* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NETWORK OPERATING SYSTEMS
Survey
Document related concepts
Burroughs MCP wikipedia , lookup
Spring (operating system) wikipedia , lookup
Plan 9 from Bell Labs wikipedia , lookup
Copland (operating system) wikipedia , lookup
Distributed operating system wikipedia , lookup
Mobile operating system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
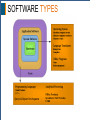
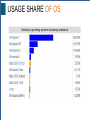
NETWORK OPERATING SYSTEMS By: Waqas Ahmed (C.E.O at Treesol) LEARN THE BASICS The ABC of Network Operating System HARDWARE VS SOFTWARE Hardware: The physical part of the computer. We can touch it. Software: Logical part of the computer which Is a collection of code and instructions. We cannot touch it. Question: Can a computer run without hardware? Question: Can a computer run without software? SOFTWARE TYPES There are two main types: 1. Application Software 2. System Software We can touch it. Application Software: These softwares are actually use to solve a problem. And the problem to be solved is user specific. You can simply say them end user programs or productivity programs, as they facilitate users to complete different tasks. System Software: Software which actually interacts with hardware. It makes it possible to allow communication between hardware and other types of softwares. These are designed to operate, control, and extend the processing capabilities of the computer itself. SOFTWARE TYPES OPERATING SYSTEM Operating System is a type of system software. It is a collection of programs that 1. Provides user interface so that human can interact with machine. 2. Manages the computer resources and hardware 3. Control and manages all other softwares. Etc… Without an operating system computer is just a collection of machine which we cannot control according to our needs. OPERATING SYSTEM Examples of Operating system. 1. Windows 2. Unix 3. Linux 4. Mac OS 5. Sun 6. Android 7. Red Hat 8. DOS 9. iOS (Ipohone OS) 10. BlackBerry OS OPERATING SYSTEM Operating system further can be divided: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Single-Tasking Multi-Tasking Single User Multi-User Distributed Templated Embedded OPERATING SYSTEM Single-Tasking: Can run single program at a time. Example is Palm OS. Multi-Tasking: Can run multiple programs at a time. Examples are: Windows XP, Linux etc. Single User: Only single user can interact at a time. Example is Palm OS. Windows 7, etc. Multi User: Multiple users can interact at a time. Unix/Linux is the example of this. Distributed: Make group of computers act as a single computer to make it even more powerful. Grid Computing is the main example. OPERATING SYSTEM Templated: Single virtual machine for multiple users. We can run virtual operating system by VMWare. Embedded: Specially designed for embedded systems computer systems. Like small devices. Example is Windows CE. Real Time: It guarantees to process specific task or data in a certain short given time. Examples are: LynxOS, VxWorks. Network Operating System: It is an operating system that specially made for computer network. Examples are Cent OS, Windows Server, etc. NETWORK OPERATING SYSTEM Network Operating System is software that is specially made for computer network oriented. It can run on server that allows multiple computers to communicate, share files and hardware devices with one another. It can manage resources and allow time sharing and etc.. For Example: Unix, Linux, Windows Server, etc… It can be also embedded on router, switch, etc.. to provide different options to network manager. For Example: JUNOS, Cisco iOS, etc… NOS TYPES There are basically two types of Network Operating system 1. Peer to Peer 2. Client Server Peer to Peer NOS Peer-to-peer network operating systems allow users to share resources and files located on their computers and to access shared resources found on other computers. AppleShare and Windows for Workgroups are examples. Client Server In client server environment, server is central part and enables multiple clients to share files, resources and providing security, etc. NOS FEATURES • Provides basic operating system features; support for processors, protocols, automatic hardware detection, support multi-tasking of applications • Security features; authentication, authorization, access control • Provides files, print, web services, back-up services • Supports Internetworking such as routing and WAN ports • User management and support for login and logoff, remote access, system management • Fault tolerant and high availability systems USAGE SHARE OF OS USAGE SHARE OF OS USAGE SHARE OF OS