* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Answers
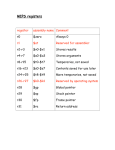
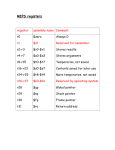
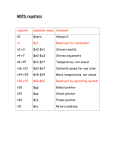
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Microcontroller wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Hardware description language wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Digital electronics wikipedia , lookup
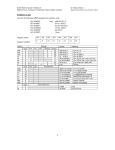
CS/EE 260 – Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design Mid-Term Exam Solutions Jon Turner 3/13/03 1. (6 points) List all the minterms for the expression (B′ + A)C + AC ′ + BC. Expanding the expression gives B′C + AC + AC ′ + BC = A′B′C + AB′C + ABC + AB′C ′ + ABC ′ + A′BC All the minterms appear at right. Numerically, they are 1, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7. List the maxterms for the expression. The “missing minterms” are 0 and 2. These correspond to the two maxterms of the expression (A +B + C) and (A +B′ + C) 2. (5 points) Show that the following Boolean equation is true using algebraic simplification (not Karnaugh maps). Show your work. AB + BC ′ + CD = (B + C)(B + D)(A + C’ + D) Expanding the right side gives (B + C)(B + D)(A + C’ + D) = (B + BC + BD+ CD)(A + C’ + D) = (B + CD)(A + C’ + D) = AB + BC’ + BD + (ACD + CD) = AB + BC’ + BD + CD = AB + BC’ + (BC’D + BCD) + CD = AB + (BC’ + BC’D) + (BCD + CD) = AB + BC’ + CD -1- 3. (8 points) The attached simulation output is from an execution of the simple processor introduced in section 1 of the lecture notes. The instruction set for the processor appears below. Answer the following questions using the simulation output. What does the instruction stored at location 000C do? This instruction is A011. It adds the content of memory location 011 to the accumulator. What is the value of memory location 0011 at time 6 µs? 0021 What is the value of the program counter at time 4450 ns? 000f What is the value of memory location 0010 at time 7 µs? 0011 0000 0001 1xxx 2xxx 3xxx 4xxx 5xxx 6xxx 7xxx 8xxx 9xxx axxx halt execution negate the value in the ACC change the value of the ACC to xxx load the contents of memory location xxx into the ACC load the ACC from the memory location whose address is stored in memory location xxx store the value in the ACC in memory location xxx store the value in the ACC in the memory location whose address is stored in memory location xxx change the value of the PC to xxx change the value of the PC to xxx if ACC = 0 change the value of the PC to xxx if ACC > 0 change the value of the PC to xxx if ACC < 0 add the value in memory location xxx to the ACC -2- /testbench/reset /testbench/mem_enx /testbench/mem_rwx /testbench/abusx 0000 /testbench/dbusx 0011 0020 0000 0021 000E 0000 6004 0004 0000 1030 0005 0000 0001 0006 0000 A011 0011 0000 0021 0007 0000 0008 700F 0000 3011 0011 0000 0021 0021 0010 /testbench/clk /testbench/pcx 000D 000E 000F /testbench/iregx 4011 6004 0004 0005 0006 1030 0007 0001 0008 A011 700F 3011 /testbench/iarx 0020 0021 /testbench/accx 0021 0030 /testbench/alux 0000 4 us 0009 FFD0 FFD0 4200 ns 4400 ns 4600 ns FFF1 0000 4800 ns Entity:testbench Architecture:testbench_arch Date: Sun Mar 02 15:29:10 Central Standard Time 2003 Row: 1 Page: 1 FFF1 5 us 0012 0000 5200 ns 5400 ns 5600 ns /testbench/reset /testbench/mem_enx /testbench/mem_rwx /testbench/abusx 0021 0000 /testbench/dbusx 0010 0009 0000 A010 0010 0000 0001 000A 0000 4010 0010 0001 0000 0011 000B 0000 000C 1001 0000 A011 0011 0000 0021 000D 0000 4011 0011 0021 0000 000E 0022 6004 /testbench/clk /testbench/pcx 0009 /testbench/iregx 3011 000A 000B A010 000C 4010 000D 1001 000E A011 4011 /testbench/iarx 0021 /testbench/accx FFF1 0010 /testbench/alux 0000 5800 ns 0011 0011 6 us 0012 0001 0000 6200 ns 0022 0022 6400 ns 6600 ns Entity:testbench Architecture:testbench_arch Date: Sun Mar 02 15:29:10 Central Standard Time 2003 Row: 2 Page: 2 6800 ns 0043 7 us 0000 7200 ns 7400 ns 4. (10 points) Draw a logic circuit using the smallest possible number of simple gates (AND, OR and inverters, only) for the logic expression UX ′ + X(V + Z′) + (V′ + U)X′Z′. XZ 00 01 11 10 00 01 UV 11 10 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 UX´ + VX + V´Z´ U X V Z How many transistors are required by a CMOS version of this circuit? Show how to improve it by using NAND and NOR gates. How many transistors does this version require? The circuit above requires 36 transistors if implemented directly in CMOS. The circuit shown below uses just 24 transistors. U X V Z 5. (8 points) Use a Karnaugh map to find the simplest sum-of-products expression for F(X,Y,Z) = Σm(1,2,4), d(X,Y,Z) = Σm(3,6) YZ 00 01 11 10 X 0 1 0 1 x 1 1 0 0 x X´Y + X´Z + XZ´ Use a Karnaugh map to find the simplest product-of-sums expression for F(A,B,C,D) = Σm(1,2,6,7,8,9,15), d(A,B,C,D) = Σm(3,4,5,11) CD 00 01 11 10 00 AB 01 11 10 0 x 0 1 1 x 0 1 x 1 1 x 1 1 0 0 F´ = A´C´D´ + BC´ + ACD´ F = (A + C + D)(B´ +C)(A´ + C´ + D) -3- 6. (5 points) Show how to implement the function F(A,B,C,D) = Σm(0,2,5,7,8,9,11), d(A,B,C,D) = Σm(3,4,6,15) using an 8 input multiplexor. ABCD 0000 0001 0010 0011 0100 0101 0110 0111 1000 1001 1010 1011 1100 1101 1110 1111 F 1 0 1 x x 1 x 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 x D D’ 1 1 1 1 0 1 D 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ABC 0 0 -4- 7. (10 points) The circuit below shows a combinational circuit that implements a 5 bit version of the parallel pulse-parity function from design problem 2. What is the worst-case propagation delay for a 64 bit version of this circuit, using only simple gates with a delay of 1 ns? (The worst-case propagation delay is the maximum time from when an input changes until all outputs reach their final value.) a0 0 1 0 a1 a2 a3 a4 all1i n all1out all1i n all1out all1i n all1out all1i n all1out all1i n all1out ppint ppint ppint ppint ppint ppout x0 ppout ai−1ai ppout x1 x2 ppout x3 ppout x4 all1out all1in ppout ppin The worst-case delay is 63+4=67 ns. The circuit outlined below is a lookahead version of the same circuit. The boxes represent a repeated sub-circuit. In the rightmost box, fill in this circuit. What is the worst-case delay for a 64 bit version of this circuit, implemented using simple gates? a4 a a2 3 a a0 1 0 1 x0 x1 x2 The 64 bit version would have a delay of 6+3+6=15 ns. -5- x3 x4 8. (15 points) The circuit shown below implements a ternary (base 3) half-adder. The pair of input bits (A_i,B_i) represents a single ternary digit (the bit pair 00 represent the ternary digit 0, the bit pair 01 represents the ternary digit 1 and the bit pair 10 represents the ternary digit 2). Similarly for the outputs (X_i,Y_i). We can build a ternary increment circuit by combining these ternary half-adder circuits together, in the same way as with a binary ripple-carry increment circuit. Suppose that the input presented to a ternary increment circuit with four ternary digits corresponds to the ternary value 1022. What are the values of the nine output bits? Fill in your answer below the output signals listed below. Cout, (X_3, Y_3), (X_2, Y_2), (X_1, Y_1), (X_0, Y_0) 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 Cin A0 X0 B0 Y0 C0 A1 X1 B1 Y1 C1 A2 X2 B2 Y2 C2 A3 X3 B3 Y3 C3=Cout -6- The partial VHDL module below implements a ternary increment circuit with 8 ternary digits. Complete the missing parts. Your VHDL should be complete and syntactically correct. library IEEE; use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL; use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_ARITH.ALL; use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_UNSIGNED.ALL; entity ternaryInc is Port ( A, B : in std_logic_vector(7 downto 0); Cin : in std_logic; X, Y : out std_logic_vector(7 downto 0); Cout : out std_logic ); end ternaryInc; architecture arch1 of ternaryInc is signal C: std_logic_vector(7 downto 0); begin process(A, B, Cin, C) begin X(0) <= (A(0) and (not Cin)) or (B(0) and Cin); Y(0) <= (B(0) and (not Cin)) or ((not A(0)) and (not B(0)) and Cin); C(0) <= A(0) and Cin; for i in 1 to 7 loop X(i) <= (A(i) and (not C(i-1))) or (B(i) and C(i-1)); Y(i) <= (B(i) and (not C(i-1))) or ((not A(i)) and (not B(i)) and C(i-1)); C(i) <= A(i) and C(i-1); end loop; Cout <= C(7); end process; end arch1; -7- 9. (10 points) The figure shown below is a state diagram for a sequential circuit with one input A and two outputs X and Y. Is this a Moore model circuit or a Mealy model circuit? Fill in the values in the next state table. It’s a Moore model circuit. S 1S 0 00 00 01 01 10 10 11 11 1 0 00/10 1 0 11/01 1 0 10/11 A 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 XY D1D0 10 00 10 11 xx xx xx xx 11 10 11 00 01 10 01 11 What are the next state equations for the circuit? SA D1 00 010 11 10 S1 0 1 0 1 x x 1 0 1 1 D1= S0 + S1´A + S1A´ SA D0 00 010 11 10 S1 0 1 0 1 x x 0 0 1 0 D0= S1´A + S0A -8-