW_L 2 ATAPI_DIOR_L 2 ATAPI_DMAACK_L 2 AtapiAddr1 2 5 6 7 8 RP31 33/RP 4 3 2 1 DI OW DI OR DMACK ATA_A1 AtapiAddr0 AtapiAddr2 AtapiAddr3 AtapiAddr4 5 6 7 8 RP32 33/RP 4 3 2 1 ATA_A0 ATA_A2 CS1FX CS3FX 2 2 2 2 RSTATA HD_AT7 HD_AT6 HD_AT5 HD_AT4 HD_AT3 HD_AT2 HD_AT1 HD_AT0 FB5 FB6 FB8 FB10 FB12 FB14 FB16 FB18 FB20 B601 B601 B601 B601 B601 B601 B601 B601 B601 DMARQ DI OW DI OR I ORDY DMACK INT_ATA ATA_A1 ATA_A0 CS1FX FB22 FB23 FB24 FB25 FB26 FB27 FB28 FB29 FB31 B601 B601 B601 B601 B601 B601 B601 B601 B601 HD[15..0] HD0 HD1 HD2 HD3 HD4 HD5 HD6 HD7 J3 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 27 29 31 33 35 37 39 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 HEADER 20X2 FB7 FB9 FB11 FB13 FB15 FB17 FB19 FB21 B601 B601 B601 B601 B601 B601 B601 B601 HD_AT8 HD_AT9 HD_AT10 HD_AT11 HD_AT12 HD_AT13 HD_AT14 HD_AT15 KEYWAY (NO PIN) V33 DNS-4.7K DNS-4.7K DNS-4.7K DNS-4.7K DNS-4.7K DNS-4.7K DNS-4.7K DNS-4.7K INT_ATA I ORDY DMARQ R105 5 6 7 8 10K 4.7K ATAPI_RESET 2 2 2 2 R93 R94 R95 R96 R97 R98 R99 R100 R91 ATAPI_DATA8 ATAPI_DATA7 ATAPI_DATA9 ATAPI_DATA6 DNS-4.7K DNS-4.7K DNS-4.7K DNS-4.7K DNS-4.7K DNS-4.7K DNS-4.7K DNS-4.7K R92 2 HOST Read VCC R107 R108 R109 R110 R111 R112 R113 R114 VCC CAB_SEL R115 FB30 FB32 B601 B601 ATA_A2 CS3FX 2,5 V33 U8 HD[1:0] 0 HD[3:2] HD[7] 00 01 10 11 10 00 01 11 0 1 Samsung - K4H281638D-TCB3 Micron - MT46V8M16-55 ESMT - M13S128168A-6T Nanya 64Mb DDR SDRAM 128Mb DDR SDRAM 256Mb DDR SDRAM Reserve Normal Mode (Jumper 1-2) Debuge Mode (Jumper 2-3) 1394 RDS /RBDS PRE-PROCESSOR FIREWIRE PHY VCC CR3 104 RR3 470K C160 CR4 104 PHY_XI RR4 1K 27PF Y2 24.576MHz VCC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 YR1 PHY_XO C162 104 27PF BIO_LREQ C163 R117 51 GND_PHY_D V33_PHY_D 56PF 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 GND_PHY_D 2 E5_GPIOx0 SYSCLK CTL0 CTL1 D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 PD TSB41AB1 S-PQFP-48-TI CR6 151 CR7 331 RDS_MPX + CR9 2.2u/50 R121 56.2/1% 56.2/1% TPBIAS PA+ PAPB+ PB- GND_PHY_A C164 105 T1 GND_PHY_A 1 2 3 4 R126 R127 56.2/1% 56.2/1% 5 6 7 8 TPA+ TPATPB+ TPBCN1 6P2.0 L 1 2 3 4 5 6 TPBTPB+ TPATPA+ R129 GND_PHY_D GND_PHY_A BIO_LPS BIO_LINK_ON R131 PHY_SE PHY_SM 2 PHY_PC0 PHY_PC1 PHY_PC2 PHY_ISO PHY_CPS DNS-10K 2 PHY_R1 PHY_R0 C165 224 R120 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 - 144 - R128 2.2K V33_PHY_D 36 35 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 AGND AVDD R1 R0 AGND TPBIAS TPA+ TPATPB+ TPBAGND AVDD LPS DGND C/LKON PC0 PC1 PC2 ISO CPS DVDD TESTM SE SM C148 101 22 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37 22 2 BIO_PHY_CLK 2 BIO_PHY_CTL0 2 BIO_PHY_CTL1 2 BIO_PHY_DATA0 2 BIO_PHY_DATA1 RR2 CR2 47PF LVIN CIN SCOUT VREF MPXIN VSSA VDDA AFIN MAD PSWN TPBIAS LREQ DGND DGND DVDD DVDD XO XI PLLGND PLLVDD FILTER1 FILTER0 RESET R119 4.332MHz MRO MPTH TCON OSCO OSCI VSSD VDDD DAVN SDA SCL R118 1M/1% V33_PHY_A E5_GPIO1 U10 CR1 82PF 2 RDS_DATA 2,6,9,11,12 SDA 2,6,9,11,12 SCL PHY_R1 2 RR1 10K 6.34K/1% CR8 47u/16 PHY_R0 BIO_LREQ PHY_FILT1 PHY_FILT0 2 R116 + UR1 SAA6588 C161 GND_PHY_D CR5 104 C166 R130 221 5.11K/1% R17 FB221 GND_PHY_A R132 R133 GND_PHY_A 1K 1K GND_PHY_A 10K GND_PHY_D USB GND_PHY_D R135 R138 R141 GND_PHY_D GND_PHY_A 680 680 680 PHY_PC0 PHY_PC1 PHY_PC2 R136 10K PHY_ISO R142 10K V33_PHY_D J4 2 USB_D0- 2 USB_D0+ B601 C169 C175 104 + + C170 T47u/16 47u/16 C176 C177 104 104 GND_PHY_A E5_VPAD L23 V33_PHY_D B601 C168 + 10u/16 R134 R139 V33_PHY_A L6 C171 C172 C173 C174 103 103 103 104 GND_PHY_D VCC V33_PHY_D GND_PHY_D E5_VPAD C167 104 2 USB_OC0 2 USB_PO0 R143 R144 15K 15K 22 22 USB_BDM0 USB_BDP0 R137 R140 FB34 FB35 0 0 B601 B601 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 *7P2.0 4 2_5V C184 220u/16 ADJ GND R145 *1K 4 5 VC 2 + C185 104 VCC V18 U11 PQ018EZ02/PQ070XZ02 1 VIN VOUT 3 VCC_VOUT_A L7 C180 C183 104 + C182 330u/16 104 B601 C178 + C179 C181 + 100u/16 100u/16 R146 *2.2K 104 GND_VOUT VCC_AOUT_A DV33 VCC U12 LT1117-3.3 3 V33 C186 2 VOUT 1 - 145 - C189 104 L9 *FB R147 *1K C190 + 104 C188 47u/16 U13 PQ025EZ01 C191 103 C196 220u/16 C197 104 ADJ 3 R149 *1K 4 5 2 C143 *104 + V25 VOUT GND VIN VC 1 C187 220u/16 R148 0 V33 B601 + ADJ VIN L8 R150 *1K + C194 330u/16 C195 104 C192 104 104 GND_AOUT R164 SPDATA(B) 0 0 1 1 C205 474 39 12 R_Y_IN R160 SPLRCK(A) 0 1 0 1 SOURCE REAR_Y & C_IN FRONT_Y & C_IN R_CVBS IN&TV_CVBS_IN F_CVBS IN&R_SC2_SC1_CVBS_IN C204 474 39 12V 12 F_Y_IN C303 105 GND_VIN C304 105 C305 105 474 39 C201 474 R154 39 C206 474 R168 VDD 39 13 Y 3 GND_VIN U18 4052 V18_VIA C308 474UF 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 FCM1608-601T02 FB36 C309 104 R226 100k V18_VIA AIP1A AIP1B PLL_AGND PLL_AVDD XTAL1/OSC XTAL2 AGND RESETB Y3 2 R_SC2_SC1_CVBS_IN C209 474 R171 R151 R169 R252 14.31818MHz 39 39 39 39 12V C198 27PF GND_VIN C200 27PF C221 R176 100 R246 104 GND 10K 2 V33 Q3 3904 E5_GPIOx32 - 146 - 3.3K GND_VIN R174 33 R248 VI_VSYNC 2 SDA SCL 2,6,7,11,12 2,6,7,11,12 C310 104 V18_VID GND 10K GND VI_CLK0 2 E5_GPIOx7 2 V33_VID R249 10K C311 104 R250 2 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 GND_VIN R247 2 R152 DNS-33 VSYNC/PALI FID/GLCO SDA SCL DVDD DGND YOUT0 YOUT1 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 R172 2 E5_GPIOx3 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 Y0 Y1 Y2 Y3 INH A B 8 12 TV_CVBS_IN 1 5 2 4 6 10 9 X E5_GPIOx6 VI_D1A VI_D0A C208 X0 X1 X2 X3 U14 TVP5150 TQFP_32 C306 0.1UF CH_AVDD CH_AGND REFM REFP PDN INTERQ/GPCL AVID HSYNC 39 12 R_C_IN 12 14 15 11 VEE 39 R170 C307 474 16 R157 39 VSS R161 39 R175 DNS-33 7 R165 12 F_C_IN D11 6.2V 1/2W* C207 104 12 F_CVBS_IN PCLK/SCLK IO_DVDD YOUT7 YOUT6 YOUT5 YOUT4 YOUT3 YOUT2 39 V33_VID R178 1k C202 474 VI_D7A VI_D6A VI_D5A VI_D4A VI_D3A VI_D2A R156 R251 10K GND GND Q4 3904 E5_GPIOx33 3.3K VI_D[7..0]A V18_VID V18 L12 FB(0805) V18_VIA L14 FB(0805) C217 C218 104 104 VI_D[7..0] C222 CN2 12P1.0 2,5 E5_GPIOx35 2 DO 2 CL 2 DI 2 CE 7 RDS_MPX DO CL DI CE 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 C228 104 + 100U/16V GND DV33 L11 V33_VID FB(0805) C210 C211 104 + 100U/16V GND_VIN GND VI_D0A VI_D1A VI_D2A VI_D3A RP33 1 2 3 4 33/RP 8 VI_D0 7 VI_D1 6 VI_D2 5 VI_D3 VI_D4A VI_D5A VI_D6A VI_D7A RP34 1 2 3 4 33/RP 8 VI_D4 7 VI_D5 6 VI_D6 5 VI_D7 2 C234 *22PF 2 Y R179 C236 *220 *331 L15 1.8uH C235 *22PF Y_O 122 C C237 101 R180 C238 *220 *331 Y/G R182 C244 *220 *331 L18 1.8uH Y/G_O 12 Pb/B_O 12 2 Pr/R R181 C242 *220 *331 C245 101 L17 1.8uH C243 101 C246 *22PF - 147 - 2 Pb/B R183 C247 *220 *331 L19 1.8uH C248 101 C249 *22PF CVBS R188 C251 180 *331 L20 1.8uH VCC_VOUT_A C250 220u/10 R185 6.8K Q2 3904 + 2 C_O 12 Pr/R_O 12 C239 101 C240 *22PF C241 *22PF 2 L16 1.8uH C252 101 CVBS_O R189 6.8K R184 470 12 SCL SDA E5_GPIO3 2,6,7,9,12 2,6,7,9,12 2 R230 2.2K M2 AD0/CS SCL SDA RST 1 14 8 22 VLS VLC VD VA VCC_AOUT_A AOUTL2 AOUTR2 MUTEC2 24 23 25 AOUTL3 AOUTR3 MUTEC3 20 19 18 FILT+ VQ 16 17 GND1 GND2 9 21 MUTECS MUTELRS + C272 104 C273 104 C269 103 10u/16 C256 10u/16 C257 10u/16 C258 10u/16 R191 5.6K R192 5.6K R193 5.6K R194 5.6K R195 5.6K CENTER 12 SUBWOOFER 12 REAR_L 12 REAR_R 12 A_L_OUT 12 A_R_OUT 12 4 MUTELR C259 122 + CS4360 C271 104 C270 1u/50 C255 + 15 13 11 12 10 AOUTL1 AOUTR1 MUTEC1 + MCLK BCLK LRCK SDATA1 SDATA2 SDATA3 27 26 28 10u/16 5.6K + 7 5 6 2 3 4 C254 R190 + 2 2 2 2 2 2 10u/16 + AO_MCLKO AO_SCLK AO_FSYNC AO_D3 AO_D2 AO_D1 U15 C253 + DV33 + C265 3.3u/16 C267 104 C266 3.3u/16 C268 104 C260 122 C261 122 C262 122 C263 122 C264 122 GND_AOUT 2,12 3 IR_FMUTE MUTE 2,12 GND_AOUT GND_AOUT - 148 - GND_AIN V33_AIN_A A_L_IN A_R_IN R212 0 12 V33_AIN_A R186 6.8K DV33 R210 *0 ADC_DIF R211 *0 ADC_DIV 2 R122 U17 R124 6.8K 12 R213 0 C281 102 GND_AIN GND_AOUT DV33 + C287 10u/16 L10 C282 R125 R123 B601 102 6.8K 6.8K V33_AIN_A /RST_AUDIO 5,12 R216 R217 C289 104 10K 10K C288 104 C193 + 10u/16 GND_AIN GND_AIN 10 AINL 12 AINR 9 1 16 RST M0 M1 6 3 13 VD VL VA 10K MCLK SCLK LRCK SDOUT FILT+ VQ 2 7 8 4 AIN_D R214 R215 15 11 C285 + 104 REF_GND GND 22 *10K AI_MCLKO AI_SCLK AI_FSYNC AI_D0 GND_AIN 14 5 CS5340 GND_AIN C283 1u/50 C286 104 + C284 1u/50 2 2 2 2 CN3 24P1.0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 FRONT PANEL INTERFACE L25 FCM1608-601T02 5V_STB CN4 10P2.0 2 E5_GPIOx42 2 E5_GPIOx41 2 E5_GPIOx25 2,11 IR_FMUTE 5 /RST_HOST 2 2 E5_GPIO0 E5_GPIOx24 D_FM FP_SCLK RDY_FM R218 R219 R220 2.2K 33 33 /FP_RST D_HOST ATN_FM R221 R222 33 2.2K VFD_DIO L26 VFD_CLK L27 VFD_STB L28 IR_FMUTE L29 5V_STB L30 /RST_HOSTL31 P_CTL L32 L33 L34 FCM1608-601T02 FCM1608-601T02 FCM1608-601T02 FCM1608-601T02 FCM1608-601T02 FCM1608-601T02 FCM1608-601T02 FCM1608-601T02 FCM1608-601T02 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 OPTICAL SPDIF_OUT 5 5 SUBWOOFER MUTE CENTER /RST_AUDIO REAR_R 11 2,11 11 5,11 11 REAR_L 11 A_R_OUT 11 A_L_OUT E5_GPIOx5 2 GPIO1 2 E5_GPIOx2 E5_GPIOx4 E5_GPIO4 E5_GPIO5 SDA SCL 11 2 2 2 AUDIO_SEL0 2 AUDIO_SEL1 2,6,7,9,11 2,6,7,9,11 5V_STB C290 C291 C292 C293 C294 47PF 47PF 47PF 47PF 47PF+ C295 10u/16 GND_AOUT - 149 - CN5 26P1.0 VCC 5V_STB CN6 10P2.5 V33 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 P_CTL 5VSTB +3.3V VCC GND GND +2.5V +2.5V L21 FB 12V FB L13 R223 1K 2_5V L24 *FB L22 FB + + + C300 C296 C297 C298 104 104 330u/16 104 330u/16 C301 C299 330u/16 A/V I/O Connector 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 S_Y_OUT S_C_OUT V_OUT R_V_OUT G_Y_OUT B_U_OUT R_C_IN R_ Y_IN V3_IN V4_IN V1_IN A_L_IN A_R_IN GND_AIN E5_GPIOx1 Y_O 2 10 C_O 10 CVBS_O 10 Pr/R_O 10 Y/G_O 10 Pb/B_O 10 R_C_IN 9 R_Y_IN F_Y_IN F_CVBS_IN 9 9 9 R_SC2_SC1_CVBS_IN F_C_IN 9 TV_CVBS_IN 9 A_L_IN 11 A_R_IN 11 2 1 R2 1 8.2k 3 3 C6 105 C7 105 EXT_AUDIO_IN_L 105 EXT_AUDIO_IN_R C8 R3 *10k BTSC_AINL IN_L BTSC_AINR C9 105 R4 *10K IN_R CS-09 R9 *0 1 1 S 3 4 2 3 4 2 V2_IN R12 B601 R_ Y_IN Y0 Y1 Y2 Y3 INH A B V2_IN - 150 - C15 105 C16 105 F_AUDIO_IN_R C17 105 Y A_R_IN -12V C18 105 F_AUDIO_IN_L R23 B601 V4_IN F_C_IN V4_IN F_ Y_IN +5V CN1 24P1.0 -6.2V R8 4.7k C10 104 R6 1k R7 4.7k ADC_SEL1 VCC1 1 BT 2 VCC2 3 SCL 4 IIC_SCL SDA 5 IIC_SDA AS 6 AFC 7 NC 8 NC 9 C11 103 C12 103 VCC_TUNER R14 *0 + A 1 0 1 0 ADC_SEL1 1 1 0 0 ADC_SEL0 1 0 1 0 SOURCE R_AUDIO TUNER&SCART F_AUDIO FM OR LOOP 2nd SIF 11 12 VCC3 13 Audio Out 14 A+12V TV_IF C29 7 104 Q31 3904 V1_IN R20 0R/*4.7K 8 R21 *10K TV_MONO R182 150K C19 *4.7u/50 C20 *102 TV_MONO 7,8 R178 *8.2K C21 *105 R179 *8.2K C22 *105 R25 *8.2K C23 *105 R26 *8.2K C24 *105 L_OUT 7,8 R_OUT 7,8 SC2_L_IN 7,8 R27 *10K R28 *10K SC2_R_IN 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 CN2 26P1.0 R181 330K 10 Video Out +5V C14 104 R15 0 B 1 1 0 0 L1 FB C13 2200uF A21 FS0 V3_IN F_CVBS V3_IN +5V ADC_SEL0 AGC R22 B601 R24 B601 A_L_IN U1 4052 TUN1 JS-6B2F/L121-D5 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 13 3 8 R _C_IN R19 *10K CN3 7P2.0/4P2.0 X R5 1k R17 *10K R18 8.2k 1 5 2 4 6 10 9 R10 *0 CVBS/S_VIDEO IN R16 8.2k X0 X1 X2 X3 V2_IN R_CVBS_IN R11 B601 R13 B601 12 14 15 11 8 S2 R1 8.2k 2 C4 104 + AV2-8.4-6G 105 VEE BTSC_AINL 105 C5 16 S1 7 C3 VDD AUDIO IN +5V VSS TV,scart1,scart2 come from 3415 105 7 BTSC_AINR 105 C2 5.2.2 AV Board 7 C1 7,8 Q33 3904 R190 R183 4.7k 4.7k 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 OPTICAL SPDIF_OUT 6 6 SUBWOOFER MUTE CENTER /RST_BTSC REAR_R MICDET 5 3 R161 5 0 7 4 REAR_L 4 A_R_OUT 3 A_L_OUT TVP5146_C7 TVP5146_C8 E5_GPIOx2 E5_GPIOx4 ADC_SEL0 E5_GPIO4 ADC_SEL1 E5_GPIO5 IIC_SDA IIC_SCL E5_GPIOx35 SCART1 SCART2 3 8 8 8 CPUMUTE(for DMN8600) 8 E5_GPIO3(for DMN8600) 2,7 2,7 5V_STB 8 -12V E5_GPIO1(for DMN8600) E5_GPIOx1_RTC_INT 2,8 S_Y_OUT 2 S_C_OUT 2 V_OUT 2,8 R_V_OUT G_Y_OUT B_U_OUT R_V_OUT 8 G_Y_OUT 8 B_U_OUT 8 R _C_IN R_ Y_IN F_ Y_IN V3_IN V4_IN TV_V1_IN A_L_IN A_R_IN 3 R_SC2_SC1_CVBS_IN 8 V_OUT 1,8 R29 B221 CVBS/S-VIDEO +5V R30 6.8K S_Y_OUT C26 220u/16 1 1 C25 104 S 3 4 2 + Q1 3904 R32 6.8K R33 180 1 R31 3 4 2 B601 R34 470 S3 CS-09 5V_STB - 151 - R35 B601 -12V +5V R37 0(OPEN) R36 4.7K(OPEN) 1,8 E5_GPIOx1_RTC_INT R38 12K R39 0(OPEN) 5V_STB C27 1 Q2 3904 474 R41 180 R40 12K R42 470 1 2 3 4 D2 LL60P X1 32.768KHZ/20PF BT1 3V C30 20PF C31 20PF(open) A21 FS0 S_C_OUT D1 1N4148 U2 M41T80(OPEN)/PCF8563 X1 VCC 8 X2 SQW 7 INT SCL 6 GND SDA 5 IIC_SDA 1,7 IIC_SCL 1,7 C28 104 R46 1K R61 100 C45 104 + C44 470u/16 -12V R43 C32 C46 104 151 5 15K C34 102 C35 102 7 4558 U3B 6,8 AMUTE 4,5 Q3 3904 3906 R53 R51 220 3.3k C39 + 3.3k MICDET R159 15K A+12V MIC to AV Vc=5.6V C115 *105 R162 0 AV to MIC C113 101 R164 56k R158 3.3K C114 C40 102 Mix_out Mix_in Q5 3904 R60 2.7k Q6 3906 D4 1n4148 Q7 3906 + A+12V MUTE 1 R63 2.2K R62 10K C47 + 1000u/10V Q8 3904 +5V 10u/16 C127 105 R174 27k Vpp=4V R171 Q32 3904 R166 5.6k -0.8V 2mA 0V *0 Vpp=3V +3V3 A-12V A-12V R165 Rf 100k Ve Vb=0V Rb [Rb/(Rf+Rb)](Vc-Ve)+Ve=Vb ==> Rb=[(Vb-Ve)/(Vc-Vb)]Rf Q30 3904 1 6,8 5V_STB C37 10u/16 4558 U3A L_OUT 15k C118 104 U11 SN1699/PT2399 C119 + C145 105 3 1000u/16V L_OUT 105 2mA OK_MIC to AV MIC_DET R189 C43 104 A+12V CN6 6PIN-2.0 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 C42 104 C112 +5V A-12V R58 47K 4 + 2 8 - 152 - 1 2 3 4 5 1K A+12V R59 10 C41 47u/16 -12V AGND +12V +3V3 +5V 151 + CN4 5P2.0 +5V +12V C36 R56 A-12V C38 102 -12V 4.7K + 1 R55 20K - A_L_OUT R54 4.7K D3 1n4148 A+12V R52 R50 5V_STB Q4 R49 10K C33 10u/16 8 R160 6 + 1 A-12V - A_R_OUT R_OUT A-12V R47 47K 4 R45 4.7K R44 4.7K R_OUT 20K + A-12V OK_out MIC to 2399 R173 C128 105 10k C125 101 R172 10k C123 101 R175 22k C126 392 R48 15K R57 22k 10k R169 10k C121 104 C124 LPF1-IN VCC LPF1-OUT REF LPF2-OUT AGND LPF2-IN DGND OP2-OUT CLK_O OP2-IN VCO OP1-IN CC1 OP1-OUT CC0 332 C129 105 R176 10k C130 105 R170 16 15 LPF2_O 14 13 12 11 10 9 R177 15k LPF2_O C131 102 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 47u/16 C142 *473 R168 15k C117 104 104 C122 C116 104 R64 20K C48 4 R65 4.7K R69 C49 10u/16 1 4558 U4A R67 1K + 3 8 C50 102 R66 4.7K 2 + 1 A-12V - REAR_R 151 A+12V R68 47K REAR_R_OUT Q9 3904 C51 102 20K REAR_R_OUT 6 - 153 - R70 3.3k C52 151 A-12V C53 10u/16 7 4558 U4B 3.3k R74 1K + 5 8 C54 102 R73 4.7K 6 + 1 - REAR_L 3,5 R71 4 R72 4.7K AMUTE A+12V R75 47K C55 102 LT_OUT REAR_L_OUT Q10 3904 REAR_L_OUT 6 R76 20K A-12V 4 C56 151 C58 102 R78 4.7K C57 10u/16 1 4558 U5A R79 1K + 3 8 R77 4.7K 2 + 1 - CENTER A+12V R80 47K CENTER_OUT CENTER_OUT 6 Q11 3904 C59 102 R81 20K R82 3.3k AMUTE 3,4 R83 4 R84 4.7K C61 10u/16 7 4558 U5B 3.3k R86 1K + 5 8 C62 102 R85 4.7K 6 + SUBWOOFER 1 A-12V - - 154 - C60 151 A+12V SUBWOOFER_OUT SUBWOOFER_OUT 6 R87 47K C63 102 Q12 3904 5V_STB C64 105 +5V R88 10K 1 C65 R_V 106 Q13 3904 R90 10K R89 B601 R92 4.7k B_Cr 8 R_Cr 8 G_Cr 8 OP1 GP1F32T OPTICAL 1 2 3 C66 104 S4 AV4-8.4-6G-3 5V_STB R93 B601 R94 B601 1 C67 105 R95 SPDIF_OUT 1 2 3 4 5 6 B221 R96 10K S5 AV8-8.4-6G-3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 3,8 L_OUT - 155 - C68 B_U 106 3,8 R_OUT 5 CENTER_OUT Q14 3904 5 SUBWOOFER_OUT 4 REAR_L_OUT R97 10K R99 4.7k 4 REAR_R_OUT 3,8 L_OUT 3,8 R_OUT 5V_STB C69 105 C70 220u/16 4 1 2 5 8 11 Q15 3904 + G_Y R100 12k 5 R101 12k R103 4.7k 6 2 AV4-8.4-6G-3 TOPVIEW 3 1 3 4 6 AV8-8.4-6G-3 TOPVIEW 7 9 10 12 105 C139 C72 8 SC1_R_IN 1,8 SC2_L_IN 105 105 C73 105 C140 1,8 SC2_R_IN 105 C75 105 C141 105 + C77 10u/16 BTSC IDC Slave Addr: 0x80/81 C76 2 101 56PF 10PF - 156 - X2 18.432MHz C88 10PF 2 C89 10u/16 C91 C90 152 AHVSUP +5V DVSUP 471 + C93 103 C92 47u/16 AVSUP 1,2 1,2 1 IIC_SCL IIC_SDA /RST_BTSC C79 10u/16 AHVSUP NC SC1_OUT_L SC1_OUT_R VREF1 NC DACM_L DACM_R VREF2 NC NC 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 8AV_MODE_SEL1 1 VCC_AIN + R110 75K AVSUP ANA_IN1+ ANA_INTESTEN XTAL_IN XTAL_OUT TP D_CTR_I/O_1 D_CTR_I/O_0 ADR_SEL STANDBYQ I2C_SCL I2C_SDA I2S_CL I2S_WS I2S_DA_OUT I2S_DA_IN1 TP_CO DVSUP DVSS I2S_DA_IN2 RESETQ C85 1 2 3 4 CLK_MSP_XIN 5 CLK_MSP_XOUT 6 7 8 9 10 11 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 AVSS MONO_IN VREFTOP SC1_IN_R SC1_IN_L ASG1 SC2_IN_R SC2_IN_L AGNDC AHVSS CAPL_M U6 C84 56PF R105 1 330 + C81 R107 1K FB2 B601 +12V Q16 s8050 R104 *0 BDCOMP FB1 B601 104 C78 104 TV_MONO TV_MONO C80 TV_IF +5V 3.3u/50 2 VCC_AIN 1,8 1 C74 1 + C71 SC1_L_IN 1 8 105 2 C138 C82 104 33 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 MSP3415G-PMQFP44 C83 105 R106 820 R108 7.5K R109 7.5K C86 102 C87 102 R111 *10K R112 *10K BTSC_AINL 1 BTSC_AINR 1 Q17 s8050 +12V Function select(AV CONTROL) Pin8 E5_GPIOx35 Levele of P8 R192 47k R115 0 R116 0 AV mode R114 Wide-screen 1k SC2_R_OUT 12mA SC2_L_OUT R117 *0 R119 *0 4mA AV_MODE_SEL1 7 SC2_L_IN 1,7 SC2_B AV_CONTROL 15k D6 1N4148 Q20 3904 0.12mA R127 470 1/10w R185 470 1/10w R193 4.7k Q19 3904 1 E5_GPIOx2 R122 R123 R124 1 U7 74HC4053 R_V_OUT LOOP_DECODER_C R130 15k 1 SC2_R VI_FSS 1 G_Y_OUT B_U_OUT 12 13 SC2_G 2 1 Y0 Y1 SC2_B 5 3 Z0 Z1 R163 R121 180 180 SC2_CVBS_IN R91 180 FB3 B601 CVBS R131 *B601 SC2_CVBS_OUT R134 B601 1,2 14 Y 15 Z 4 R_V G _Y B_U R_V 6 G_Y 6 B_U 6 5V_STB A B C C96 104 R129 12K 6 EN 7 VEE -6.2V C98 104 Q21 3904 SC2_OUT SC2_CVBS_OUT 6 G_Cr 6 5V_STB +5V VEE 15 Z 4 7 VEE SC2_OUT SC2_R_OUT V2_IN C102 104 R135 12K R138 *0 V2_IN SC2_CVBS_IN SC1_CVBS_IN 5V_STB -6.2V D7 1N4148 R142 75 LOOP_DECODER_C C105 103 SC1_OUT 12 14 15 11 X0 X1 X2 X3 1 5 2 4 6 10 9 Y0 Y1 Y2 Y3 INH A B X 13 Y 3 Q22 3904 SC1_CVBS_OUT R139 SC1_IN_EN C108 12K R140 4.7k 101 +5V U10 74HC4052 SOP -6.2V R186 220k C136 474 C137 104 Q34 3904 C111 103 R148 4.7k SC1_IN_EN R146 470 R133 4.7k 5V_STB R_SC2_SC1_CVBS_IN 16 EN C110 104 5V_STB R132 12K 5V_STB 1 6 Q23 S8050 R147 180 SC1_CVBS_OUT SC1_CVBS_IN A B C LOOP_DECODER_C Q24 3904 CVBS 11 10 9 C109 *104 LOOP_DECODER_C 6 Z0 Z1 Y 1 C103 220u/16 VDD 16 EN R141 1K R145 4.7k R_Cr 7 SC1_R_IN Y0 Y1 5 3 -6.2V 8 B_Cr 7 C107 10u/16 14 VEE 6 SC1_L_IN 2 1 X VSS A B C 7 SC1_R_OUT C104 10u/16 X0 X1 8 11 10 9 Z C101 SC2_L_OUT 16 Z0 Z1 15 4 VCC 5 3 Y 12 13 TV_MONO GND SC1_L_OUT Y0 Y1 1,7 SC1_OUT 220u/16 8 SC1_R_OUT 2 1 14 X + + SC2_R_IN C106 10u/16 X0 X1 U9 74HC4053 + R_OUT R137 *0 12 13 C97 101 C99 104 SC1_L_OUT VCC + U8 74HC4053 GND L_OUT C100 10u/16 3,6 FB4 *B601 X SC1_CVBS_IN R136 *0 SC2 TO TV 5V_STB X0 X1 + 7 5V_STB + - 157 - SC1_L_IN R126 180 R102 180 11 10 LOOP_DECODER_C9 V1_IN SC2_CVBS_IN SC2_L_IN 7 1 CVBS V_OUT R98 180 5V_STB SC2_R SC2_G *0 *0 *0 16 R128 SC2_L_IN Stuff these Registers, no stuff U11,When no SCART. R120 *4.7k 1,7 VCC SC2_R_IN + GND R118 1.5k C94 220u/16 8 SC2_R_IN SC1_R_IN Low(0-2V) SC1'P8 controled by SC2'P8 (LOOP_DECODER_C=H) -- SC1_L_OUT SC1_R_OUT 3,6 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 Mid(5-8V) 7 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 High(9.5-12V) H L TV/DECODER status 5V_STB SC1 SCART IN L Q35 3904 R187 R149 510 C120 102 D8 1N4148 R_SC2_SC1_CVBS_IN Q25 3904 FB5 B601 R201 75 SC1_CVBS_RGB_SEL TVP5146_C8 1 TVP5146_C7 1 330k R191 4.7k R188 4.7k Q26 3906 R150 3.3K VI_FSS 1,2 E5_GPIOx1_RTC_INT E5_GPIO1(for DMN8600) R152 R155 75 C132 102 R156 Q27 3904 R157 3.3K High(1-3V) RGB Low(0-0.4V) Composite R143R144 75 75 R153 4.7k R154 4.7k +5V_STB +5V Fast Blanking Pin16 10 SC1_CVBS_RGB_SEL R151 1K 1K Q28 3904 E5_GPIOx4 1 Q29 3904 SCART LOOP AND DECODER Function NET STATE LOOP DECODER OFF_C E5_GPIOx1_RTC_INT SC1_AUDIO_OUT SC2_AUDIO_OUT SC1_CVBS_OUT SC1_RGB STANDBY/DECODER OFF H POWER OFF SC2_AUDIO_IN SC1_AUDIO_IN SC2_CVBS_IN SC2_RGB SC2_CVBS_OUT SC1_CVBS_IN POWER ON/DECODER ON L H RW_AUDIO_OUT TV_MONO RW_CVBS_OUT RW_RGB_OUT TUNER_CVBS_IN POWER ON/DECODER OFF H L SC2_AUDIO_IN SC1_AUDIO_IN SC2_CVBS_IN RW_RGB_OUT SC1_CVBS_IN REAR/SC2/SC1_CVBS_SEL M1227 Pin2,Pin4 Pin2(SW1) Pin4(SW2) Pin7(OUT) L L R_CVBS_IN H L SC2_CVBS_IN L/H H SC1_CVBS_IN 5.2.3 DV Board To AVIO Board J1 GND_PHY6 F_CVBS F_CVBS AIN_L_F AIN_R_F G ND TPA+ TPA- G ND AIN_L_F AIN_R_F ST-066-060-500 1 2 3 4 4P/2.0MM 1 2 3 4 JP1 FIREWIRE Interface - 158 - 1 ST-066-060-500 2 3 TPB+ TPB- J2 CHASS_GND 4 3 TPA+ TPA- 2 1 TPB+ TPB- GND_PHY5 CHASS_GND 1394 CON/TH 4 CHASSIS_GND 1 2 3 4 TO MAIN BOARD JP2 1 2 3 4 5 6 TPBTPB+ TPATPA+ 6P2.0 GND_PHY 5.2.4 USB Board USB Interface TO MAIN BOARD JP1 V5_USB U1 USB_PVCC0 USB_BDM0 USB_BDP0 USB_UGND0 CA1 C1 + 100UF/16V USB PORT 0.1UF 6 7 8 OUT OUT OUT GND - 159 - 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 J1 IN IN 2 3 OC EN 5 4 R1 10K R2 10K TPS2041AD USB_BDM0 USB_BDP0 USB_OC USB_EN PH7/2MM C2 0.1UF CHASSIS_GND CHASSIS_GND CHASSIS_GND CHASSIS_GND CHASSIS_GND CHASSIS_GND 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 -9VA C5 682 1K 50K(C) CE4 U1A R6 15K +9VA 21 2R9 4.7K C8 10U R10 104 D2 1N4148 +12V C14 683 CN1 5 4 3 2 1 MIC_OUT MIC_DET C13 683 R22 562 R24 MIC2 IN L3 3 2 4 1 L4 FB FB 1 2 R14 1K 10U U1B +9VA 102 47K +12V Q2 R25 47K 3904 +9VA 2N3906/TO R5 1K 1U +12V -9VA -12V R2 R1 -12V 2.2k 220U/16V CE1 CE6 C4 Q1 3906 47U/16V + R15 2.2k CE2 220U/16V 10k CE7 R16 47U/16V MIC_OUT C12 R13 MIC_DET Q4 3906 Q3 3904 2N3904/TO 1K + J2 15K R12 391 CE5 7 R17 101 D1 1N4148 R19 101 R18 5.6K 5 4558 + - 160 - -12V 6 8 R4 FB VR1 + L2 3 511 + 511 R21 10U 3 R7 100P -9VA CE3 1 1U 1 8 C3 2 C11 + MIC1 IN FB 104 4558 6.2K 4 4 + L1 3 2 4 1 + 2.2k 1/6W R8 511 - 2.2k 1/6W 22U/16V CE8 + R23 R11 + 682 - C6 C7 R20 J1 15K 5.2.5 MIC Board +12V R3 10k R2 Q2 9015 220 STB_LED P[1:16] LD1 CN1 5P2.0 *R 2.2 1/6W F+ F-24V C1 22u/50 + VCC CN3 4P2.0 K2 1 2 3 4 K4 K7 K5 SW K8 F- C2 104 C3 103 SW K3 SW K6 SW K9 SW -24V SW D1 1N4148 KEY_04 D2 1N4148 KEY03 D3 1N4148 KEY02 R3 270K R6 10K LD3 *G/DVD R8 *220 LD2 *G/HDD R7 *220 LD5 B/LED R11 220 LD4 *R/REC R9 220 Y1 5MHZ/20pF C6 30PF/0603 C7 30PF/0603 VDD FIP23 FIP22 FIP21 FIP20 FIP19 FIP18 FIP17 FIP16 FIP15 FIP14 FIP13 VLOAD VDD1 U1 UPD16316 FIP12 FIP11 FIP10 FIP9 FIP8 FIP7 FIP6 FIP5 FIP4 FIP3 FIP2 FIP1 FIP0 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 R12 100/0603 Y2 32.766KHZ/20pF VDD R14 10K R23 JUMP(7.5mm) + K5 CH+ 小丝印 GND 2 OUT 1 2 C18 10u/16 1 HS0038A2 大丝印 OUT 3 VCC 2 GND 1 C19 103 R19 2.7K 34 35 F2 F2 1 ZD1 *4.3V 1/2W 1 2 3 4 5 6 /RST_HOST_LED 7 P_CTL_PSW 8 D_HOST 9 ATN_FM 10 D_FM FP_SCLK RDY_FM 5V_STB VDD CN2 10P2.0 GND VFD_DIO VFD_CLK VFD_STB MUTE /FP_RST CN4 4P2.0 L1 221(0805) 1 2 3 4 副面板(9DW9916-1) VDD + C21 103/0603 C15 22PF LD6 RED R18 2.7K D5 1N4148 P16 P15 P14 P13 P12 P11 P10 P9 P8 P7 P6 P5 P4 P3 P2 P1 NX NX NX NX NX 8G 7G 6G 5G 4G 3G 2G 1G 5V_STB C12 C13 C14 C16 22PF 22PF 22PF 22PF 5V_STB R25 10 *U2 F1 F1 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 R10 10/0603 1 C17 102 F+ 1 2 K1 R17 2.7K HS0038B3V 3 K7 PAUSE K8 PLAY K9 STOP K4 SOURCE 0603封装 VCC K6 REC C10 20PF/0603 U2 Q1 8050D C79 471/*221 C9 20PF/0603 G1 G2 G3 G4 G5 G6 G7 G8 D_HOST ATN_FM + D4 1N4148 R24 10K R22 4.7K C5 103 K3 OPEN/CLOSE VDD R13 *10K 2 1 C11 4.7u/16 C4 103 K1 STANDBY/ON K2 CH- P13 P12 P11 P10 P9 P8 P7 P6 P5 P4 P3 P2 P1 C8 102/0603 2 - 161 - VCC FIP24 P00 P01 P02 P03 P04 P05 P06 P07 IC X2 X1 VSS0 VDD0 XT1 XT2 RESET P10 P11 P12 SCK SO SI INTP0 INTP1 TI 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 R5 10K VDD SW KEYC KEYB KEYA R4 10K P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6 P7 P8 P9 P10 P11 P12 P13 P14 P15 P16 P_CTL_PSW 39 38 37 36 35 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 27 STB_LED SW VFD1 HNV-08SS62 R15 4.7K G8 G7 G6 G5 G4 G3 G2 G1 P16 P15 P14 R1 5 4 3 2 1 C20 47u/16 5.2.6 KEY SCAN Board G[1:8] VDD BCK-28-0778 HV Ip=1.5A DC 115-375V -12V 2 +12V 16 -12V 50mA 15 12V 800mA 14 5V 1A 13 3.3V 2A 5T 8T 1.3mH 60T for FSDL0380R +5V 4T 3 750uH 45T for FSD0565R 3T GND - 162 - 12 4 VCC 15mA 6 15T 10T -26V 7 11 10 10mA -26V F+ 200mA 4T 9 F- 5.2.7 POWER Board T CE16 CD11T 25V100U Q11 FB L1 + C1 471 AC400 D10 1N4007 CE1 CD11T 25V10U CE5 LT 400V100U/68uF -12V 16 C5 2 +12V D11 1N4007 C4 103/1KV R2 68K 2W D9 1N4007 C17 R6 3 39K 2W for 0565 470K for 0380 D12 1N4007 >12.7V B+12V CE3 CD288H220u/25 471/500V D18 L3 SR1060SR1060/SR10A0 + C3 */*/471 500V CE9 CD288H470u D4 HER107 J22 0/0/* 10uH G ND + C16 */*/1000u R29 */*/0 R5 10/4A(104MS) GND C20 6 IC1 */FSDM0565R/FSD0565 t 6 5 N.C 4 Vfb 3 Vcc Drain 1 GND 2 -26V 7 D8 10 471/500V 1 4 VCC D GND FB 3 4 2 1 2 3 C23 333 J24 R15 470 CN4 4P3.96 +12V +5V R20 5.6K ?% Q2 * *1296 C7 104 0 R17 4.7K *1296 CE2 CH288H470u/10 Q3 */*/D965 R9 33K R24 IC3 TL431 R33 C6 471 AC400V 0 +5V Q3 D13 5.1V 1/2W J4 R32 39R 1W + R18 5.1K 1% 5VSTB +5V * J23 Q2 D965 J25 C12 104 + C22 473 IC5 AZ431 CE12 CD11T 25V47U R14 1.2K CN3 10P2.5 P_CTL 1 *5MM 5VSTB 2 +3.3V 3 +3.3V 4 +5V 5 G ND 6 G ND 7 8 +2.5V/5 9 +2.5V/G 10 HER105 IC2 HS817 IC6 KA5L0380R/*/* R19 3.3K V_Crl C19 LF2 40mHX2 10uH 11 9 CE11 CD11T 50V47u L5 R11 4.7K 1% F1 250V/T2AL */*/39R 1W Q13 *3904 0 V_Crl V_Crl R3 *3.3k FBF+ 1 2 BCN1 2P7.92 CE13 CD11T 50V10u B+12V 本电路 岣逷_CTL的电平,输出为V_Crl. V_Crl Q9 3906 R26 1.2K Q1 3904 BF+ R7 F+ 180 D20 3.9V 1/2W F- R27 1k 1/6W R16 1.2k P_CTL Q6 3904/9014 1 2 3 4 5 10MM in normal recorder,use one diode . 101/500V D6 HER105 R23 */2.4K /2.4k GND/3.3V +5V C28 104 + - 163 - RV1 680K/1/2W HV Vstr D16 1N5401 J26 */*/0 CE8 CD288H1000u/10 D7 HER105 33 + D21 BYW-200/SR1060/SR1060 + 4 RT1 C13 104/~275 12 J11 R21 1.8K 1/6W±1% CE17 R30 +3.3V CD11T 16V220U 75R + LF1 40mHX2 -12V G ND R12 1.5k 1/6w 1% J12 +12V D23 1n4001 13 L4 FB R13 5.6k 1/6w 1% IC4 AZ431 1PP15N03L 14 CN2 5P2.5 V_Crl Q7 1 2 R31 2.2K 1/6w D22 1n4001 C24 104 CN1 *2P2.5 +12V D30 1n4001 L2 FB D2 15 + 2.1V 10mA sf34/byw-200/byw-200 + +5V + R10 1K 1/6w 102/500V +12V <200mA R4 47R 3W Q10 3904 2.8V -12V D1 HER105 T1 BCK-28-0778 SB772 TO-126 CN5 5P2.0 F+ F-25V G ND +5V 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 TO HDD TO fan Chapter six BOM List MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION DW9918K(RU) SILVER [8602] AV BOARD 5448138 0090001 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 0O±5% 0603 R115,R116,R161,R15,R162 0090003 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 10O±5% 0603 R59,R152 0090006 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 75O±5% 0603 R142,R143,R144,R155 0090007 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 180O±5% 0603 R33,R41,R91,R98,R102,R147 0090008 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 220O±5% R53 0090022 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 8.2K±5% R1,R2,R16,R18 0090009 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 330O±5% 0603 R105 0090011 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 470O±5% 0603 R34,R42,R146 0090181 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 100O±5% 0603 R61,R196 0090046 SMD RESISTOR 1/10W 470O±5% 0805 R185,R127 0090249 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 510O±5% 0603 R149 0390025 SMDMAGNETIC BEADS BGH2012B601L R11,R12,R13,R22,R23,R24,R29,R31,R35,R89, R93,R94,R95,R134,FB1,FB2,FB3,FB5 0090235 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 820O±5% 0603 R106 0090014 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 1K±5% 0603 R5,R6,R107,R114,R151,R156,R141 0090016 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 1.5K±5% 0603 R118,R46,R56,R67,R74,R79,R86 0090017 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 2.2K±5% 0603 R63 0090018 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 3.3K±5% 0603 R157,R150,R51,R52,R70,R71,R82,R83,R158, R60 0090019 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 4.7K±5% 0603 R7,R8,R44,R45,R54,R55,R65,R66,R72,R73,R 77,R78,R84,R85,R92,R99,R103,R120,R133,R1 40,R145,R153,R154,R183,R188,R190,R191,R 148 0090021 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 6.8K±5% 0603 R30,R32 0090186 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 7.5K±5% 0603 R108,R109 0090023 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 10K±5% 0603 R49,R62,R169,R170,R172,R173,R176,R88,R9 0,R96,R97 0090187 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 12K±5% R38,R40,R100,R101,R129,R132,R135,R139 0090225 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 5.6K±5% 0603 R166 0090024 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 15K±5% 0603 R128,R130,R171,R175,R177,R168,R48,R159, R160 0090025 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 20K±5% 0603 R43,R50,R64,R69,R76,R81 0090026 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 22K±5% 0603 R57 - 164 - MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION 0090029 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 47K±5% 0603 R47,R58,R68,R75,R80,R87 0090030 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 56K±5% 0603 R164 0090034 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 100K±5% 0603 R165 0090197 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 150K±5% 0603 R182 0090201 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 220K±5% 0603 R186 0090205 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 330K±5% 0603 R187,R181 0090242 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 75K±5% 0603 R110 0881080 IC PCF8563T SO8 U2 02607139 CD CD11T 16V220U±20%6×12 C5 BELT C44 02604379 CD CD11 16V10U±20%5×11C5 BELT C33,C37,C49,C53,C57,C61,C77,C79,C89,C10 0,C104,C106,C107,C114 02606499 CD CD11 10V1000U±20%8×16 C5 BELT C47 02600029 CD CD11 16V47U±20%5×11 C5 BELT C41,C92,C119 02603859 CD CD11 16V470U±20%8×12 C5 BELT C39 02601819 CD CD11 16V220U±20%6×12 C5 BELT C26,C70,C94,C101,C103 02607629 CD CD11 50V3.3U±20%5×11 C5 BELT C74 0260303 CD CD11 16V2200u±20%10×30 5 C13 0310047 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 101 ±5% NPO 0603 C80,C97,C108,C113 0310048 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 151 ±5% NPO 0603 C32,C36,C48,C52,C56,C60 0310066 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 102 ±10% 0603 C34,C35,C38,C40,C50,C51,C54,C55,C58,C59, C62,C63,C86,C87,C120,C131,C132 0310067 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 152 ±10% 0603 C90 0310072 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 103 ±10% 0603 C11,C12,C93,C105,C111 0310188 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 10P ±5% NPO 0603 C88,C85 0310085 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 20P ±5% NPO 0603 C30 0310192 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 56P ±5% NPO 0603 C84,C81 0310196 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 471 ±10% 0603 C91 0310323 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 392 ±10% X7R 0603 C126 0310119 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 332 ±5% X7R 0603 C124 0310197 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 561 ±10% X7R 0603 C125,C123 0310216 SMD CAPACITOR 10V 105 +80%-20% 0603 C2,C5,C7,C9,C16,C18,C64,C67,C69,C83,C1,C 3,C6,C8,C15,C17,C73,C75,C71,C72,C138,C13 9,C140,C141,C112,C127,C128,C129,C130,C1 45 0310207 SMD CAPACITOR 50V104 ±20% 0603 C4,C10,C14,C25,C28,C29,C42,C43,C45,C46, C66,C76,C78,C82,C109,C96,C99,C102,C110, C116,C117,C118,C121,C122,C137,C98 - 165 - MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION 0310379 SMD CAPACITOR 25V 474 +80%-20% Y5V 0603 C27,C136 ① 0310542 SMD CAPACITOR 16V 474±10% 0603 C27,C136 ① 0780085 SMD TRIODE 8050D Q23,Q16,Q17 0310389 SMD CAPACITOR 10V 106 +80%-20% Y5V 0805 C65,C68 0680057 SMD SCHOTTKY DIODE LL60P MINI-MELF D2 0090027 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 27K±5% 0603 R174 0700007 SMD DIODE 1N4148 D1,D3,D4,D6,D7,D8 0780040 SMD TRIODE 3904(100-300) SOT-23 Q1,Q2,Q3,Q5,Q8,Q9,Q10,Q11,Q12,Q15,Q19, Q20,Q21,Q22,Q24,Q25,Q27,Q28,Q29,Q30,Q3 1,Q33,Q34,Q35,Q32,Q13,Q14 0780041 SMD TRIODE 3906(100-300) SOT-23 Q4,Q6,Q7,Q26 0881693 IC TL 74HC4052D SOP U1,U10 ② 0881965 IC MAX4052A SOP U1,U10 ② 0881226 IC RC4558D SOP U3,U4,U5 0881842 IC MSP3415G QFP U6 0881992 IC HC4053M SOIC U7,U8,U9 0881659 IC SN1699 DIP U11 0960238 CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR 18.432MHz±10PPM 49-S X2 0960017 CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR 32.768KHz 3×9 X1 1020071 TUNER TCSM0601DD25A TUN1 1090009 ELECTROOPTICTRANSFORMER GP1F32T OP1 ③ 1090024 ELECTROOPTICTRANSFORMER TX179AT OP1 ③ 1633045 PCB 7DW9918K-1 1860122 SCART SOCKET DOUBLE DECK FEMALE SEAT B LINK BODY,FLEX INSERT SC1 1910159 TERMINAL SOCKET CS TERMINAL DASW-02 S3,S2 1910062 TERMINAL SOCKET AV2-8.4--6G S1 1910078 TERMINAL SOCKET AV4-8.4-6G-3 S4 1910079 TERMINAL SOCKET AV8-8.4-6G-3 S5 0390052 MAGNETIC BEADS INDUCTOR FB L1 1940024 SOCKET 5P 2.0mm CN4,CN6 1940022 SOCKET 4P 2.0mm CN3(CLOSE TO AL ON RIGHT SIDE OF SOCKET) 1940120 CABLE SOCKET 13P1.0mm DUAL LINE TOUCH POINT DUAL LINE STRAIGHT PLUG CN2 - 166 - MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS 12P 1.0mm DUAL RANK TOUCH POINT,DUAL RANK STRAIGHT INSERT LOCATION 1940161 CABLE SOCKET 3630281 BATTEMETAL OXIDE 1403G7-GBK4B FILM RESISTOR HOLDER BT1 ④ 3630185 BATTEMETAL OXIDE 1403G6-GBK4B FILM RESISTOR HOLDER BT1 ④ CN1 DW9918K(RU) SILVER [8602] DECODE BOARD 2DW9916-6 1.5/4.1 0090001 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 0O±5% 0603 L5,R72,R83,R84,R90,R101,R115,R137, R140,R148,R212,R213,R17,R155 0090004 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 22O±5% 0603 R19,R20,R21,R23,R24,R26,R27,R28,R29, R30,R31,R32,R33,R34,R35,R52,R53,R55, R57,R65,R119,R134,R139,R214 0090005 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 33O±5% 0603 R76,R174,R175,R219,R220,R221 0090237 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 39O±5% 0603 R164,R165,R160,R161,R156,R157,R170, R171,R168,R154,R151,R172,R169,R252 0090220 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 51O±5% 0603 R44,R45,R46,R47,R48,R49,R50,R51,R54, R56,R58,R59,R60,R61,R62,R63,R64,R66, R67,R68,R117 0090291 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 56O±5% 0603 R120,R121,R126,R127 0090273 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 82O±5% 0603 R102,R103,R104 3580117 HEAT RADIATION BOARD 28×28×12 BBK9906(HK) WITH CARD CLASP FOR U1 HEAT RADIATION 0090181 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 100O±5% 0603 R176 0090221 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 120O±5% 0603 R79 0090007 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 180O±5% 0603 R188 0090009 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 330O±5% 0603 R78 0090011 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 470O±5% 0603 R184 0090013 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 680O±5% 0603 R105,R135,R138,R141 0090014 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 1K±5% 0603 R132,R133,R223,R178 0090175 PRECISION SMD RESISTOR 1/10W 1.18K±1% 0805 R43 0090017 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 2.2K±5% 0603 R128,R218,R222,R230 0090018 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 3.3K±5% 0603 R247,R250 0090019 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 4.7K±5% 0603 R91,R106 0090020 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 5.1K±5% 0603 R130 0090225 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 5.6K±5% 0603 R190,R191,R192,R193,R194,R195,R88,R89 0090185 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 6.2K±5% 0603 R116 0090021 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 6.8K±5% 0603 R185,R189,R186,R123,R124,R125 - 167 - MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION 0090023 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 10K±5% 0603 R1,R2,R3,R4,R5,R7,R8,R11,R12,R13, R14,R15,R18,R22,R25,R36,R37,R38,R39, R40,R41,R69,R71,R73,R82,R92,R131, R136,R142,R216,R217,R122, R158, R159,R153,R163,R246, R249,R248,R251,R9 0090024 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 15K±5% 0603 R143,R144 0090034 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 100K±5% 0603 R226 0090109 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 1MO±5% 0603 R118 1/16W 22O±5% 8P RP16,RP18,RP20,RP22,RP24,RP26 1/16W 33O±5% 8P RP27,RP28,RP29,RP30,RP31,RP32,RP33, RP34 0100028 0100019 SMD RESISTOR NETWORK SMD RESISTOR NETWORKS 0100030 SMD RESISTOR NETWORK 1/16W 51O±5% 8P RP1,RP2,RP3,RP4,RP5,RP6,RP7,RP8,RP9,R P10,RP11,RP12,RP13,RP14,RP15,RP17,RP1 9,RP21,RP23,RP25 0260033 CD CD11 25V3.3U±20%5×11 2 C265,C266 0260019 CD CD11 16V10U±20%5×11 2 C102,C144,C168,C193,C210,C253, C254,C255,C256,C257,C258,C287,C295, C270 0260025 CD CD11 16V47U±20%5×11 2 C169,C188 0260570 CD CD11T 16V47U±20%5×11 2 C4,C23,C103,C131,C170,CA1,CA2 0260027 CD CD11 16V100U±20%6×12 2.5 C178,C179,C222 0260028 CD CD11 16V220U±20%6×12 2.5 CA3,CA4,C184,C186,C196,C250 0260214 CD CD11 16V330U±20%8×12 3.5 C182,C194,C296,C298, C299 0310043 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 22P ±5% NPO 0603 C159 0310190 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 27P ±5% NPO 0603 C1,C2,C160,C161,C198,C200 0310045 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 47P ±5% NPO 0603 C290,C291,C292,C293, C294 0310192 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 56P ±5% NPO 0603 C163 0310047 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 101 ±5% NPO 0603 C237,C239,C243,C245, C248,C252,C148 0310049 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 221 ±5% NPO 0603 C166 0310066 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 102 ±10% 0603 C14,C15,C16,C33,C34,C35,C46,C47,C48,C56, C82,C83,C84,C87,C88,C95,C96,C97,C100,C1 01,C111,C112,C113,C120,C121,C122,C123,C 128,C129,C130,C137,C138,C139,C140,C145, C155,C281,C282 0310231 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 122 ±10% 0603 C259,C260,C261,C262,C263,C264 0310072 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 103 ±10% 0603 C7,C10,C36,C37,C49,C51,C53,C54,C59,C60, C63,C66,C67,C72,C73,C78,C79,C91,C92,C17 1,C172,C173,C191,C269 0310505 SMD CAPACITOR 25V 224 +80%-20% 0603 C165 ⑤ 0310112 SMD CAPACITOR 16V 224 ±10% 0603 C165 ⑤ 0310362 SMD CAPACITOR 16V474 +80%-20% 0603 C205,C204,C202,C201,C209,C208, C307,C308,C206 - 168 - MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION 0310207 SMD CAPACITOR 50V104 ±20% 0603 C3,C5,C6,C8,C9,C12,C13,C17~C22,C27,C28, C29,C31,C32,C40~C45,C50,C52,C55,C57,C58 ,C61,C62,C64,C65,C68~C71,C74~C77,C80,C8 1,C85,C86,C89,C90,C93,C94,C98,C99,C104~ C110,C115~C119,C125,C126,C127,C132~C13 6,C146,C147,C153,C154,C156,C157,C162,C1 67,C174~C177,C180,C181,C183,C185,C187,C 189,C190,C192,C195,C197,C211,C217,C218, C221,C228,C267,C268,C271,C272,C273,C285 ,C286,C288,C289,C297,C300,C301,C207,C30 6,C309,C310,C311 0310505 SMD CAPACITOR 25V 224 +80%-20% 0603 C165 ⑤ 0310112 SMD CAPACITOR 16V 224 ±10% 0603 C165 ⑤ 0310362 SMD CAPACITOR 16V474 +80%-20% 0603 C205,C204,C202,C201,C209,C208, C307,C308,C206 0310216 SMD CAPACITOR 10V 105 +80%-20% 0603 C283,C284,C303,C304,C305,C164 0310219 SMD CAPACITOR 16V 106 +80%-20% 1206 C11,C24,C25,C26,C38,C39,C114,C124,C141, C152 1940023 SOCKET 7P 2.0mm J4 0390052 MAGNETIC BEADS INDUCTOR FB L21,L22 0390096 SMD INDUCTOR 1.8UH ±10% 1608 L15,L16,L17,L18,L19,L20 0881127 IC RT9164-33CG SOT-223 U12 0390028 SMDMAGNETIC BEADS BGH3216B601LT L13 0390142 SMDMAGNETIC BEADS FCM1608-601T02 FB1,FB2,FB5,FB6,FB7,FB8,FB9,FB10,FB11,F B12,FB13,FB14,FB15,FB16,FB17,FB18,FB19, FB20,FB21,FB22,FB23,FB24,FB25,FB26,FB27 ,FB28,FB29,FB30,FB31,FB32,FB34,FB35,L6,L 7,L8,L10,L11,L12,L14,L1,L2,L3,L4,L23,L25~L3 4,FB36 0700007 SMD DIODE 1N4148 D2,D3,D5,D6 0780041 SMD TRIODE 3906(100-300) SOT-23 Q1 0780040 SMD TRIODE 3904(100-300) SOT-23 Q2,Q3,Q4 0100034 SMD RESISTOR NETWORKS 1/16W 0O±5% 0603×4 8P T1 0881935 IC DMN-8602 BGA U1 0882839 IC EM6353BX2SP3B-2.9V SOT23-3L U6 0881814 IC LP2995 SOP U2 0881815 IC M13S128168A-6T TSOP U3,U4 0881816 IC SN74HCT14PWR TSSOP U5 0881818 IC SN74ALVCH16373 TSSOP U7 0881819 IC TSB41AB1PHP QFP U10 0881820 IC PQ018EZ02ZP U11 - 169 - MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION 0881693 IC TL 74HC4052D SOP U18 0881821 IC PQ025EZ01ZP U13 0882873 IC LP2150A TQFP U14 0881057 IC CS4360 SSOP U15 0882353 IC CS5340 TSSOP U17 0960171 CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR 13.50MHZ 49-S Y1 0960169 CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR 24.576MHz 49-S Y2 0960229 CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR 14.31818MHZ 49-S Y3 1632853 PCB 2DW9916-6 1940005 SOCKET 6P 2.0mm CN1 1940046 SOCKET 10P 2.0mm CN4 1940030 SOCKET 10P 2.5mm CN6 1940161 CABLE SOCKET 12P 1.0mm DUAL RANK TOUCH POINT,DUAL RANK STRAIGHT INSERT CN3 1940120 CABLE SOCKET 13P1.0mm DUAL LINE TOUCH POINT DUAL LINE STRAIGHT PLUG CN5 1940337 CABLE SOCKET 34芯 0.5MM SMD,VERTICAL J5 DW9918K(RU) SILVER [8602] DV BOARD+FRONT AV BOARD 5445230 2150145 FLAT CABLE 6P350 2.0T2 2×2PSHIELD,WITH L NEEDLE,REVERSE JP2 (TO MAIN BOARD CN1) 2121501 FLAT CABLE 4P360 2.0 2 PIN,WITH L NEEDLE, REVERSE 26# CORD JP1(TO AV BOARD CN3) 1860040 1394 SOCKET IEEE1394 4P/F DIP J2 1980055 EARPHONE SOCKET CKX-3.5-20A J1 1631682 PCB CDW9916-4 DW9918K(RU) SILVER [8602] MAIN PANEL 5446248 0090003 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 10O±5% 0603 R10 0090181 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 100O±5% 0603 R12 0000381 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/6W2.2O±5% SHAPED 7.5 R1 0000118 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/6W10O±5% SHAPED 7.5 R25 0000488 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/6W220O±5% SHAPED 7.5 R2,R9,R11 0000133 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/6W4.7K±5% SHAPED 7.5 R15,R22 0000137 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/6W10K±5% SHAPED 7.5 R4,R5,R6,R14,R24 - 170 - MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION 0000667 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/6W270K±5% SHAPED 7.5 R3 0310085 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 20P ±5% NPO 0603 C9,C10 0310191 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 30P ±5% NPO 0603 C6,C7 0310196 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 471 ±10% 0603 C79 0310066 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 102 ±10% 0603 C8 0000475 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/6W2.7K±5% SHAPED 7.5 R17,R18,R19 0310043 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 22P ±5% NPO 0603 C12,C13,C14,C16 0310072 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 103 ±10% 0603 C21 0200123 PORCELAINCAPACITOR 50V 102±10% 5mm C17 0200032 PORCELAINCAPACITOR 50V 22P±5% NPO 5mm C15 0200131 PORCELAINCAPACITOR 50V 103±10% 5mm C3,C4,C5,C19 ⑥ 0200132 PORCELAINCAPACITOR 50V 103±20% 5mm C3,C4,C5,C19 ⑥ 0200139 PORCELAINCAPACITOR 50V 104 +80%-20% 5mm C2 0390095 SMDMAGNETIC BEADS FCM1608K-221T05 L1 0260076 CD CD11C 50V22U±20%6×7 2.5 C1 0260241 CD CD11C 16V4.7U±20%4×7 1.5 C11 0260196 CD CD11C 16V10U±20%4×7 1.5 C18 0260200 CD CD11C 16V47U±20%5×7 2 C20 0620076 RADIATION DIODE 3B3HC COLORLESS WITH BLUE LD5 0570006 DIODE 1N4148 D1~D5 0780033 TRIODE 9015C Q2 0780050 TRIODE S8050D Q1 0881013 IC D16316 QFP U1 0960017 CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR 32.768KHz 3×9 Y2 0960114 CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR 5.00MHZ 49-S Y1 1200610 DISPLAY SCREEN HNV-08SS62 VFD1 1340003 LIGHT TOUCH RESTORE HORIZONTAL 6×6×1 SWITCH 1632079 PCB 4DW9916-3 2100003 CONNECTED CORDS F 0.6 SHAPED 7.5mm R23 2121480 FLAT CABLE 10P160 2.0 T2 WITH L NEEDLE, TOGETHER DIRECTION, MAGNETISM RING, 26# CORD CN2 ( TO MAIN BOARD CN4) 2121626 FLAT CABLE 5P450 2.0 2 PIN, WITH L NEEDLE, REVERSE CN1 (TO POWER BOARD CN5) K2~K9 - 171 - MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION 2121475 FLAT CABLE 4P 265 2.0 2 PIN, WITH L NEEDLE, REVERSE,26# CORD CN3 (TO SUBSIDIARY PANEL CN4) 2110176 LEAD 20# 40mm BLACK,WITH WELD PIECE GROUNDING WELDING PLATE CLOSE TO R13 REAR SIDE 2110166 LEAD 20# 80mm BLACK,WITH WELD PIECE BETWEEN THE GROUNDING WELDING PLATE CLOSE TO REAR SIDE OF C20 AND SCREW ON MAIN BOARD LEFT CORNER 2360016 IR SENSOR HS0038B3V U2 ⑦ 2360024 IR SENSOR LTOP-4338 U2 ⑦ 5231458 SOFT SPONGE SPACER 10×7×5 DOUBLE-FACED, HARD UNDERLAY RECEIVER 5230060 SOFT SPONGE SPACER 10×12×3 DOUBLE-FACED,HARD UNDERLAY DISPLAY SCREEN 5230055 SOFT SPONGE SPACER 10×5×11 DOUBLE-FACED,HARD UNDERLAY LD5 DW9918K(RU) SILVER [8602] OK BOARD 5448181 0090181 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 100O±5% 0603 R19 0090249 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 510O±5% 0603 R7,R8,R21 0090014 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 1K±5% 0603 R4,R5,R12,R14,R17,R24 0090017 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 2.2K±5% 0603 R1,R2 0090104 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 2.7K±5% 0603 R11 0090019 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 4.7K±5% 0603 R9 0090225 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 5.6K±5% 0603 R18,R22 0090023 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 10K±5% 0603 R15,R16 0090024 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 15K±5% 0603 R3,R6,R10 0090029 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 47K±5% 0603 R13,R25 0310047 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 101 ±5% NPO 0603 C11 0310066 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 102 ±10% 0603 C12 0310207 SMD CAPACITOR 50V104 ±20% 0603 C7,C8 0310379 SMD CAPACITOR 25V 474 +80%-20% Y5V 0603 C13,C14 ⑧ 0310542 SMD CAPACITOR 16V 474±10% 0603 C13,C14 ⑧ 0310216 SMD CAPACITOR 10V 105 +80%-20% 0603 C3,C4 0310071 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 682 ±10% X7R 0603 C5,C6 0390142 SMDMAGNETIC BEADS FCM1608-601T02 L1,L2,L3,L4 0700007 SMD DIODE 1N4148 D1,D2 0780040 SMD TRIODE 3904(100-300) SOT-23 Q1,Q3 0780041 SMD TRIODE 3906(100-300) SOT-23 Q2,Q4 - 172 - MATERIAL CODE 0000132 MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/6W2.2K±5% SHAPED 7.5 LOCATION R20,R23 02604379 CD CD11 16V10U±20%5×11C5 BELT CE3,CE4,CE5 02600019 CD CD11 16V22U±20%5×11 C5 BELT CE8 02600029 CD CD11 16V47U±20%5×11 C5 BELT CE6,CE7 02601819 CD CD11 16V220U±20%6×12 C5 BELT CE1,CE2 0881226 IC RC4558D SOP U1 0160105 ROTATED POTENTIOMETER WH09-1AL-B10K-F25±20% VR1 1980018 MICROPHONE SOCKET CK3-6.35-24 J1,J2 2100010 CONNECTED CORDS F 0.6 SHAPED 5mm J3,J4,J5 2100003 CONNECTED CORDS F 0.6 SHAPED 7.5mm J8,J9 2100006 CONNECTION CORDS F 0.6 SHAPED 12.5mm J6 2100007 CONNECTION CORDS F 0.6 SHAPEN 15mm J7 1564221 PCB 6DW9918K-2 2121878 FLAT CABLE 5P360 2.0 2 PIN,WITH L NEEDLE,TOGETHER DIRECTION CN1(CLOSE TO DIRECTION OF -12V) 2060002 GROUND CHIP AB105KB GND1,GND2 DW9918K(RU) SILVER [8602] POWER BOARD 0000273 5448174 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/4W33O±5% SHAPED 10 R5 00000089 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/6W75O±5% BELT R30 0000574 R4 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 3W47O±5% MO SHAPED R 20×8 00007279 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1W 39O±5% BELT R32,R22 00004069 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/6W180O±5% BELT R7 00000169 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/6W470O±5% BELT R15 00000229 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/6W1K±5% BELT R10,R27 00000239 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/6W1.2K±5% BELT R14,R16,R26 0010334 R12 METAL FILM RESISTOR 1/6W1.5K±1% 00003509 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/6W2.4K±5% BELT R23 00000309 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/6W3.3K±5% BELT R19 0010197 R13,R20 METAL FILM RESISTOR 1/6W5.6K±1% SHAPED 5 00000349 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/6W4.7K±5% BELT R17 00000509 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/6W33K±5% BELT R9 0070008 HIGH VOLTAGE RESISTOR @1/2W680K±5% CQC - 173 - RV1 MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION 0010209 METAL FILM RESISTOR 1/6W2K±1% R21 0000026 CARBON FILM RESISTOR 1/6W2K±5% R31 00103099 METAL FILM RESISTOR 1/6W5.1K±1% BELT R18 0010126 METAL FILM RESISTOR 1/6W4.7K±1% SHAPED 7.5 R11 0010195 METAL OXIDE FILM RESISTOR 1/2W470K±5% SHAPED 12.5 R6 0010157 METAL OXIDE FILM RESISTOR 2W68K±5%SHAPED FLAT 15×7 R2 02003189 POLYPROPYLENECAPAC 50V 104±20% SHAPED 5mm BELT ITOR C7,C12,C24,C28 0200232 PORCELAINCAPACITOR 500V 101±10% 5mm C20 0200366 CERAMICCAPACITOR @CT81 400VAC 471±10% 10 VDE C6,C1 0200251 PORCELAINCAPACITOR 500V 102±10% 5mm C5 0200255 PORCELAINCAPACITOR 1000V 103 +80%-20% SHAPED7.5mm C4 0200377 PORCELAINCAPACITOR 500V 471±10% 5MM C17,C19,C3 0260788 CD CD288H 10V470U±20%8×12 C5 C16,CE9,CE2 TEMETAL OXIDE FILM 02100919 RESISTORLENECAPACIT 63V 473±5% 5mm BELT OR C22 TEMETAL OXIDE FILM 02100249 RESISTORLENECAPACIT 100V 333 ±10% 5mm BELT OR C23 0210207 @275V 104±20% 15mm VDE C13 02607149 CD CD11T 25V100U±20%6×12 C5 BELT CE16 0260559 CD11T 50V47u±20%6×12 2.5 CE12 02607429 CD CD11T 50V10U±20%5×11 C5 BELT CE13 0260659 CD288H 35V220U±20%10×12 5 CE3 02607159 CD CD11T 25V10U±10%5×11 C5 BELT CE1 02606849 CD CD11T 50V47u±20%6×12 C5 BELT CE11 02607139 CD CD11T 16V220U±20%6×12 C5 BELT CE17 02607269 CD CD288H 10V1000U±20%8×16 C5 BELT CE8 0570045 DIODE BYW29E-200 TO-220 D21 0260767 CD KM 400V68U±20%18×25 C10 CE5 03900529 MAGNETIC BEADS INDUCTOR FB BELT L1,L2,L4 0410077 CHOKE COIL VERTICAL 10UH 3A 5mm L3,L5 0460591 SWITCH POWER TRANSFORMER @BCK-28-0778 VDE T1 0570077 DIODE SF34 DO-27 SHAPED R 17.5×8 D2 TERYLENECAPACITOR CD CD - 174 - MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION 05700059 DIODE 1N4007 BELT D9,D10,D11,D12 0570007 1N5401 D16 05700139 DIODE HER105 BELT D1,D6,D7,D8 05700149 DIODE HER107 BELT D4 0680048 SCHOTTKY DIODE SR1060 TO-220 D18 05800069 VOLTAGE REGULATOR DIODE 5.1V±5% 1/2W BELT D13 0570003 DIODE 1N4001 D23,D22,D30 05800469 VOLTAGE REGULATOR DIODE 3.6V±5% 1/2W BELT D20 07800249 TRIODE 2N3906 BELT Q9 07800239 TRIODE 2N3904(100-300) TO-92 BELT Q1,Q6,Q10 0780328 TRIODE D965 TO-92 Q2,Q3 0790024 SMD FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR 1PP14N03L TO-220 Q7 ⑨ 0790025 SMD FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR AP40N03P TO-220 Q7 ⑨ 0790028 SMD FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR 1PP15N03L TO-220 Q7 ⑨ 0780327 TRIODE B772 TO-126 Q11 0780023 TRIODE 2N3904(100-300) TO-92 Q12 08805819 IC TL431C TO-226AA(LP) BELT IC3 0882462 IC AZ431AZ-A TO-92 IC4,IC5 0880765 IC 5L0380R YDTU IC6 1000045 FILTER OF POWER NET UT-20 33mH 10×13 115T LF2 1050012 HEAT SENSITIVITY RESISTOR @NTC SCK-104MS±20% CQC RT1 1564217 PCB @5DW9918K-1 UL 1940045 SOCKET 2P 8.0mm 2# BCN1 1940004 SOCKET 5P 2.5mm CN2 1940024 SOCKET 5P 2.0mm CN5 1940030 SOCKET 10P 2.5mm CN3 1940037 SOCKET 4P 3.96mm CN4 1080032 PHOTOELECTRIC COUPLER @HS817 VDE IC2 3580165 HEAT RADIATION BOARD 25×15×6 DW9927 IC6 3580219 HEAT RADIATION BOARD 34×17×25 DW9918K Q7 3580218 HEAT RADIATION BOARD 23.8×17×25 DW9918K D21,D18 2300048 FUSE F1 DIODE @T2AL 250V WITH LEAD FEET VDE - 175 - MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION 2100009 CONNECTION CORDS F 0.6 SHAPEN 8mm J4,J14,J15,J19 2060002 GROUND CHIP AB105KB FG1,FG2 2100003 CONNECTED CORDS F 0.6 SHAPED 7.5mm J24,J21,J1,J3,R24,R29,J6 2100011 CONNECTION CORDS F 0.6 SHAPEN 7mm J9,J27,J17,J20 2100004 CONNECTED CORDS F 0.6 SHAPED 10mm J25,J26,J16 2100006 CONNECTION CORDS F 0.6 SHAPED 12.5mm J18 2100010 CONNECTED CORDS F 0.6 SHAPED 5mm J8,J25,J10 4000073 TAPPING SCREW BT 3×8 BLACK FOR FIXING IC6,D21,Q7,D18 HEAT RADIATION BOARD DW9918K(RU) SILVER [8602] SERVO BOARD 5447967 0310112 SMD CAPACITOR 16V 224 ±10% 0603 C0406 0310047 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 101 ±5% NPO 0603 C0101,C0311 0310207 SMD CAPACITOR 50V104 ±20% 0603 C0102,C0104,C0105,C0106,C0108,C0109,C02 01,C0204,C0205,C0206,C0208,C0301,C0302, C0303,C0304,C0305,C0306,C0307,C0308,C04 03,C0404,C0405,C0412,C0414,C0419,C0424, C0425,C0426,C0427,C0428,C0429,C0430,C04 31,C0432,C0433,C0434,C0435,C0436,C0437, C0438,C0439,C0440,C0441,C0442,C0446,C04 47,C0448,C0449,C0450,C0602,C0603,C0605, C0607,C0610,C0615 0310216 SMD CAPACITOR 10V 105 +80%-20% 0603 C0608,C0614 0310049 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 221 ±5% NPO 0603 C0107 0310205 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 473 ±10% 0603 C0202,C0407,C0409,C0410, C0411 0310072 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 103 ±10% 0603 C0203,C0309,C0454 0310202 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 223 ±10% 0603 C0310 0260254 CD CD11C 10V100U±20%6×5 2.5 C0316 0310198 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 472 ±10% X7R 0603 C0312 0310042 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 15P ±5% NPO 0603 C0402,C0401 0310066 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 102 ±10% 0603 C0408 0310197 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 561 ±10% X7R 0603 C0413 0310215 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 821 ±10% X7R 0603 C0420,C0415 0310119 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 332 ±5% X7R 0603 C0416,C0417 0310048 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 151 ±5% NPO 0603 C0422,C0421 0310188 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 10P ±5% NPO 0603 C0601 0090001 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 0O±5% 0603 R0440,R0454,R0482 - 176 - MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION 0090272 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 1O±5% 0603 R0308,R0309,R0311,R0312,R0415 0090005 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 33O±5% 0603 R0443 0090230 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 47O±5% 0603 R0426,R0428,R0445 0090273 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 82O±5% 0603 R0606 0090181 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 100O±5% 0603 R0101 0090232 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 150O±5% 0603 R0425,R0435,R0437,R0446,R0456, R0457,R0480 0100033 SMD RESISTOR NETWORK 1/16W 150O±5% 0603×4 8P RP0401,RP0402,RP0403,RP0404,RP0405,RP 0406, RP0407 0090008 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 220O±5% R0422,R0453 0090009 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 330O±5% 0603 R0304 0090013 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 680O±5% 0603 R0603 0090014 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 1K±5% 0603 R0302 1/16W 1.5K±1% 0603 R0609 1/16W 4.7K±1% 0603 R0610 0090634 0090746 PRECISION SMD RESISTOR PRECISION SMD RESISTOR 0090017 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 2.2K±5% 0603 R0424,R0430 0090104 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 2.7K±5% 0603 R0455,R0410 0090018 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 3.3K±5% 0603 R0407,R0408,R0411,R0412 0090028 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 33K±5% 0603 R0203 0090019 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 4.7K±5% 0603 R0409 0090225 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 5.6K±5% 0603 R0402 1/16W 10K±5% 0603 R0301,R0303,R0315,R0316,R0317,R0413,R04 14,R0416,R0418,R0421,R0423,R0427,R0444, R0461,R0478,R0479,R0481,R0600,R0601,R06 04,R0605,R0602 1/16W 12K±1% 0603 R0306 1/16W 820O±1% 0603 R0613 1/16W 18K±1% 0603 R0307 0090023 0090288 0090676 0090492 SMD RESISTOR PRECISION SMD RESISTOR PRECISION SMD RESISTOR PRECISION SMD RESISTOR 0090188 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 18K±5% 0603 R0204 0090029 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 47K±5% 0603 R0314 0090747 PRECISION SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 1.8K±1% 0603 R0614 0090109 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 1MO±5% 0603 R0401 0090227 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 270O±5% R0608 0090039 SMD RESISTOR 1/10W 10O±5% 0805 R0611,R0612 1/16W 2.2K±1% 0603 R0403 1/16W 24K±1% 0603 R0405 0090541 0090530 PRECISION SMD RESISTOR PRECISION SMD RESISTOR - 177 - MATERIAL CODE 0090465 0100019 0100023 0100021 MATERIAL NAME PRECISION SMD RESISTOR SMD RESISTOR NETWORKS SMD RESISTOR NETWORK SMD RESISTOR NETWORK SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION 1/16W 47K±1% 0603 R0205,R0404,R0305 1/16W 33O±5% 8P RP0602,RP0603,RP0604,RP0605 1/16W 82O±5% 8P RP0606,RP0607,RP0608 1/16w 10k±5% 8P RP0601 0700007 SMD DIODE 1N4148 D0101 0780085 SMD TRIODE 8050D Q0601 0390027 SMDMAGNETIC BEADS BGH2012B601LB L0605,L0604 0390095 SMDMAGNETIC BEADS FCM1608K-221T05 L0102,L0103,L0104,L0105,L0106,L0201,L0402 ,L0403,L0404,L0602 0390028 SMDMAGNETIC BEADS BGH3216B601LT L0301,L0302,L0303,L0603,L0601 0390170 SMD INDUCTOR 10UH±10% 1608 L0101 0882752 IC TZA1050 QFP U0201 0882753 IC SA56203 TSOP U0301 0882751 IC PNX7860 BGA U0402 0882139 IC IS42S16100A1-6T TSOP U0403 0881969 IC IP1117-ADJ SOT-223 U0602 0882322 IC AZ431-2.5V SOT-23 U0601 0260199 CD CD11C 16V22U±20%4×7 1.5 C0451,C0609,C0612 0260201 CD CD11C 16V100U±20%6×7 2.5 C0313,C0604,C0606,C0611,C0613 0260200 CD CD11C 16V47U±20%5×7 2 C0314,C0452 0260419 CD CD11E 6.3V47U±20%5×5 2 C0207 0960009 CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR 16.9344MHz 49-S G0401 1940154 CABEL SOCKET 45P 0.5mm SMD,SUBMIT MEET WITH CLASP J0101 1940328 CABEL SOCKET 17芯 1.0mm DUAL RANK,TOUCH POINT,SMD,HORIZONTAL J0305 1940095 SOCKET 4P 2.0mm STRAIGHT CURVING WITH LEAF J0402,J0401 1940320 CABLE SOCKET 34P 0.5mm SMD,SUBMIT MEET WITH CLASP J603 1940160 SOCKET 5P 2.0mm STRAIGHT FLEX J0303 1940012 SOCKET 4P 2.5mm STRAIGHT CURVING J602 1632851 PCB 3DW9927-1 DW9918K(RU) SILVER [8602] SUBSIDIARY PANE 1562990 PCB 5444653 9DW9916-1 - 178 - MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION 1340003 LIGHT TOUCH RESTORE HORIZONTAL 6×6×1 SWITCH K1 1940141 SOCKET 4P 2.0mm STRAIGHT FLEX CN4 0620106 RADIATION DIODE 3R 4HD RED,CASUE FEET WITHOUT LIMIT PLACE LD6 (FOLD FROM BOTTOM PART 90DEGREE) 2110198 LEAD 20# 60mm BLACK,WITH WELD PIECE GND 5232453 SOFT SPONGE SPACER 6×6×3 DOUBLE-FACED,HARD UNDERLAY LD6 DW9918K(RU) SILVER [8602] USB BOARD 5448173 0090023 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 10K±5% 0603 R1,R2 0260027 CD CD11 16V100U±20%6×12 2.5 CA1 0310207 SMD CAPACITOR 50V104 ±20% 0603 C1,C2 2150285 FLAT CABLE 7P380 2.0 T2 2×2P SHIELD WITH L NEEDLE,TOGETHER DIRECTION, JP1 1633059 PCB CDW9918K-0 0882507 IC TPS2013A SOP U1 1860047 USB SOCKET CAM-B85-4Pin J1 0090001 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 0O±5% 0603 R4 SST39VF160-70-4C-EK TSOP MAIN BOARD U8 M29W160ET-70N6 TSOP SERVO BOARD U0401 DW9918K(RU) SILVER [8602] ROM9918KRU-0(16M) 0881236 0911605 IC ROM66.33-0S(16M) 0911578 0882048 IC - 179 -